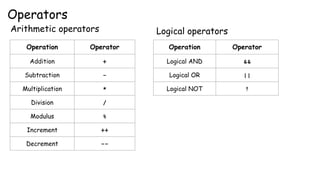
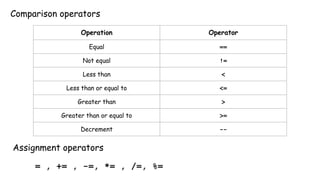
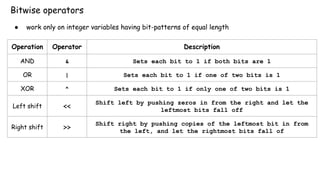
This document discusses operators in the Go programming language including arithmetic, logical, comparison, assignment, and bitwise operators. It provides examples of using each operator type on variables and integers and explains some rules for bitwise operators, such as they only work on integer variables of equal length.