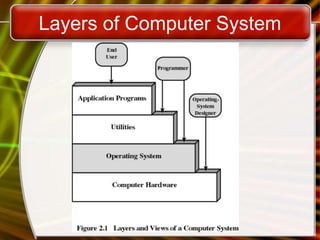
The document provides an overview of operating systems, discussing their objectives, functions, and types. It covers essential services provided by operating systems, such as program development, execution, and hardware management, along with an examination of user interfaces like GUI and command line. Additionally, it describes different operating systems including real-time, single-user, and multi-user systems, and highlights utilities that enhance OS capabilities.