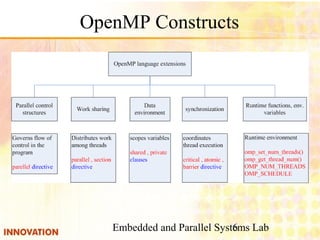
This document discusses OpenMP, a specification for parallel programming on shared memory architectures. It provides an outline of OpenMP features, basic syntax using #pragma directives, and support requirements. Examples are given of using OpenMP constructs like parallel for, sections, and directives like num_threads to parallelize loops and divide work across threads. Guidelines are also presented around avoiding data races, deadlocks, and other issues in OpenMP programming.


![Embedded and Parallel Systems Lab3
OpenMP
OpenMP 2.5
Multi-threaded & Share memory
Fortran 、 C / C++
基本語法
#pragma omp directive [clause]
OpenMP 需求及支援環境
Windows
Virtual studio 2005 standard
Intel ® C++ Compiler 9.1
Linux
gcc 4.2.0
Omni
Xbox 360 & PS3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openmp-140808095117-phpapp01/85/OpenMP-3-320.jpg)



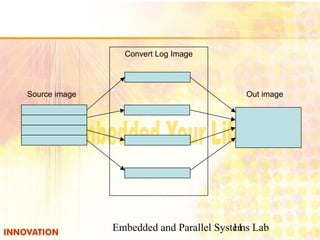
![Embedded and Parallel Systems Lab12
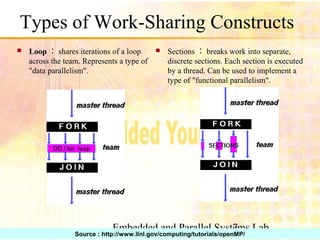
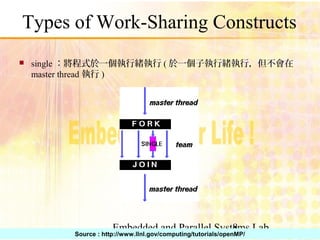
Sections Working Share
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
#pragma omp parallel sections
{
#pragma omp section
{
toPNG();
}
#pragma omp section
{
toJPG();
}
#pragma omp section
{
toTIF();
}
}
}
Input image
toPNG
toJPG
toTIF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openmp-140808095117-phpapp01/85/OpenMP-12-320.jpg)
![Embedded and Parallel Systems Lab13
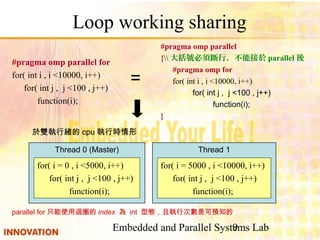
OpenMP notice
int Fe[10];
Fe[0] = 0;
Fe[1] = 1;
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(2)
for( i = 2; i < 10; ++ i )
Fe[i] = Fe[i-1] + Fe[i-2];
Data dependent
#pragma omp parallel
{
#pragma omp for
for( int i = 0; i < 1000000; ++ i )
sum += i;
}
Race conditions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openmp-140808095117-phpapp01/85/OpenMP-13-320.jpg)

![Embedded and Parallel Systems Lab15
OpenMP example:matrix(1)
#include <omp.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define RANDOM_SEED 2882 //random seed
#define VECTOR_SIZE 4 //sequare matrix width the same to height
#define MATRIX_SIZE (VECTOR_SIZE * VECTOR_SIZE) //total size of
MATRIX
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int i,j,k;
int node_id;
int *AA; //sequence use & check the d2mce right or fault
int *BB; //sequence use
int *CC; //sequence use
int computing;
int _vector_size = VECTOR_SIZE;
int _matrix_size = MATRIX_SIZE;
char c[10];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openmp-140808095117-phpapp01/85/OpenMP-15-320.jpg)
![Embedded and Parallel Systems Lab16
OpenMP example:matrix(2)
if(argc > 1){
for( i = 1 ; i < argc ;){
if(strcmp(argv[i],"-s") == 0){
_vector_size = atoi(argv[i+1]);
_matrix_size =_vector_size * _vector_size;
i+=2;
}
else{
printf("the argument only have:n");
printf("-s: the size of vector ex: -s 256n");
return 0;
}
}
}
AA =(int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * _matrix_size);
BB =(int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * _matrix_size);
CC =(int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * _matrix_size);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openmp-140808095117-phpapp01/85/OpenMP-16-320.jpg)
![Embedded and Parallel Systems Lab17
OpenMP example:matrix(3)
srand( RANDOM_SEED );
/* create matrix A and Matrix B */
for( i=0 ; i< _matrix_size ; i++){
AA[i] = rand()%10;
BB[i] = rand()%10;
}
/* computing C = A * B */
#pragma omp parallel for private(computing, j , k)
for( i=0 ; i < _vector_size ; i++){
for( j=0 ; j < _vector_size ; j++){
computing =0;
for( k=0 ; k < _vector_size ; k++)
computing += AA[ i*_vector_size + k ] *
BB[ k*_vector_size + j ];
CC[ i*_vector_size + j ] = computing;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openmp-140808095117-phpapp01/85/OpenMP-17-320.jpg)



