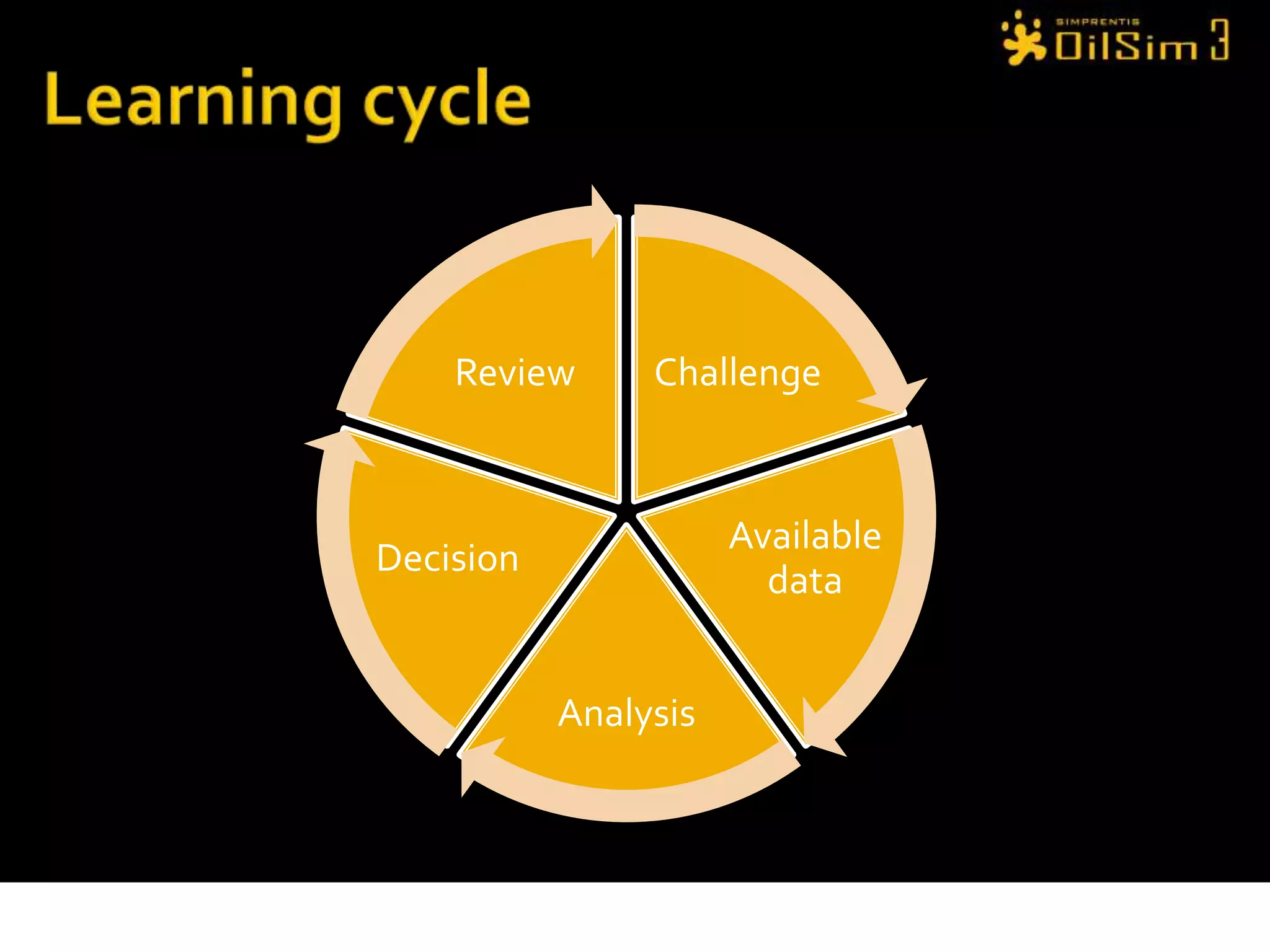
