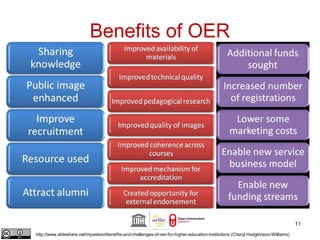
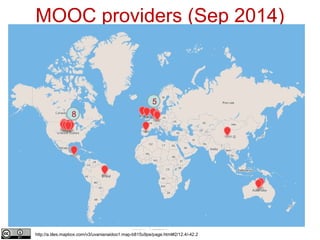
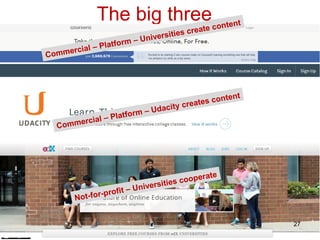
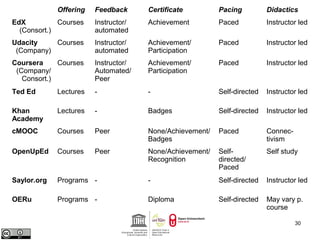
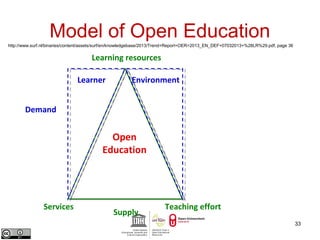
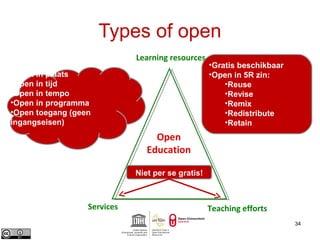
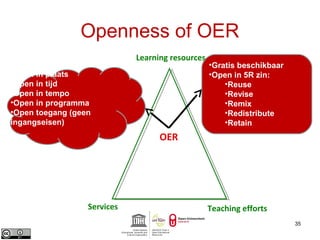
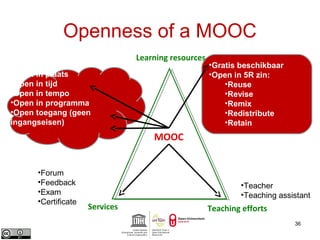
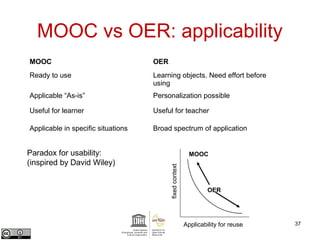
This document provides an overview of open educational resources (OER) and open education. It defines OER as digital learning materials that can be freely used, modified, and shared. Reasons for using OER include personalized learning, innovation, and moral arguments about taxpayer-funded resources. Massive open online courses (MOOCs) are also discussed, including examples of popular MOOC platforms like edX, Coursera, and Udacity. The document outlines different types and degrees of openness in education. Business models for funding OER and MOOCs are presented, along with challenges to introducing open resources like findability, quality, licensing, and human factors.