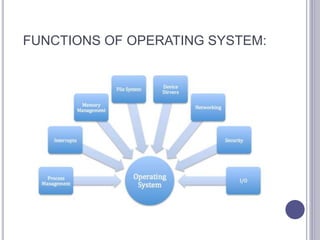
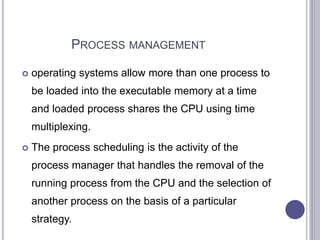
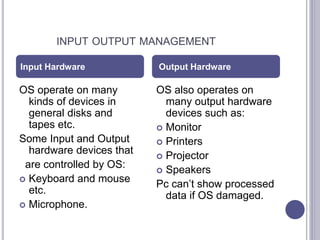
An operating system manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for programs. It has four main parts: the kernel, device drivers, user interface, and system utilities. The operating system manages resources like the CPU, memory, I/O devices, and security and networking. Common operating systems include batch, time-sharing, distributed, network, and real-time systems. It performs processes management, memory management, input/output management, security management, and networking management.