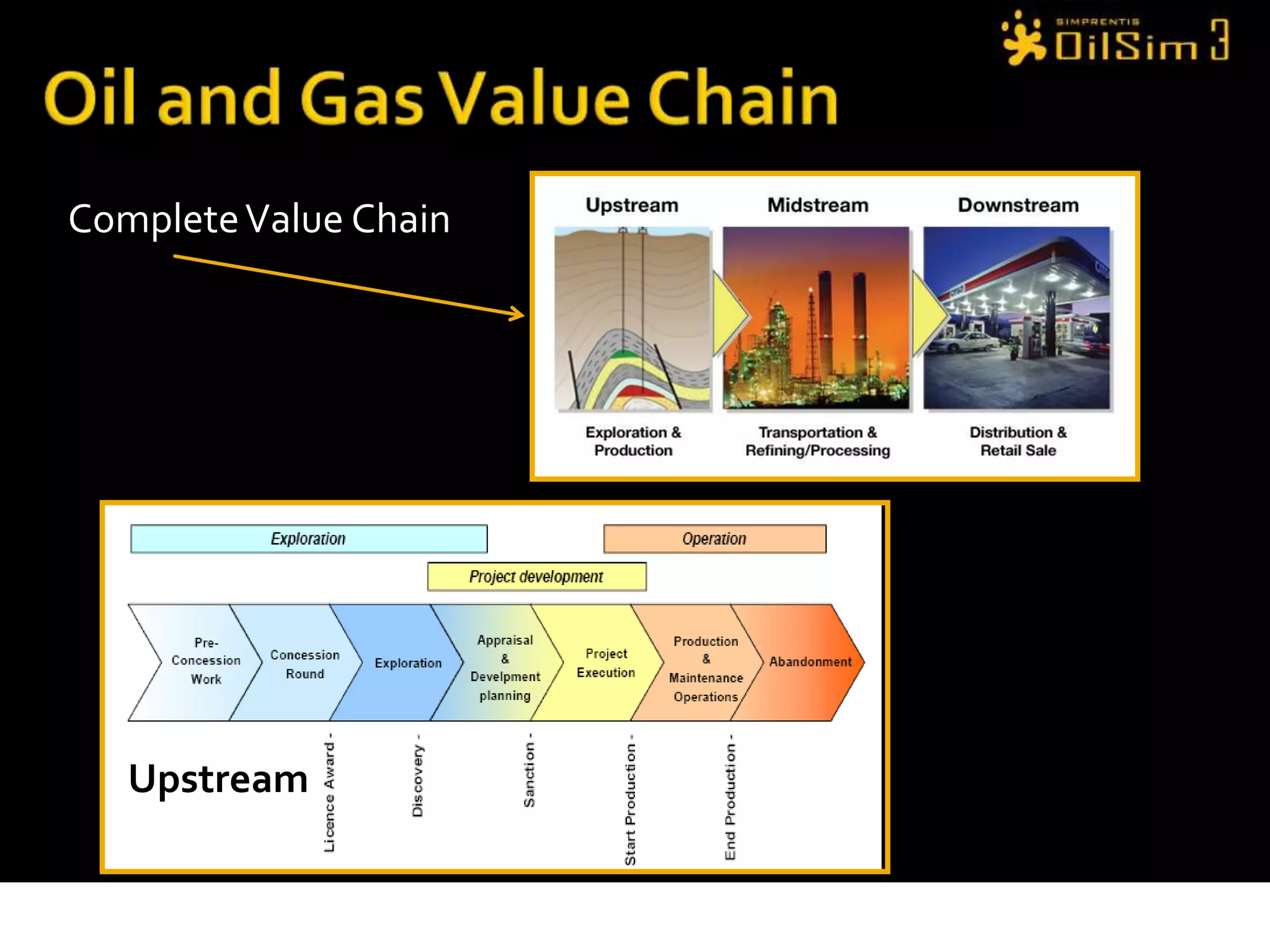
