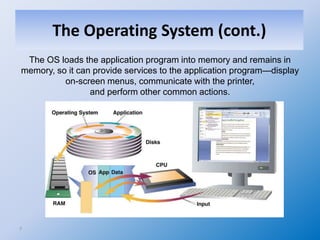
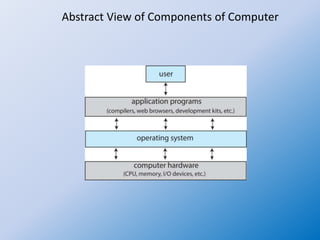
The document introduces the concept of operating systems, detailing their essential role in managing computer hardware, software, and user applications. It outlines the components of computer systems, including hardware, operating systems, application programs, and users, while explaining the functions of operating systems such as multitasking, file management, and memory management. Additionally, it highlights the importance of utility programs for system maintenance and mentions Unix and Linux as significant operating systems used in various computing environments.