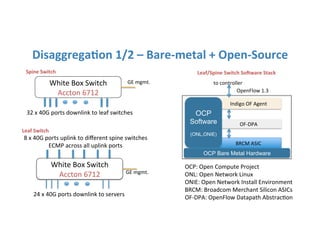
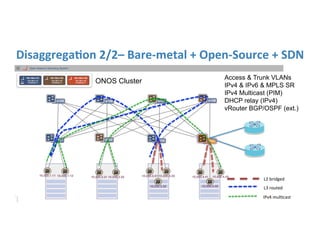
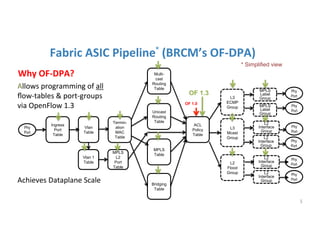
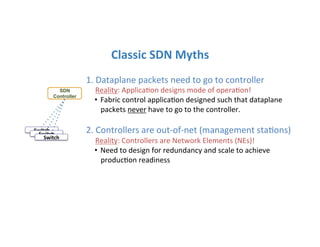
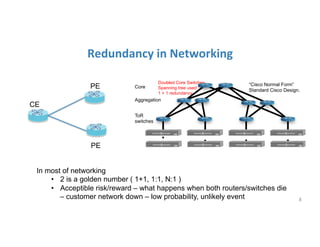
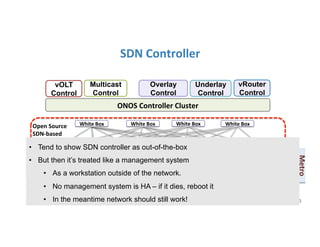
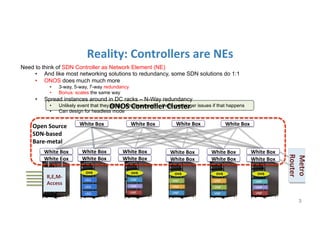
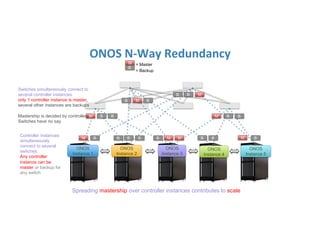
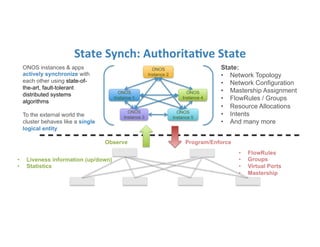
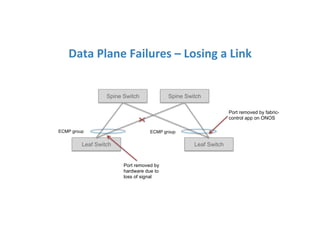
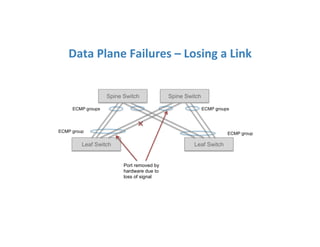
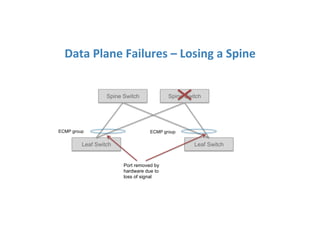
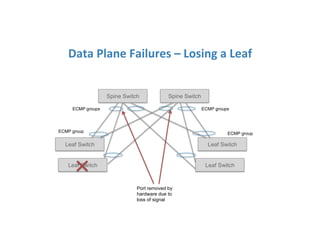
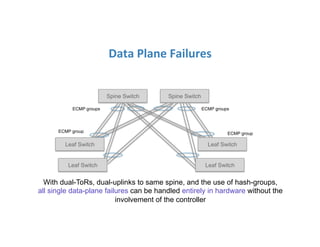
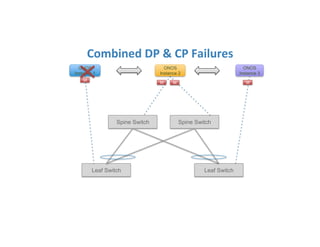
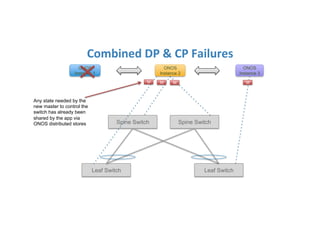
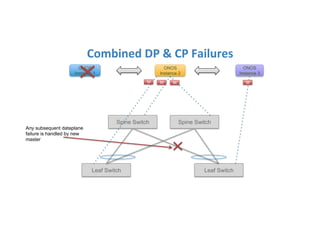
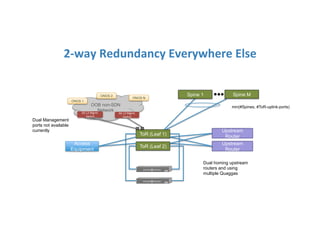
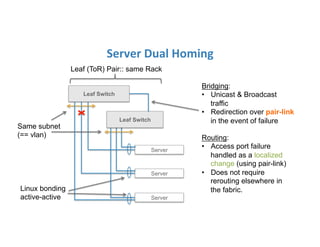
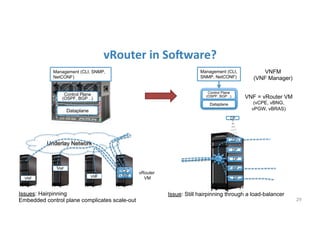
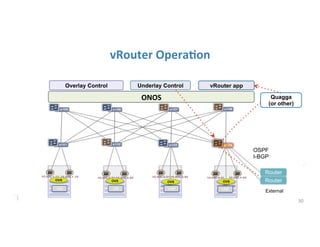
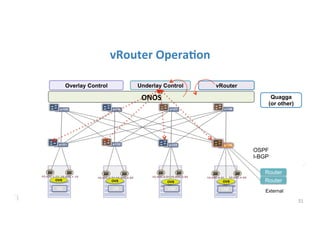
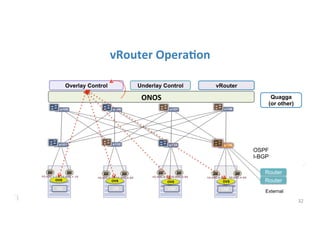
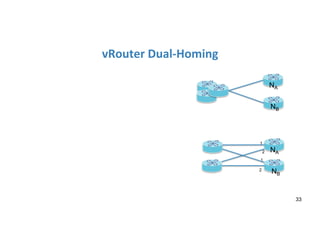
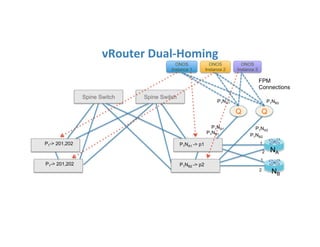
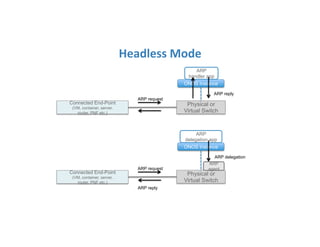
The document discusses high availability in disaggregated networks, particularly within an open-source, SDN-based leaf-spine fabric. It outlines critical concepts such as control and data plane redundancy, combined failure recovery, and the architectural role of the ONOS controller as a network element rather than a management system. Key features include n-way redundancy, state synchronization, and strategies for maintaining network functionality during failures.