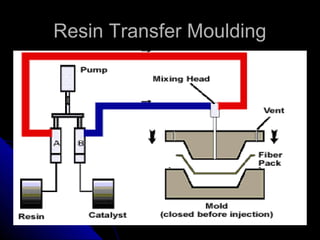
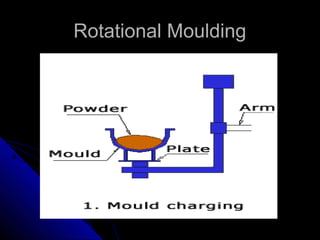
This document discusses sources of technical knowledge for the plastics industry, focusing on classifications of plastics, important properties for designers, manufacturers and customers, materials and manufacturing methods, strategies for improvement, basic economics, and case studies of high-return plastic projects. It provides information on plastic consumption trends, commodity vs engineering plastics, important design and manufacturing properties, manufacturing methods like injection molding and rotational molding, standards, design for manufacturing strategies, project cost estimation, basic economic analysis, and examples of profitable plastic product lines.