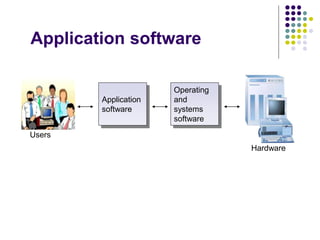
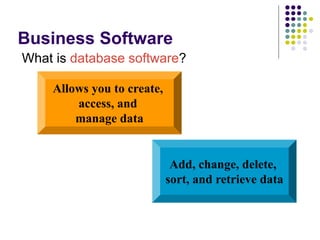
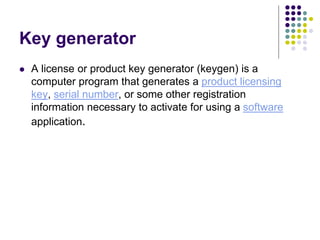
This lecture discusses application software. It defines application software as programs that run under system software and are designed to help users complete specific tasks. Examples provided include web browsers, word processors, spreadsheets, databases, presentations, graphics, and audio/video software. The lecture also discusses different types of software licenses including shareware, freeware, and paid licenses, as well as key generators. Freeware is free software available under certain usage restrictions, while shareware is trial software intended for purchase. Paid licenses grant permission to use software under copyright.