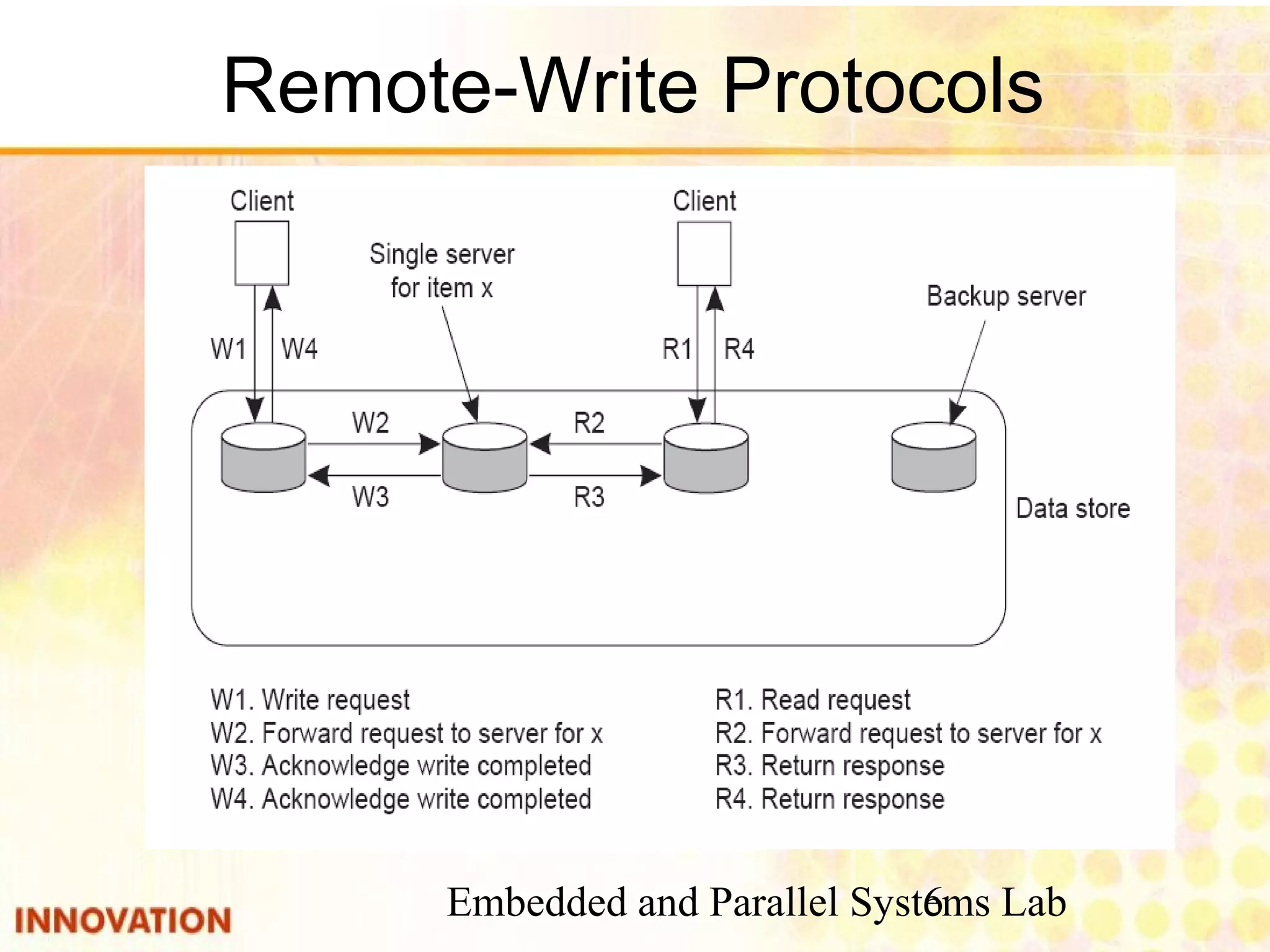
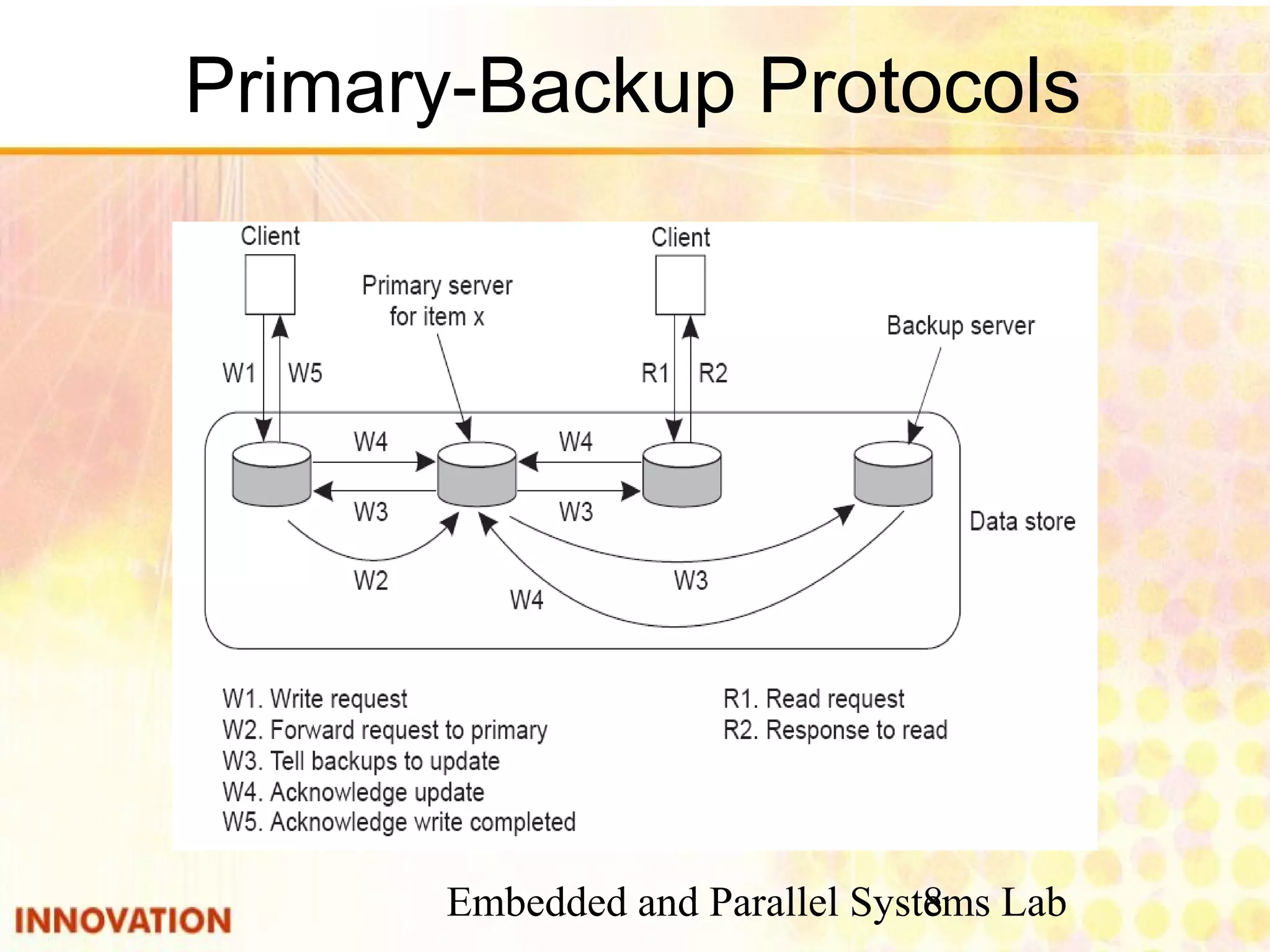
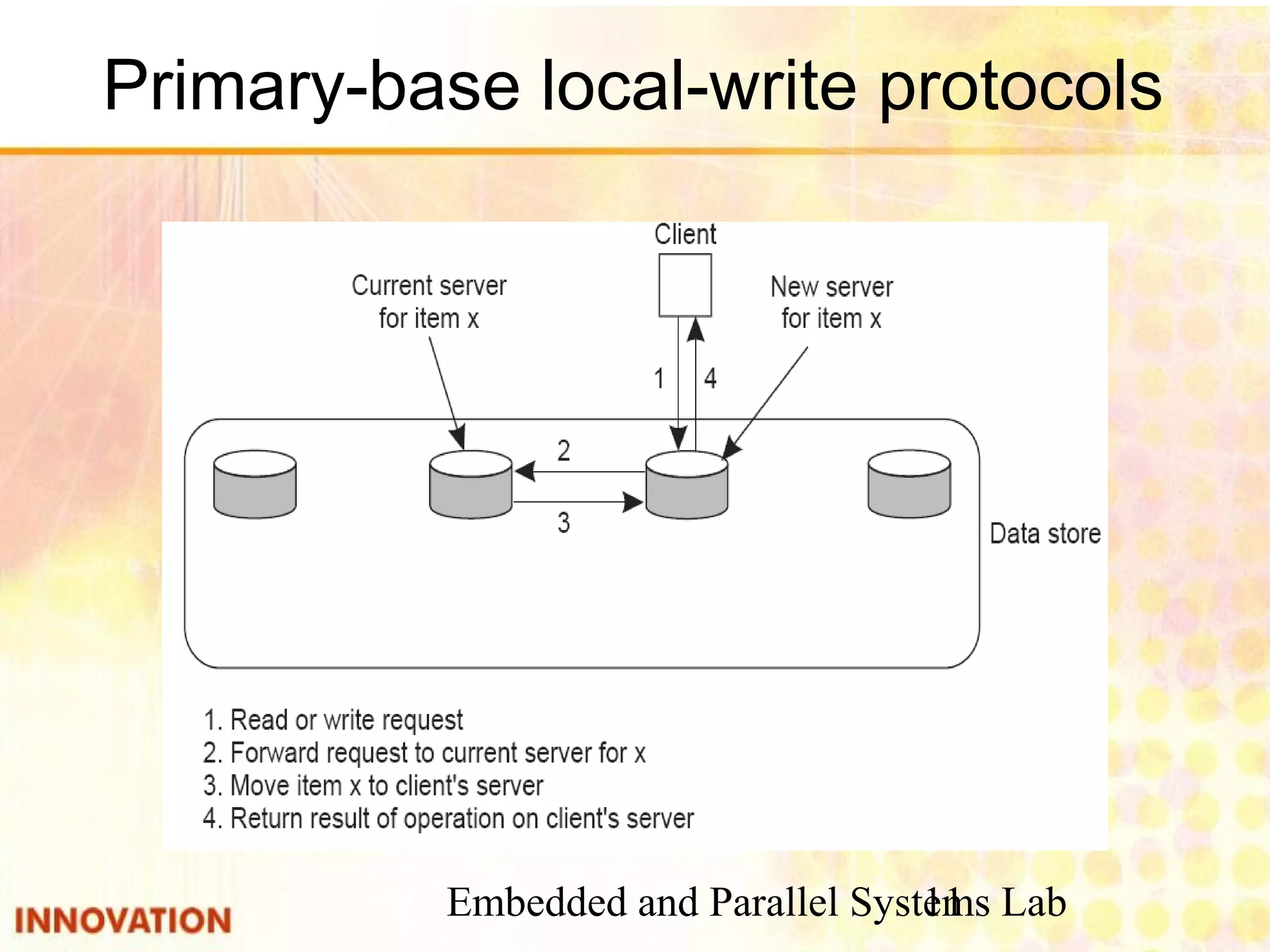
