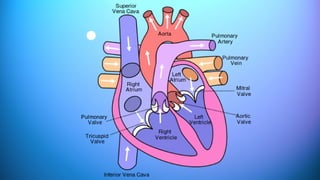
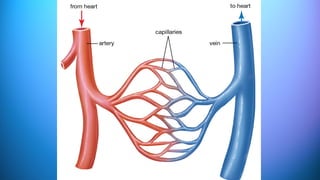
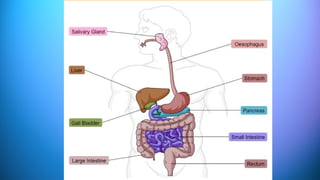
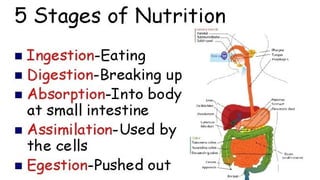
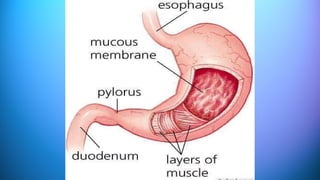
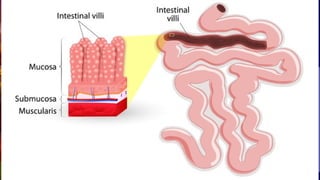
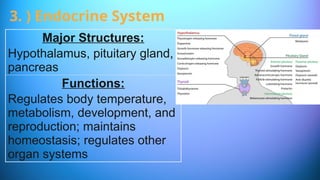
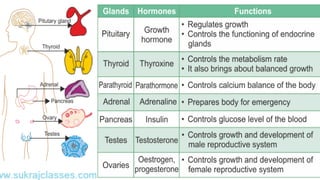
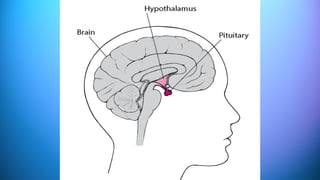
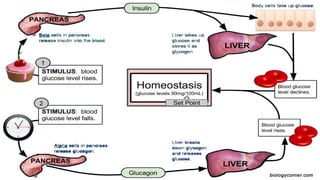
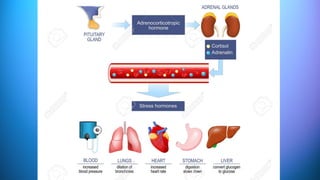
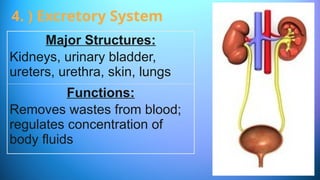
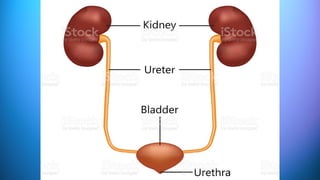
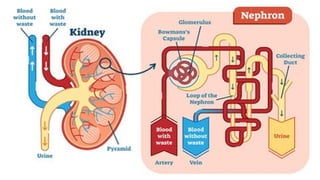
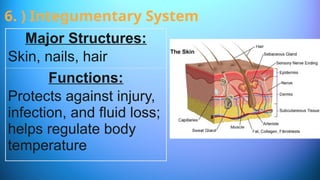
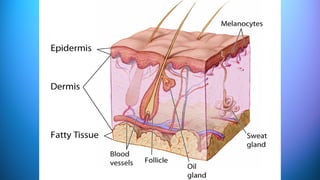
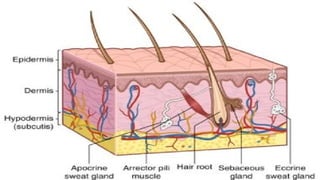
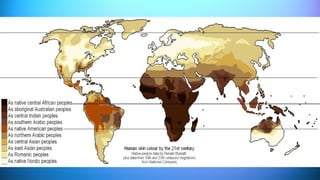
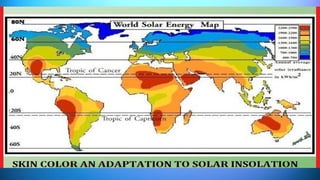
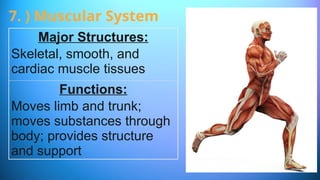
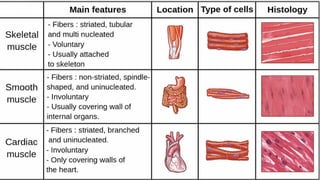
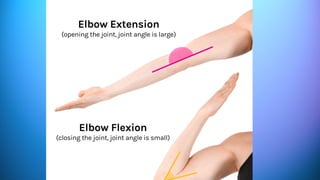
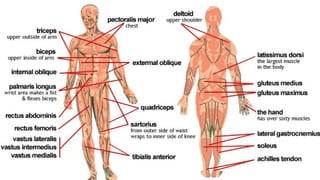
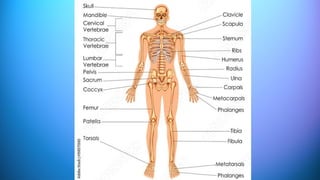
