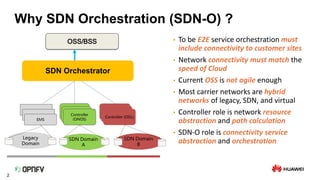
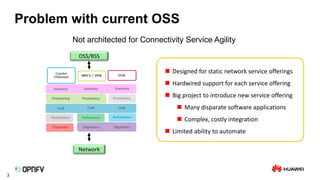
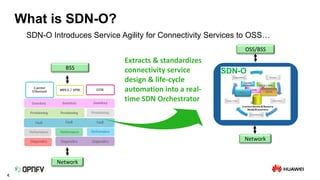
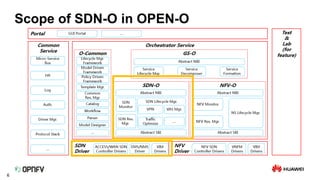
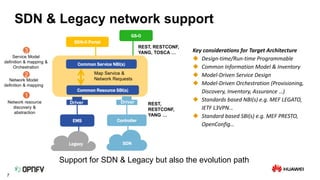
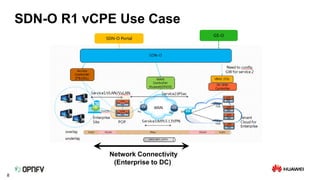
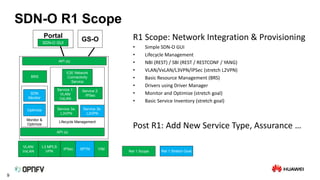
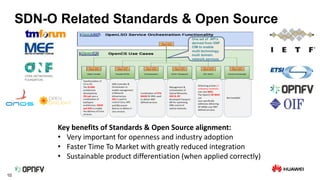
The document discusses the need for SDN orchestration (sdn-o) to provide end-to-end service management that accommodates both legacy and SDN networks, addressing current limitations in network agility. Key requirements for sdn-o include full service life-cycle automation and support for diverse technologies, aiming to enhance connectivity service design and integration. The conclusion emphasizes that sdn-o is essential for matching network connectivity speeds with cloud capabilities and underscores the importance of standards and open source for industry adoption.