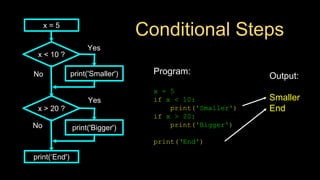
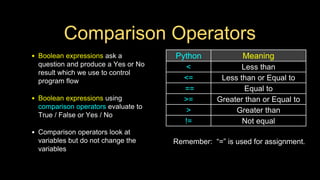
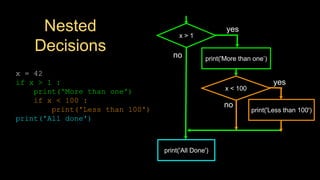
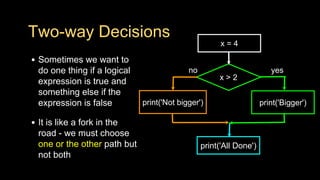
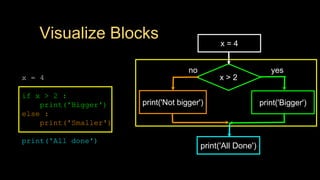
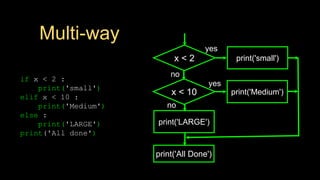
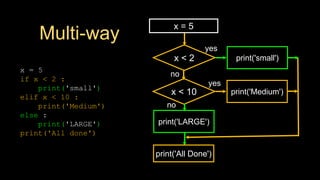
The document discusses different types of conditional control statements in Python including comparison operators, one-way decisions using if statements, two-way decisions using if/else statements, nested decisions, and multi-way decisions using if/elif/else statements. Comparison operators like ==, <=, >=, >, <, and != are used to evaluate Boolean expressions and control program flow. Indentation is used to indicate the scope of blocks of code within if, elif, and else statements. Multi-way decisions allow evaluating multiple conditions and executing different code blocks based on which condition is true.