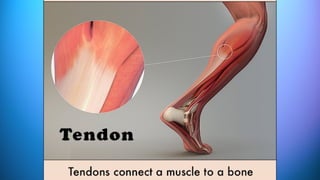
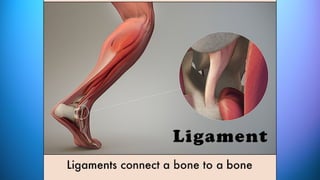
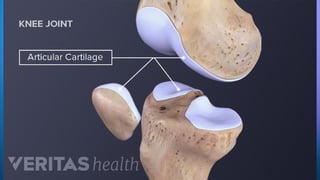
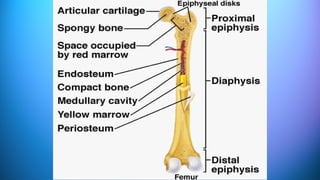
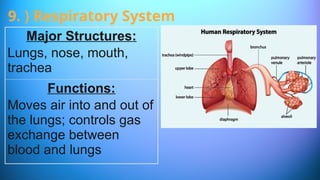
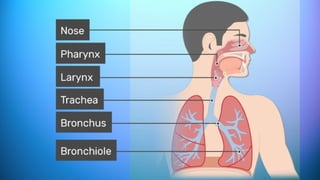
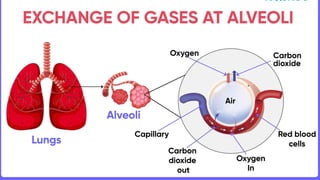
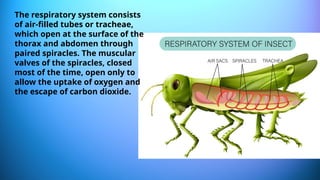
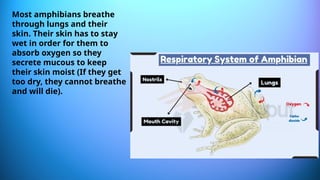
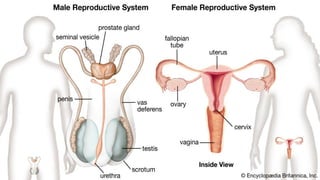
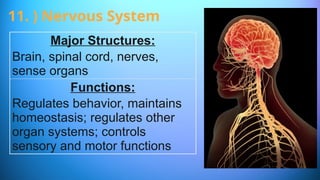
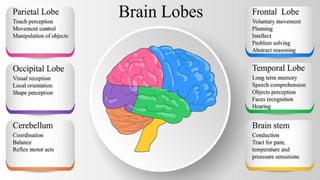
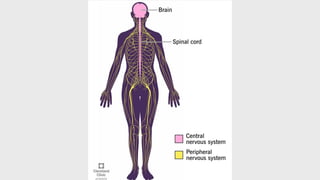
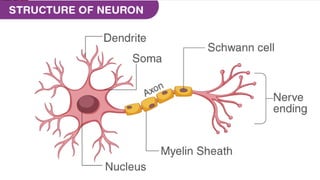
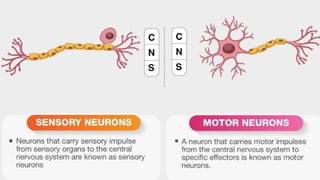
The document outlines the 11 major organ systems in the human body, detailing their major structures and functions. These systems include the circulatory, digestive, endocrine, excretory, lymphatic, integumentary, muscular, skeletal, respiratory, reproductive, and nervous systems. Each system works collaboratively to support vital processes such as nutrient transport, waste removal, and homeostasis.