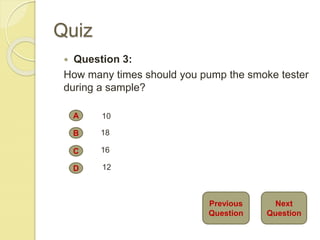
This document provides information on combustion efficiency testing for oil burners. It discusses measuring draft, smoke, CO2 levels, stack and net temperatures, and using these measurements to calculate efficiency. Safety precautions are highlighted for each test. The purpose of combustion testing is to evaluate how well the unit is using fuel and should be done annually with routine service. Key steps include measuring draft, using a smoke tester to check for smoke, measuring CO2 levels with a shaker bottle, and calculating net temperature and efficiency.