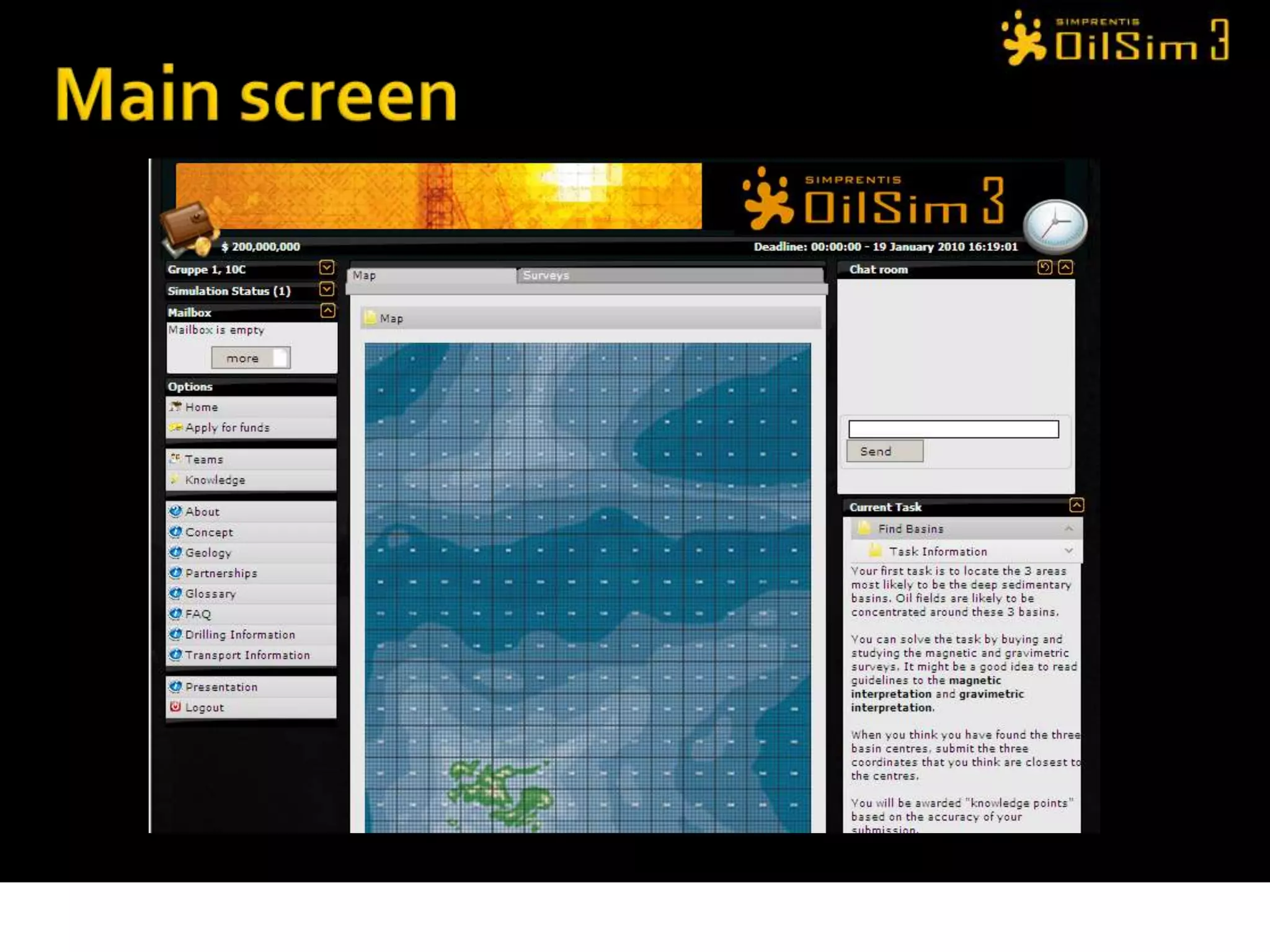
