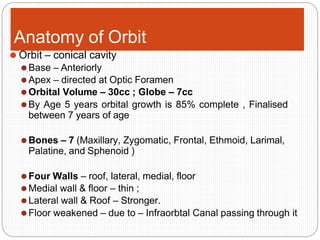
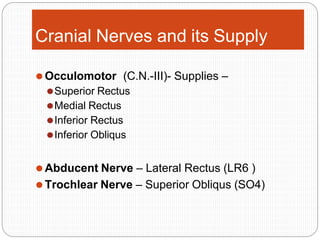
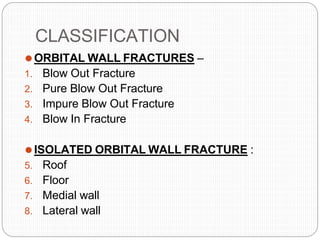
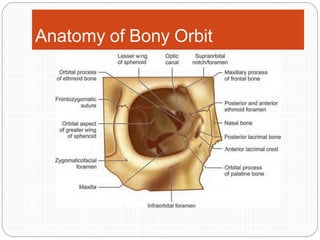
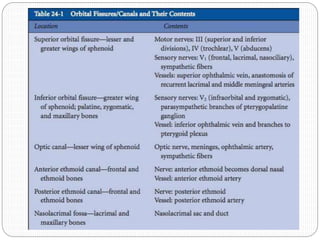
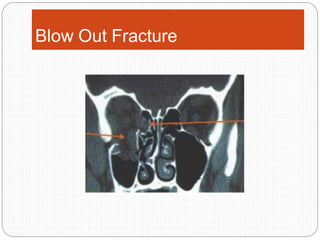
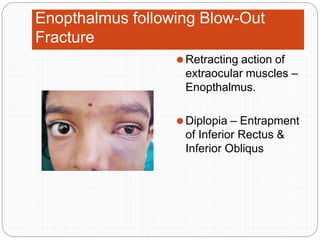
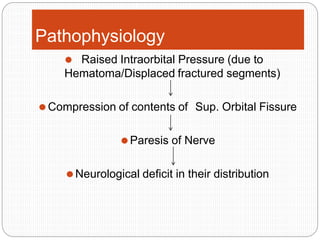
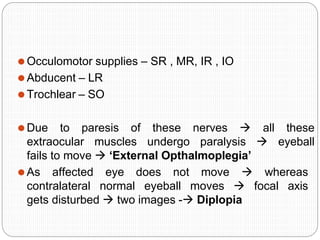
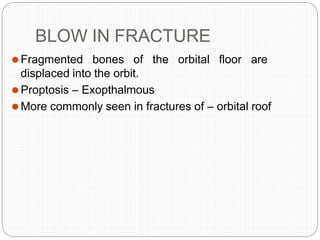
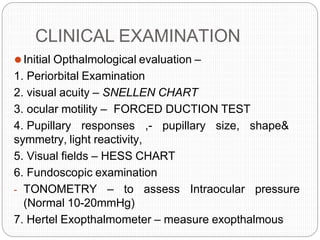
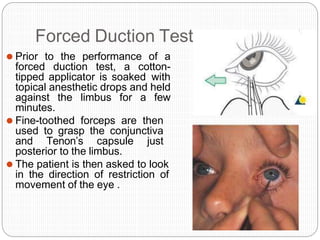
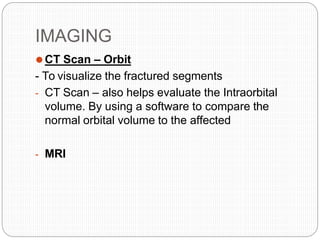
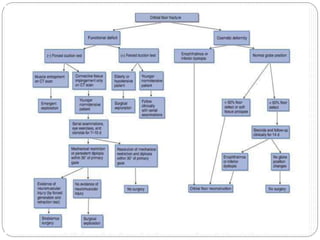
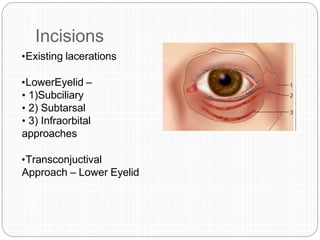
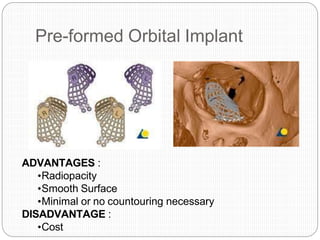
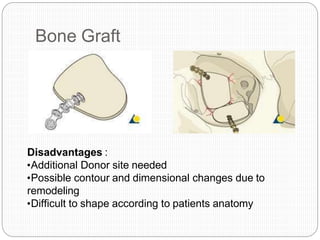
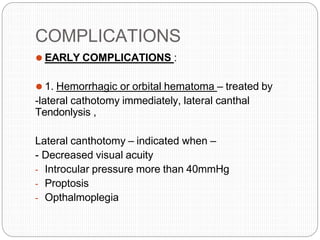
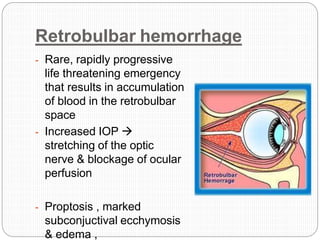
An orbital fracture occurs when one or more of the bones surrounding the eye socket (orbit) are broken. The orbit contains several thin bones that can fracture upon facial trauma, allowing bone fragments or soft tissues to be displaced into the orbit. Common types include blow-out fractures, where a bone fragment is driven into the orbit, and blow-in fractures, where a fragment is pushed in the opposite direction out of the orbit. Clinical features may include swelling, bruising, double vision from impaired eye movement, and changes in eye position. Imaging such as CT scan is used to evaluate the fracture. Treatment involves correcting any tissue or bone displacements through surgical approaches to the orbit. Complications can include issues with vision, eye movement,