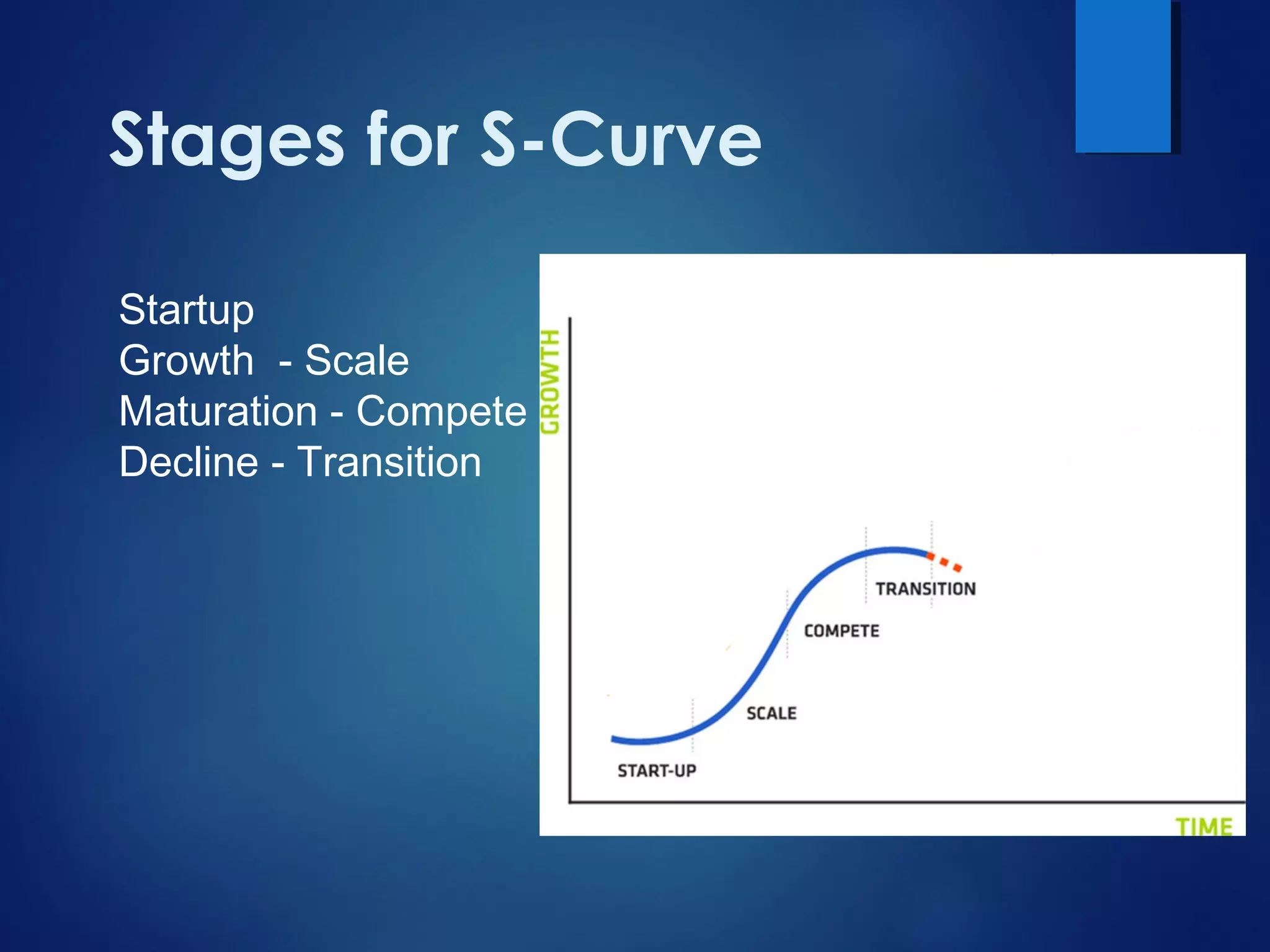
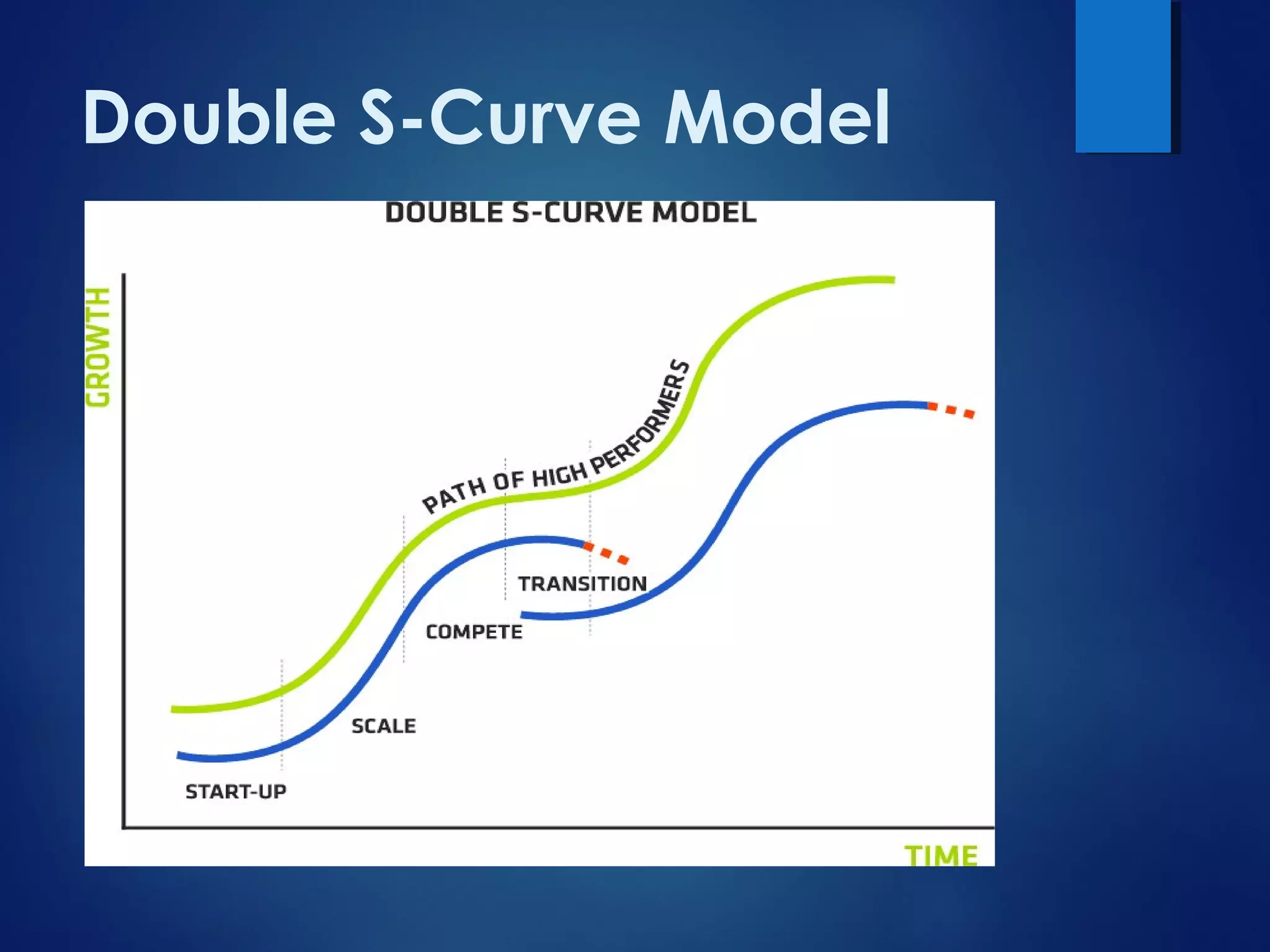
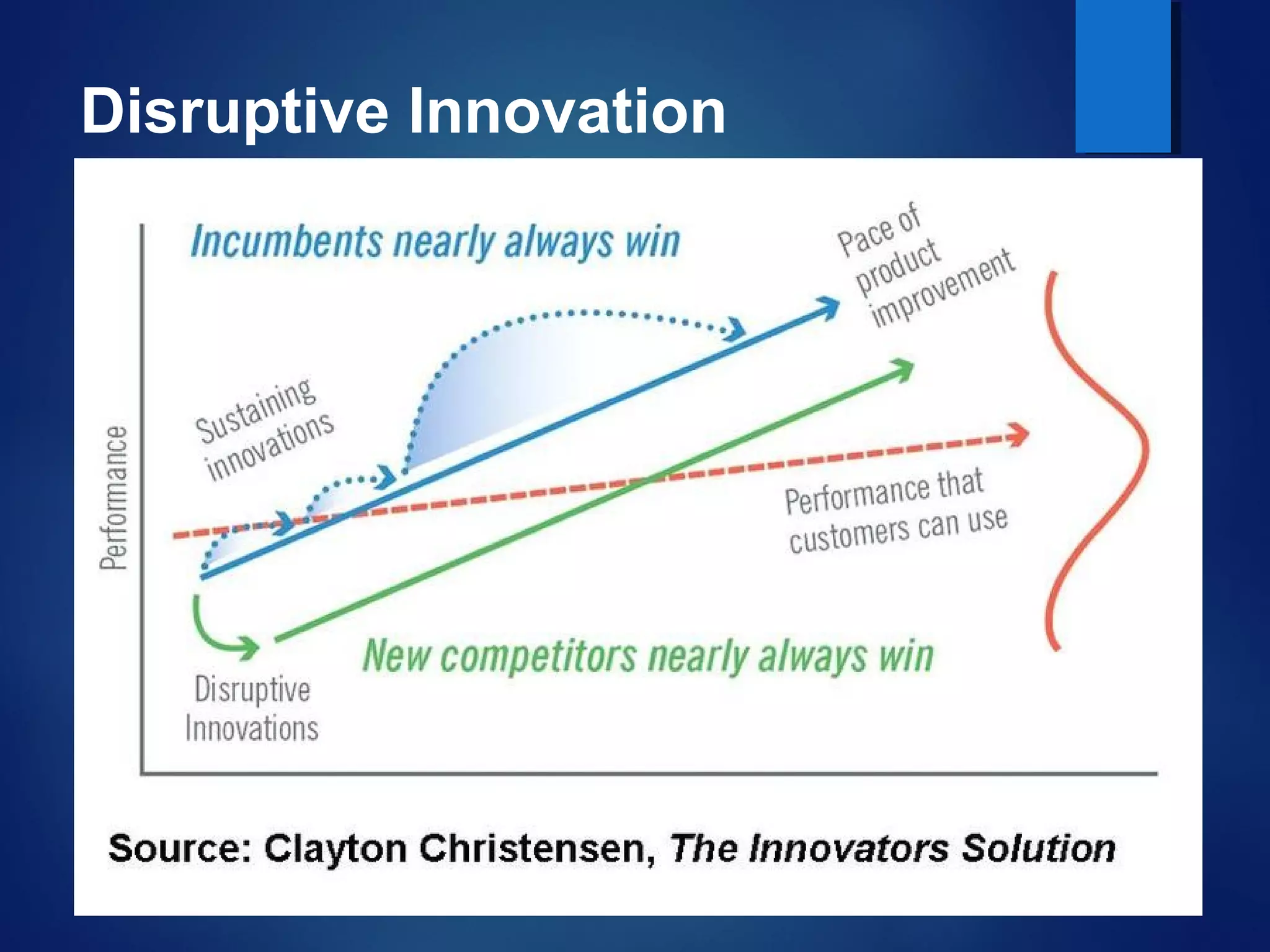
The document discusses organizational innovation, defining it as essential for business growth and highlighting three main types: process, technical, and administrative innovation. It distinguishes between incremental and radical innovations, illustrating the concept with examples from various industries and discussing the importance of the S-curve in understanding innovation adoption. Additionally, it emphasizes that effective leadership and culture are crucial for fostering innovation within organizations.