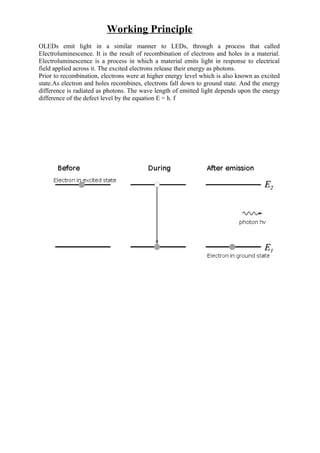
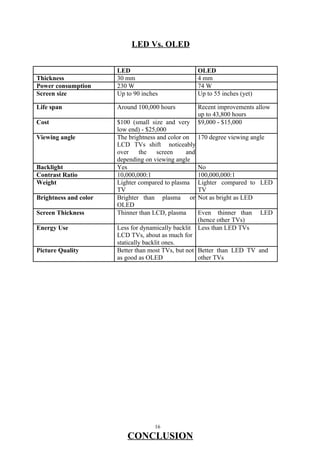
OLED (organic light emitting diode) is a solid-state device that produces light when an electrical current is applied. It consists of a series of thin organic layers placed between an anode and a cathode on a substrate. When voltage is applied, electrons and holes recombine in the organic layers, releasing energy in the form of photons that produce light. OLEDs are thinner, more efficient, and have faster response times than LCDs, but have shorter lifespans than LCDs due to organic material degradation over time. Further research and development aims to improve OLED lifespan and outdoor visibility while reducing costs.