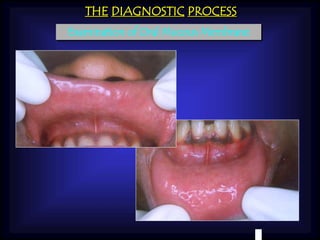
The document describes the diagnostic process for examining the periodontium and oral mucosa intra-orally. It involves examining the gingiva for signs of inflammation using indices to assess periodontal health. The oral mucosa of different areas are also examined, including inspection for lesions and palpation for tenderness or fixation. Examination of the chief complaint area compiles all observations to lead to a provisional diagnosis.