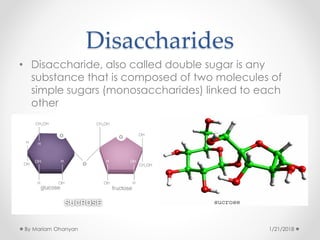
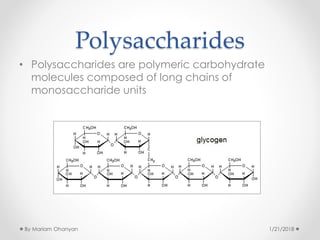
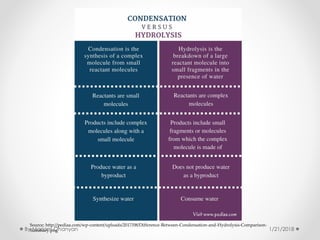
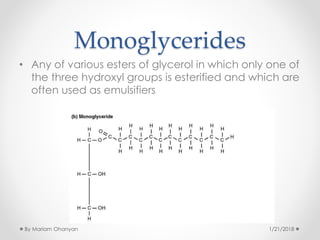
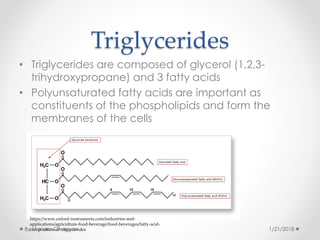
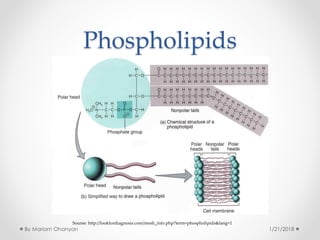
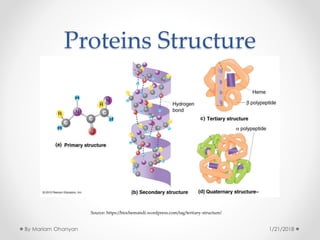
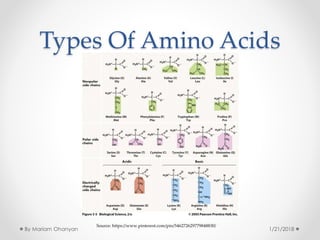
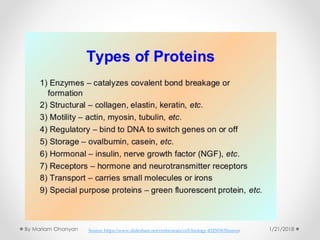
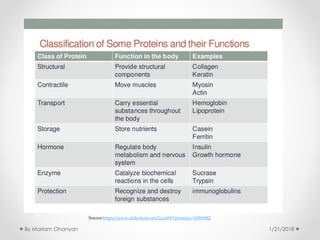
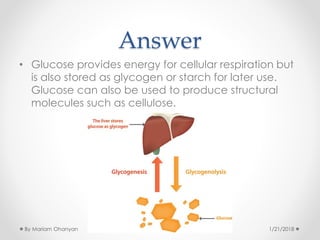
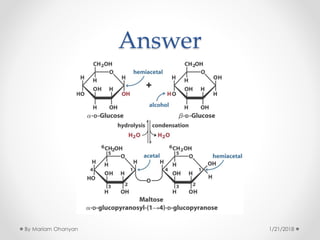
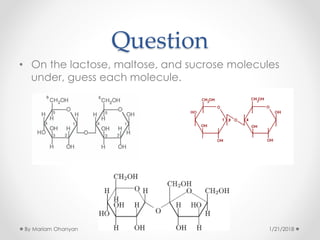
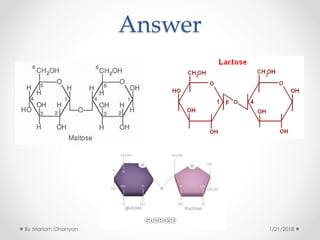
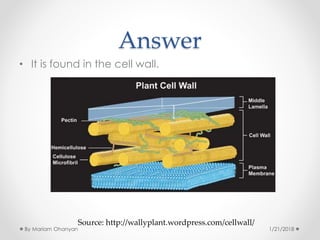
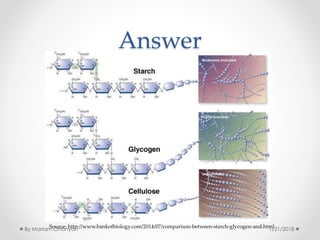
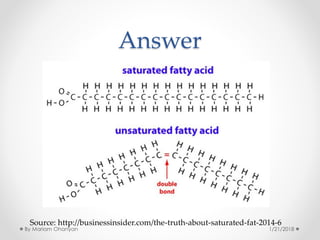
The document discusses various organic compounds, focusing on carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. It defines monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides, detailing their structures and functions, as well as the types of lipids such as triglycerides and phospholipids. Additionally, it covers the importance of amino acids in protein synthesis and how these macronutrients play critical roles in energy storage and structural integrity in living organisms.