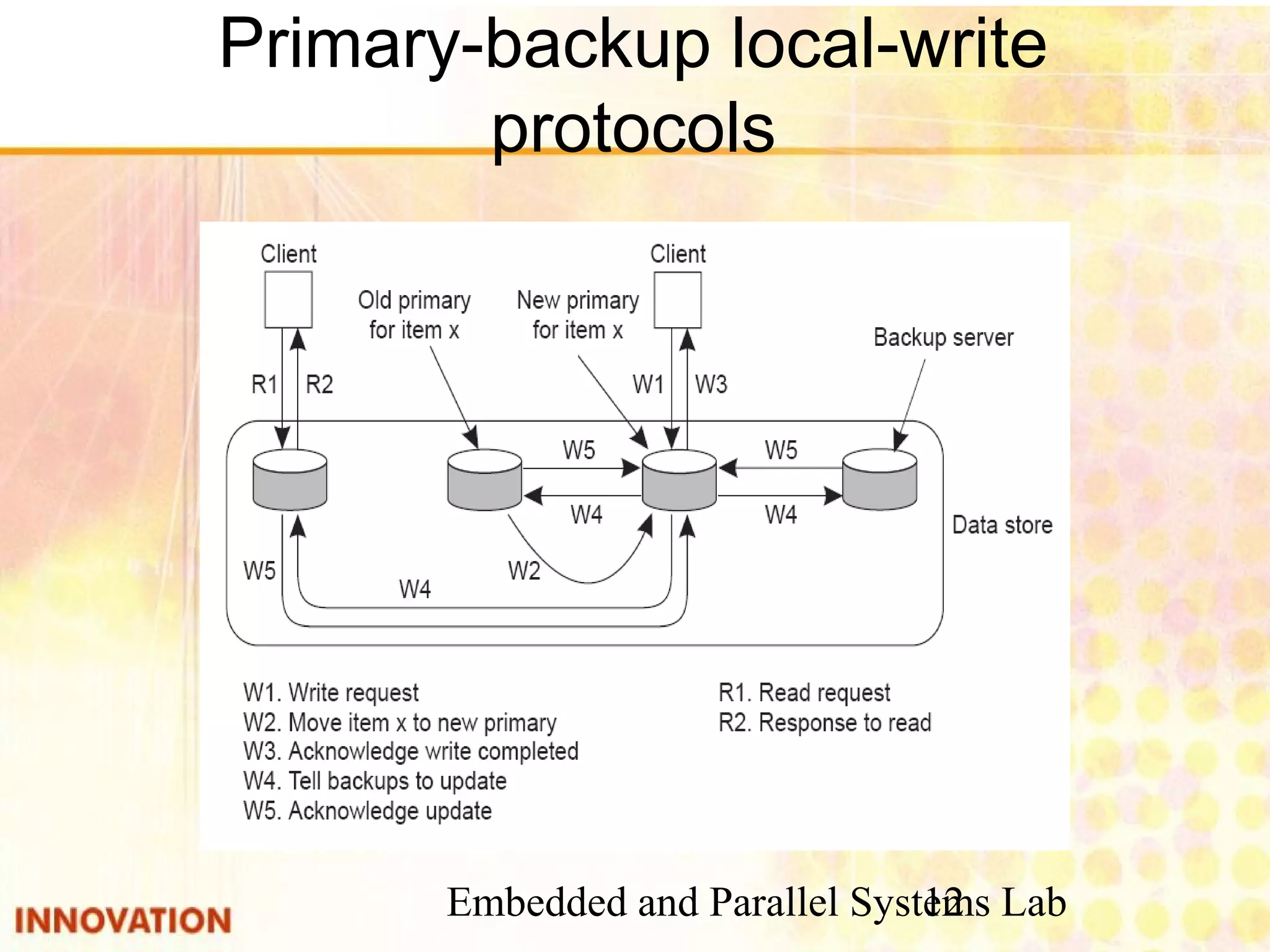
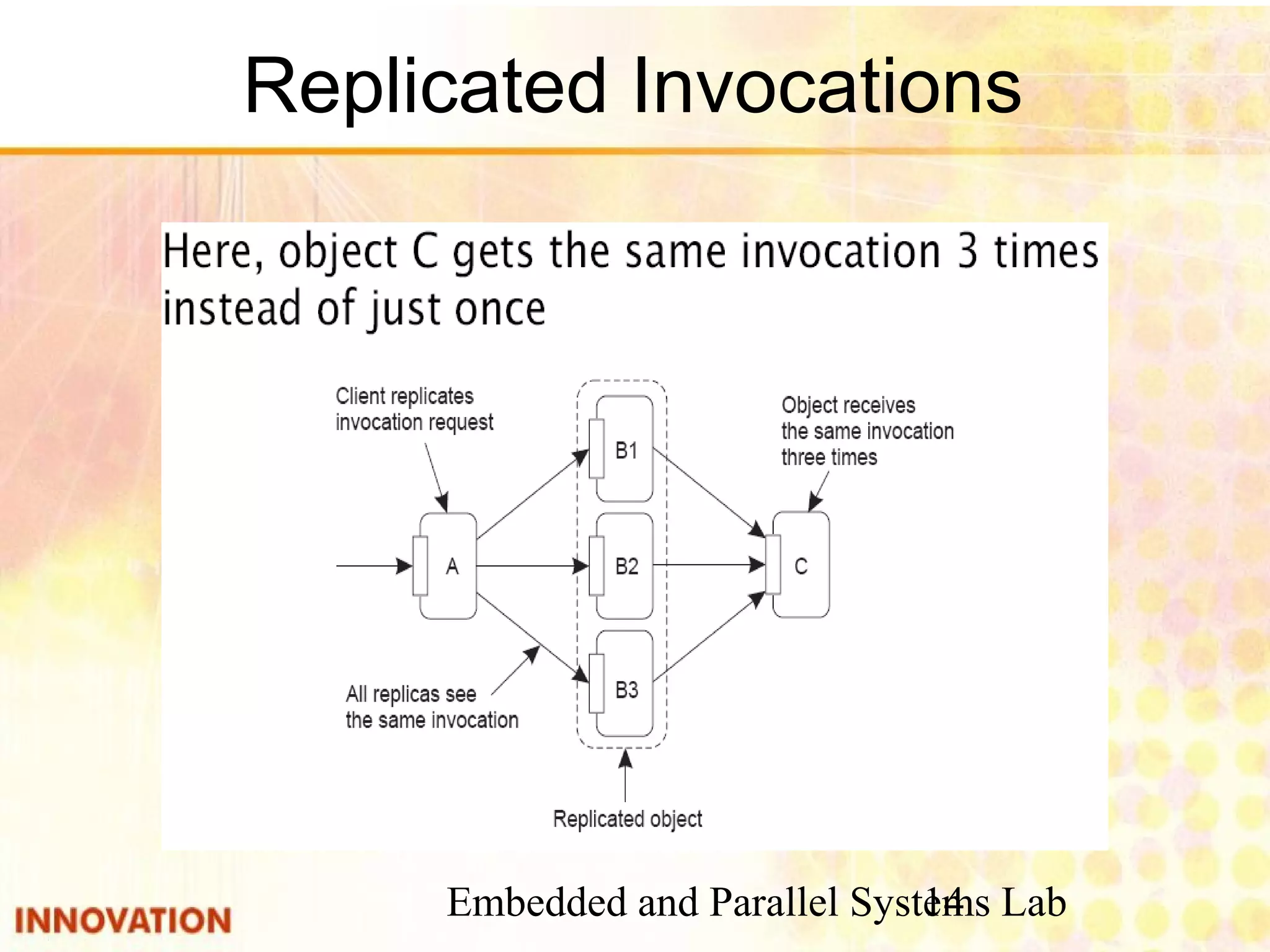
