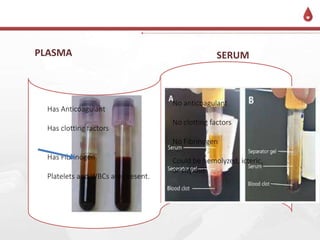
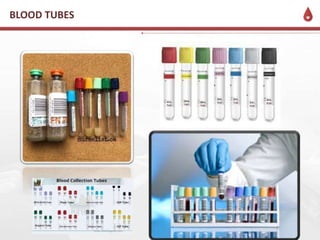
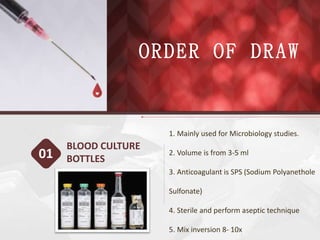
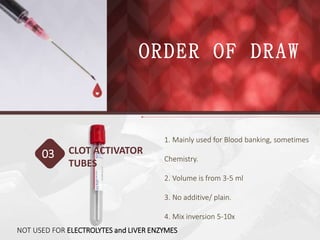
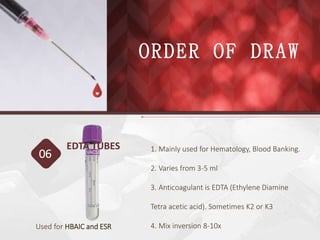
This document discusses the order of draw for blood collection tubes. It provides information on the different types of blood collection tubes used in phlebotomy, including their purposes, components, and order of collection. The recommended order is: 1) Blood culture bottles, 2) Citrate tubes, 3) Clot activator tubes, 4) Serum separator tubes, 5) Heparin tubes, 6) EDTA tubes, 7) Fluoride tubes. Following the correct order of draw is important to prevent errors and cross-contamination between tubes.