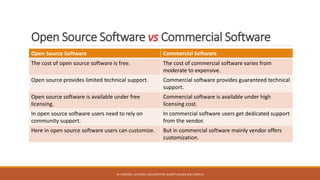
The document discusses different types of software including open source software, commercial software, freeware software, shareware software, and proprietary software. Open source software is available freely with publicly accessible source code. Commercial software requires payment of licensing fees and has proprietary source code. Freeware is free to use but retains copyright, while shareware is initially free but requires payment to continue use after a trial period. Proprietary software is owned and controlled by an individual or company.