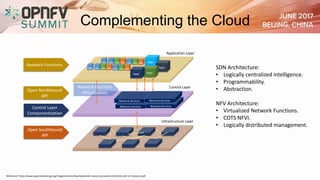
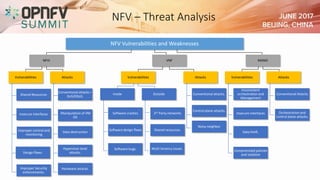
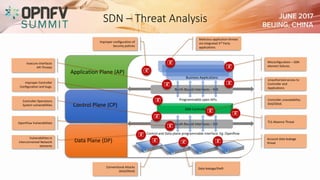
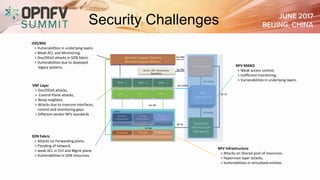
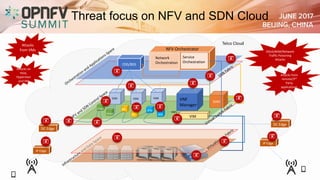
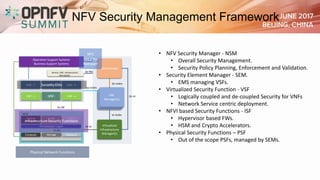
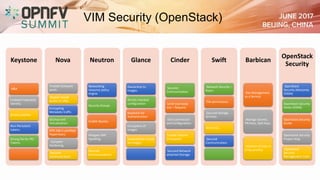
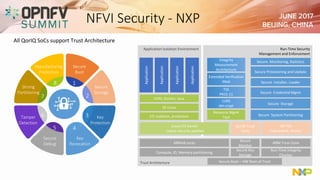
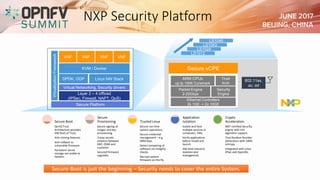
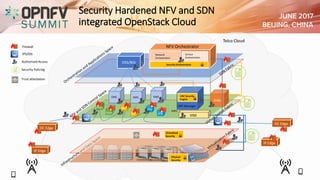
The document addresses security challenges and solutions for NFV (Network Function Virtualization) and SDN (Software-Defined Networking) within integrated OpenStack cloud environments, detailing threat analyses and various vulnerabilities. It outlines the importance of security measures such as architecture approaches, security management frameworks, and compliance initiatives by OPNFV and OpenStack. Additionally, the text emphasizes the need for robust security practices and monitoring across virtualized network infrastructures.