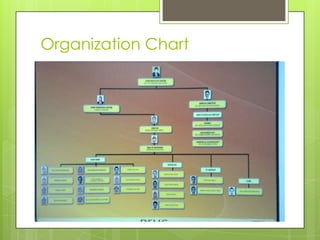
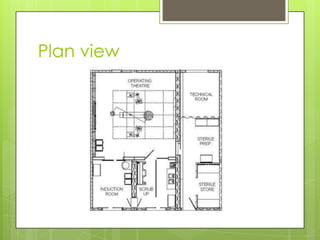
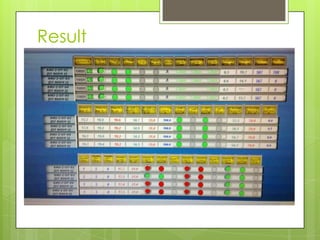
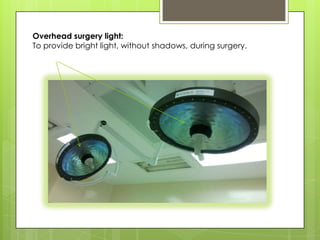
This document provides information about the operation theatre (OT) or operating room. It discusses the general requirements and organization of an OT including the attire of surgeons and staff. It details the specific OTs at DEMC hospital including the medical directors and staff. Floor plans and dimensions of major and minor OTs are presented. Ideal room conditions for temperature, humidity and air pressure are outlined. Various types of power supply including essential, UPS and normal are described. Finally, basic and additional equipment used in surgery like overhead lights, operating table, anesthetic machine are explained.