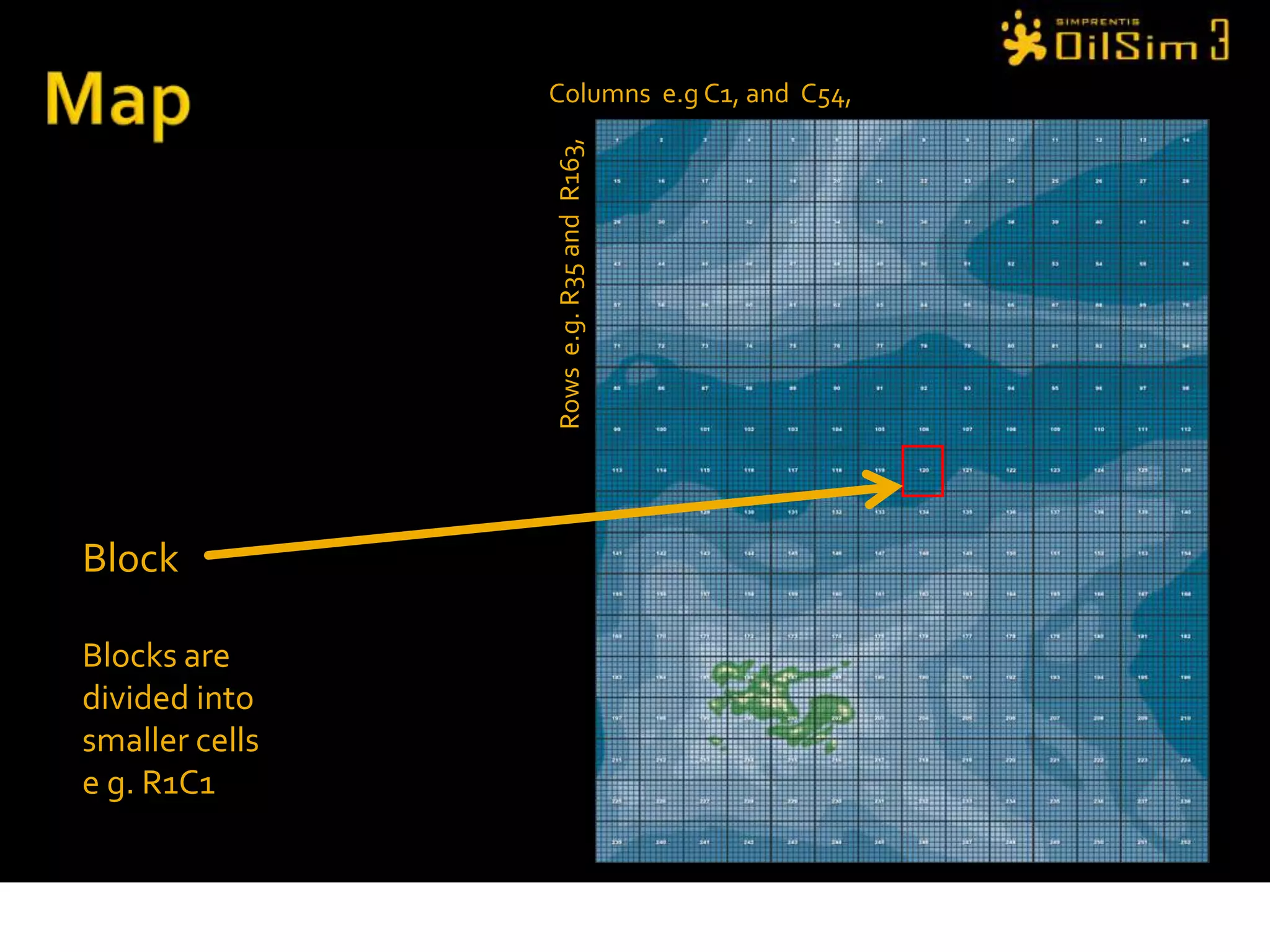