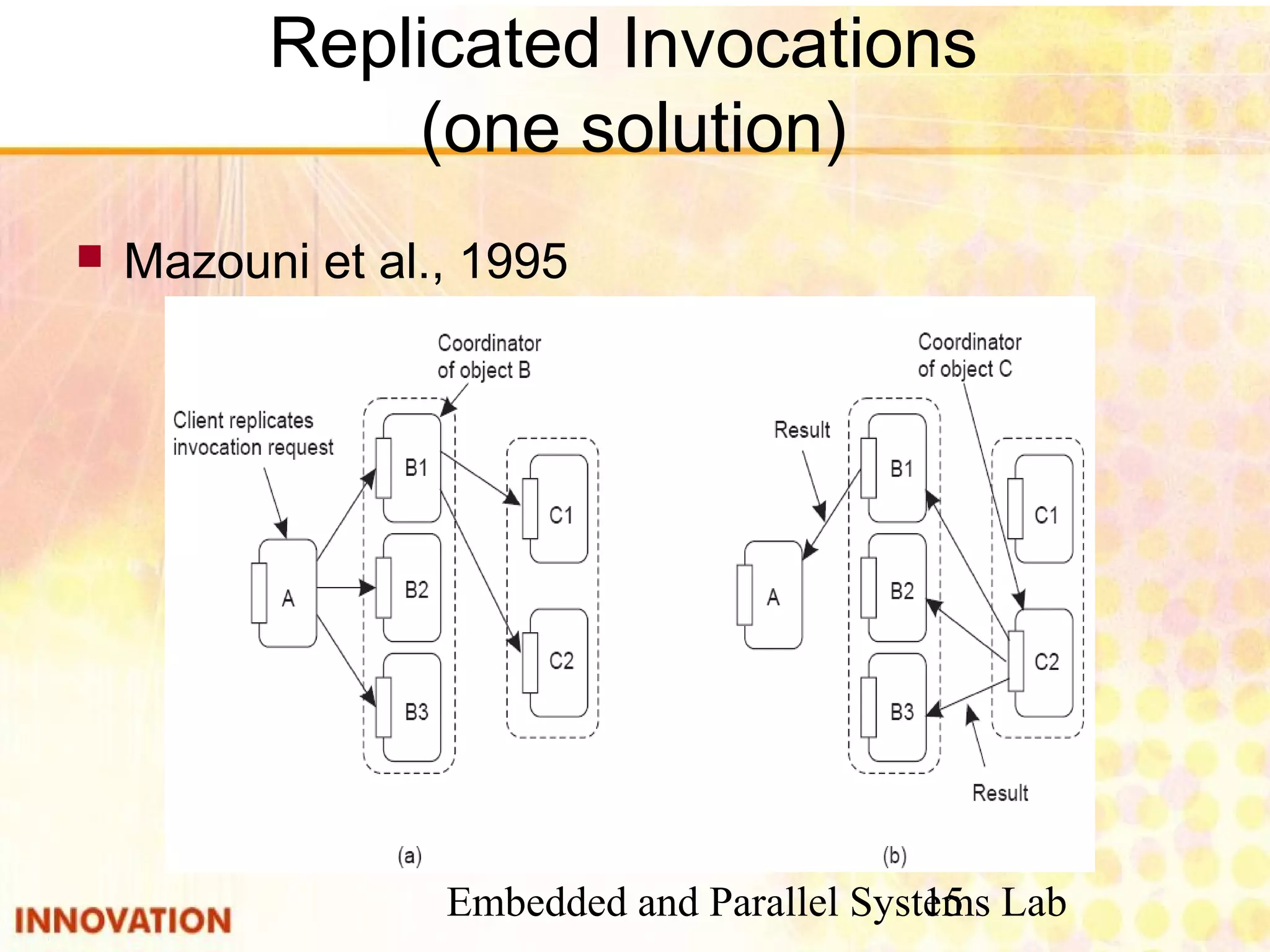
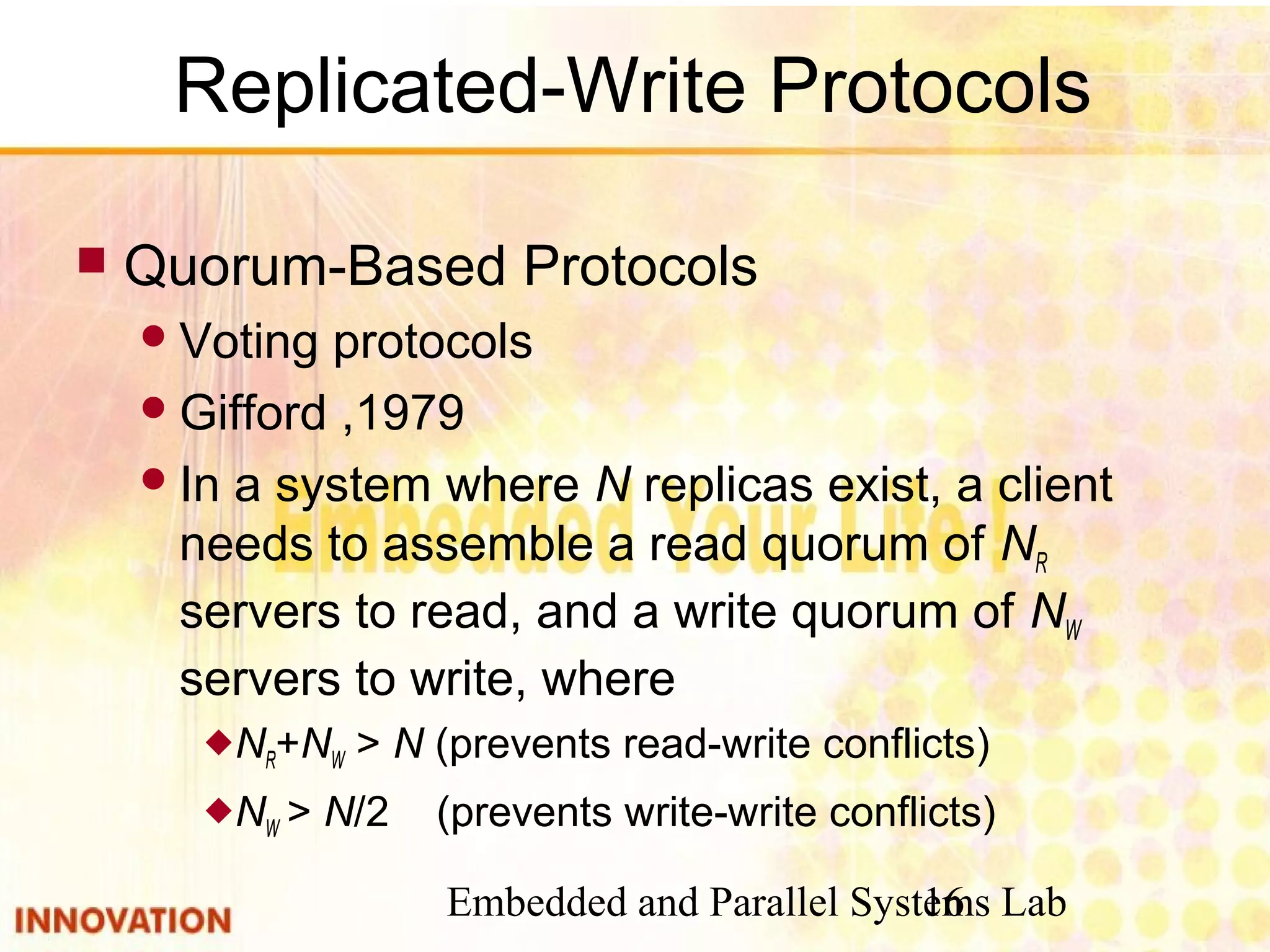
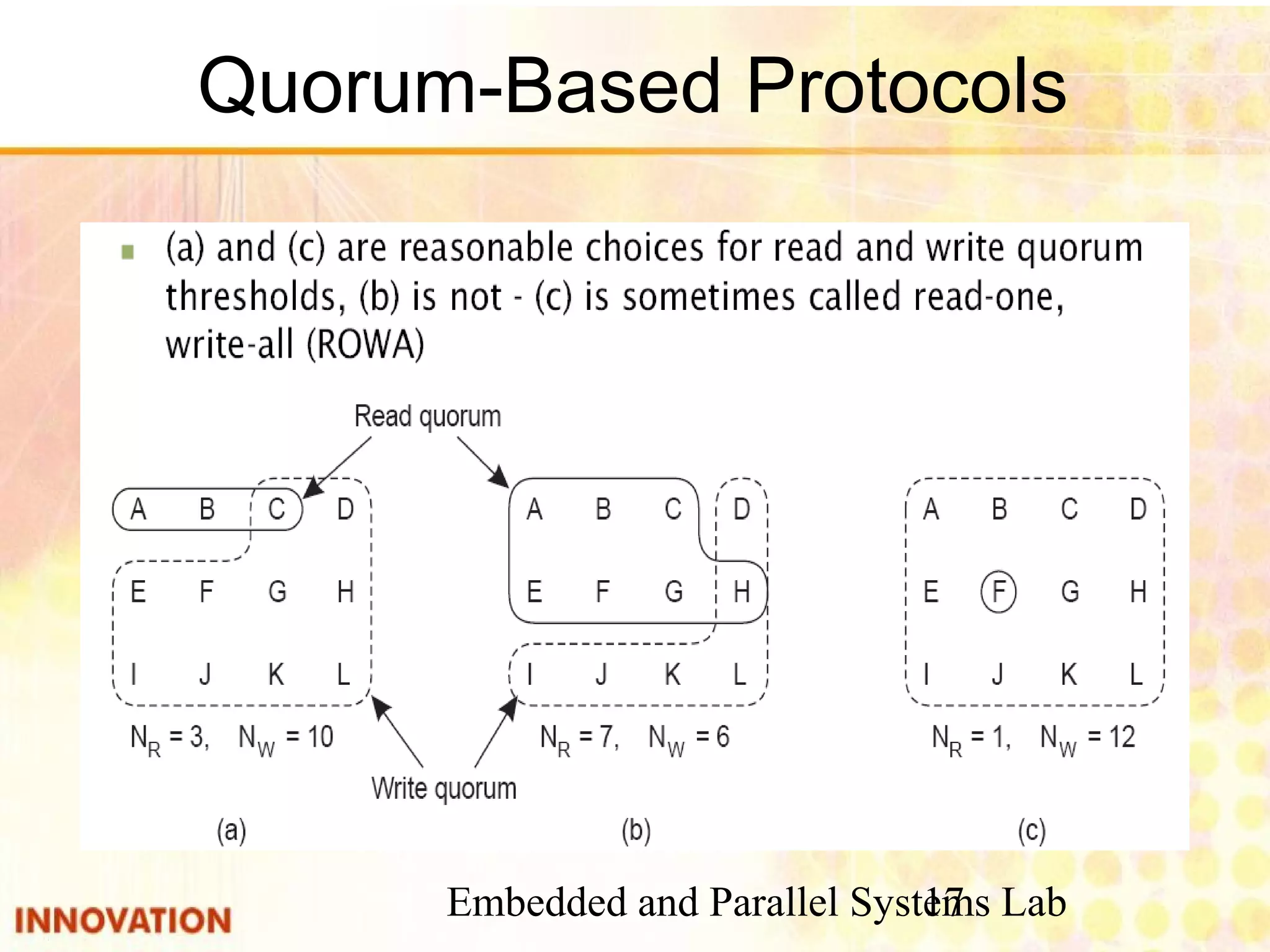
This document discusses various consistency protocols for replicated data in distributed systems. It covers primary-based protocols where each data item has a primary replica, and replication-based protocols where writes can be done at multiple replicas. For primary-based protocols, it distinguishes between remote-write protocols where operations are done remotely at the primary and local-write protocols where the primary may be copied locally. It also discusses quorum-based replication protocols that use voting to achieve consistency across replicas.