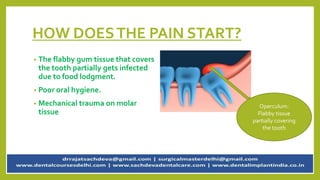
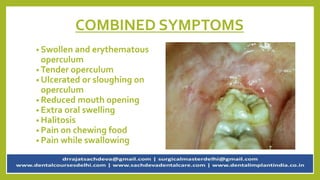
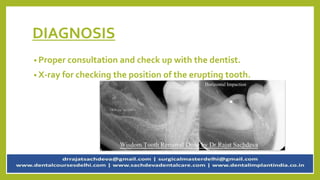
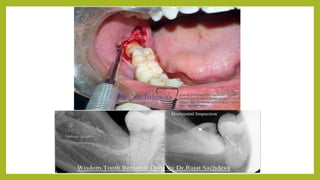
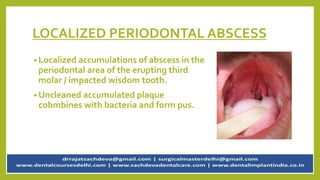
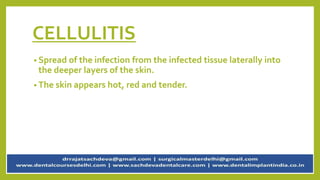
Pericoronitis is a common dental condition characterized by pain around the erupting third molar or wisdom tooth, often caused by infection of the flabby gum tissue. It can present in various forms: acute, sub-acute, and chronic, with symptoms including swollen and tender operculum, regional lymphadenopathy, and pain while chewing. Treatment options range from improving oral hygiene to surgical interventions like operculectomy or tooth extraction, with complications potentially leading to abscesses or systemic infections if untreated.