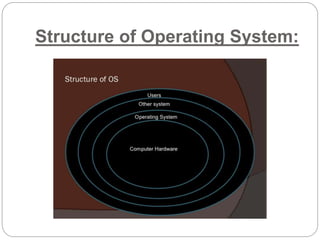
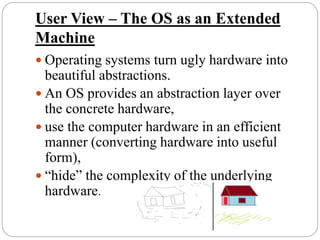
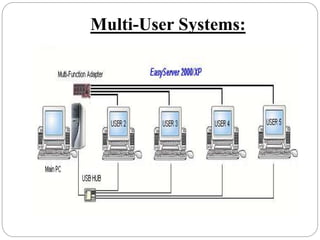
This document provides an overview of operating systems. It defines an operating system as software that enables computer programs to work by organizing hardware resources and providing common services. The document then discusses the basic functions of an OS in controlling memory, prioritizing tasks, managing devices and files. It describes the layers of an OS including the hardware, software, system programs and application programs. Finally, it discusses the history of early OS and different types of OS like single-user and multi-user systems, providing examples like Windows, Linux, and Unix.