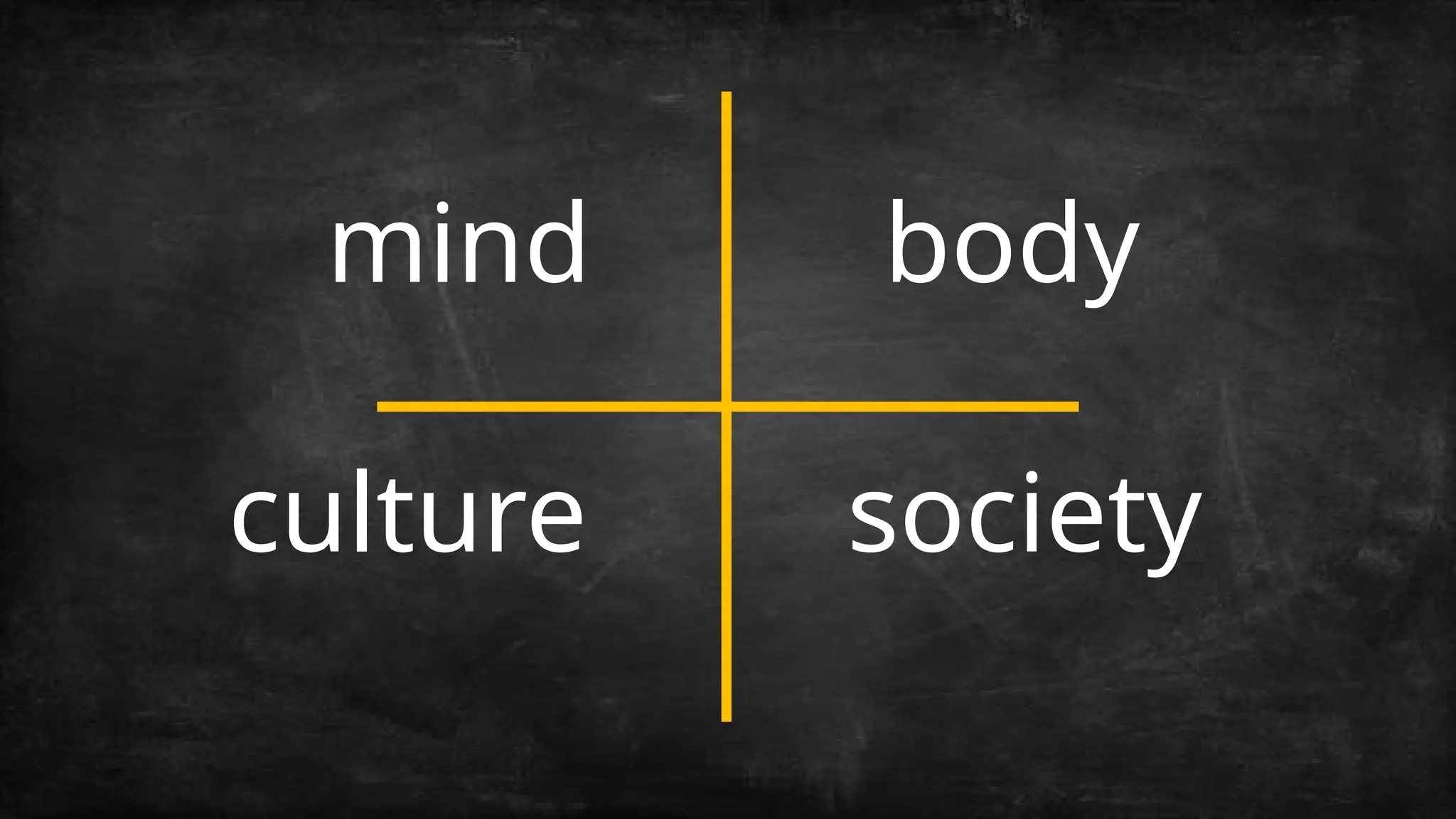
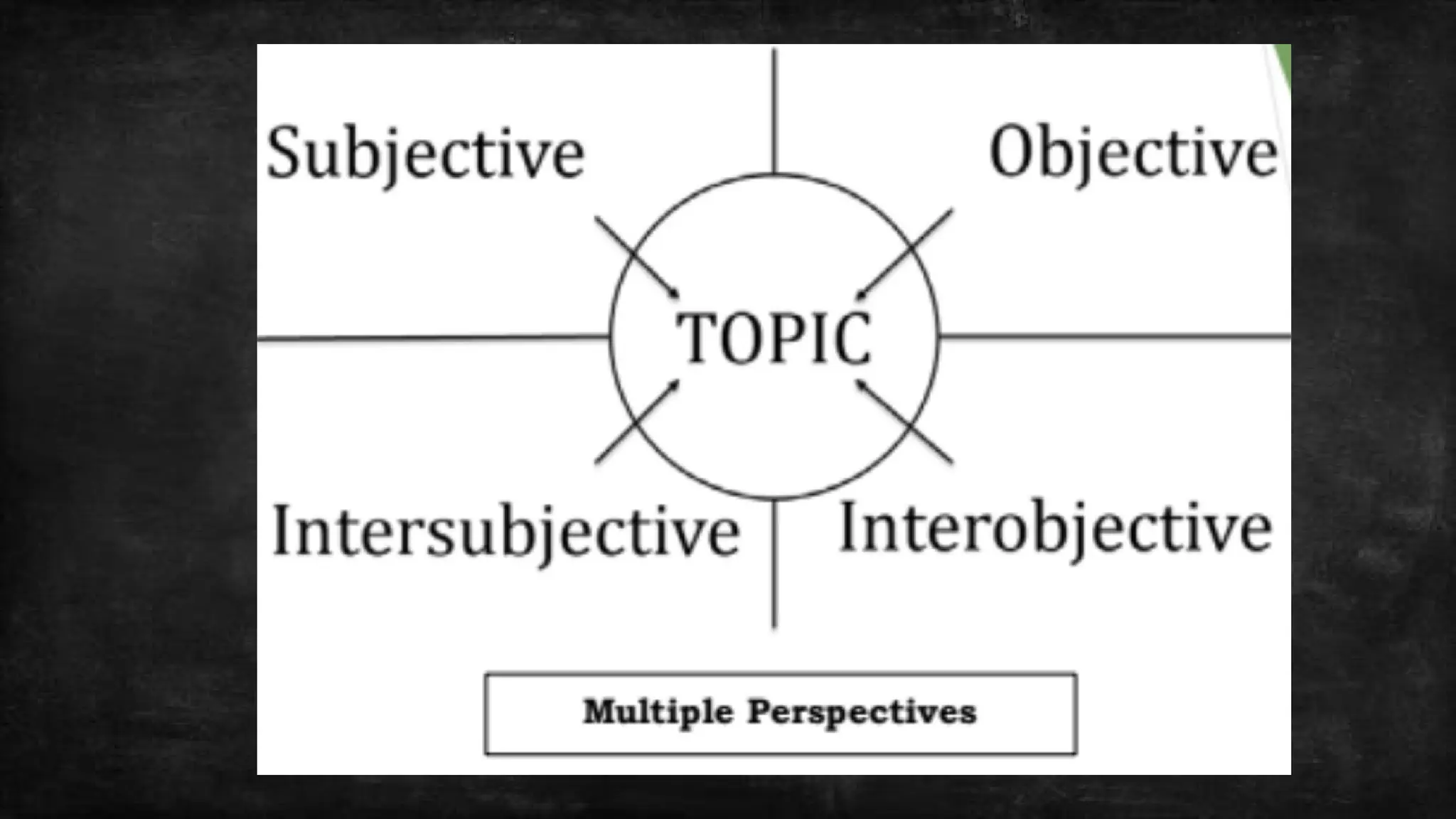
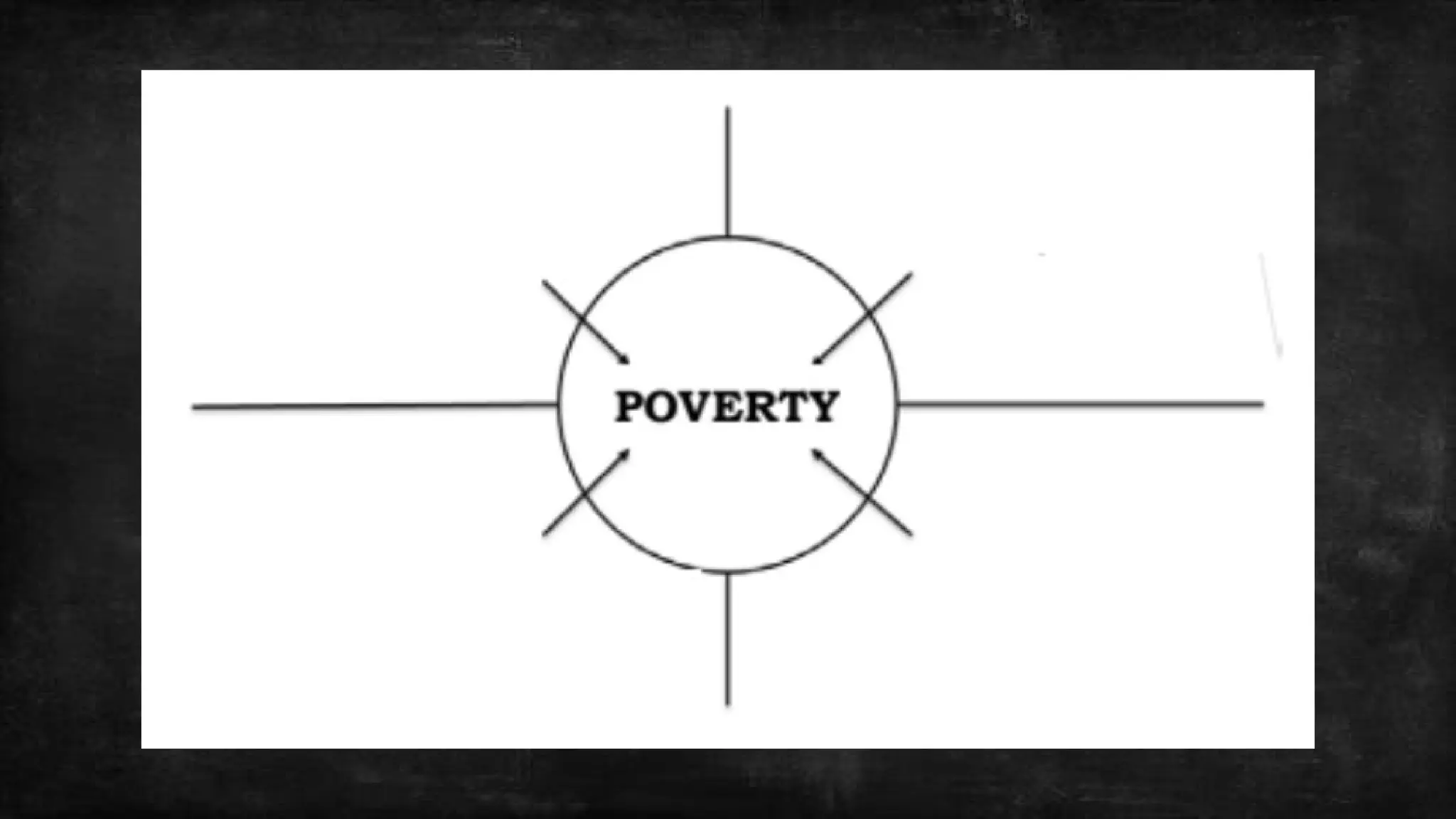
Philosophical methodology encompasses the methods used to philosophize and the study of these methods. Methods of philosophy are procedures for conducting research, creating new theories, and selecting between competing theories. In addition to the description of methods, philosophical methodology also compares and evaluates them.