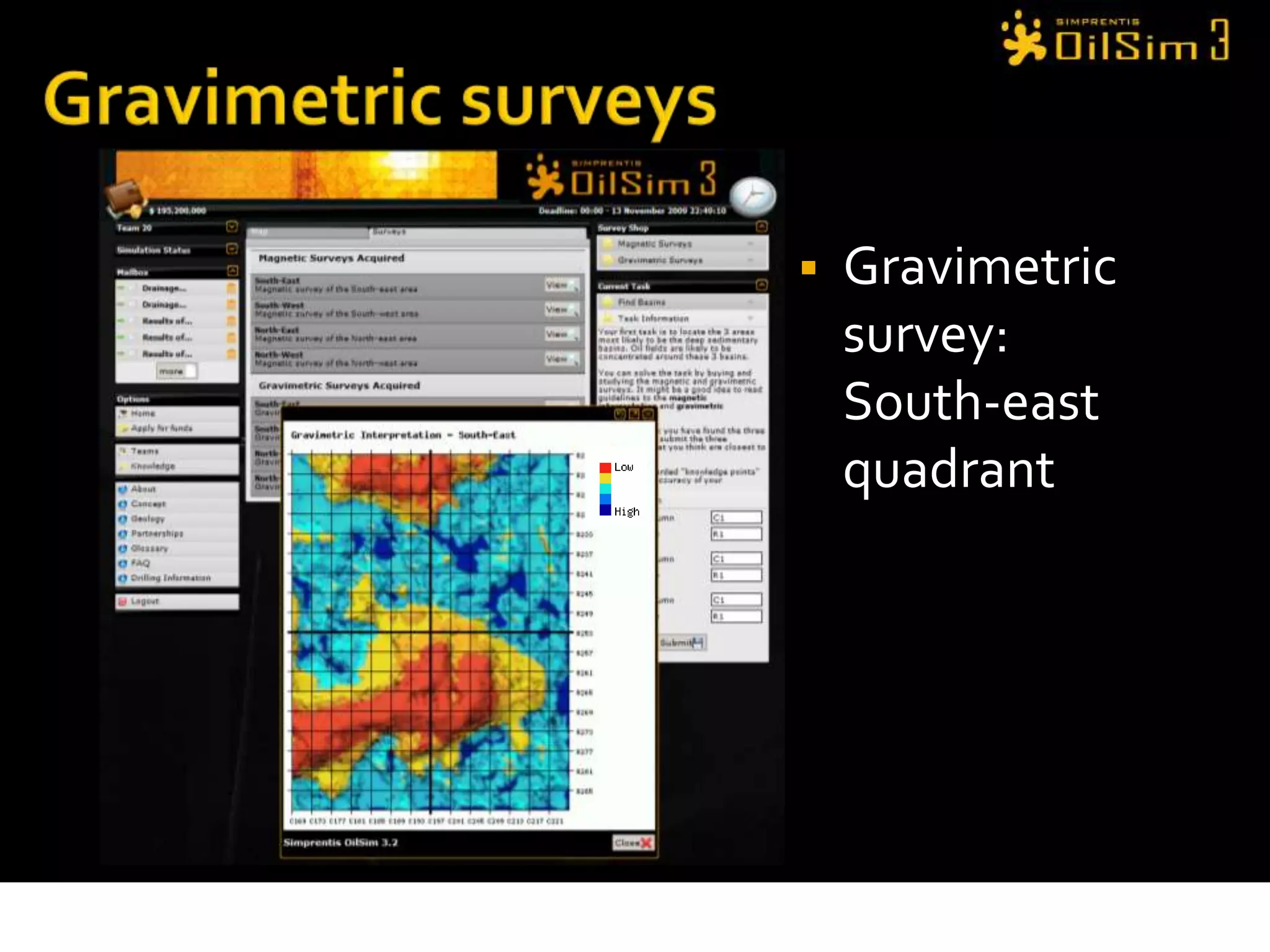
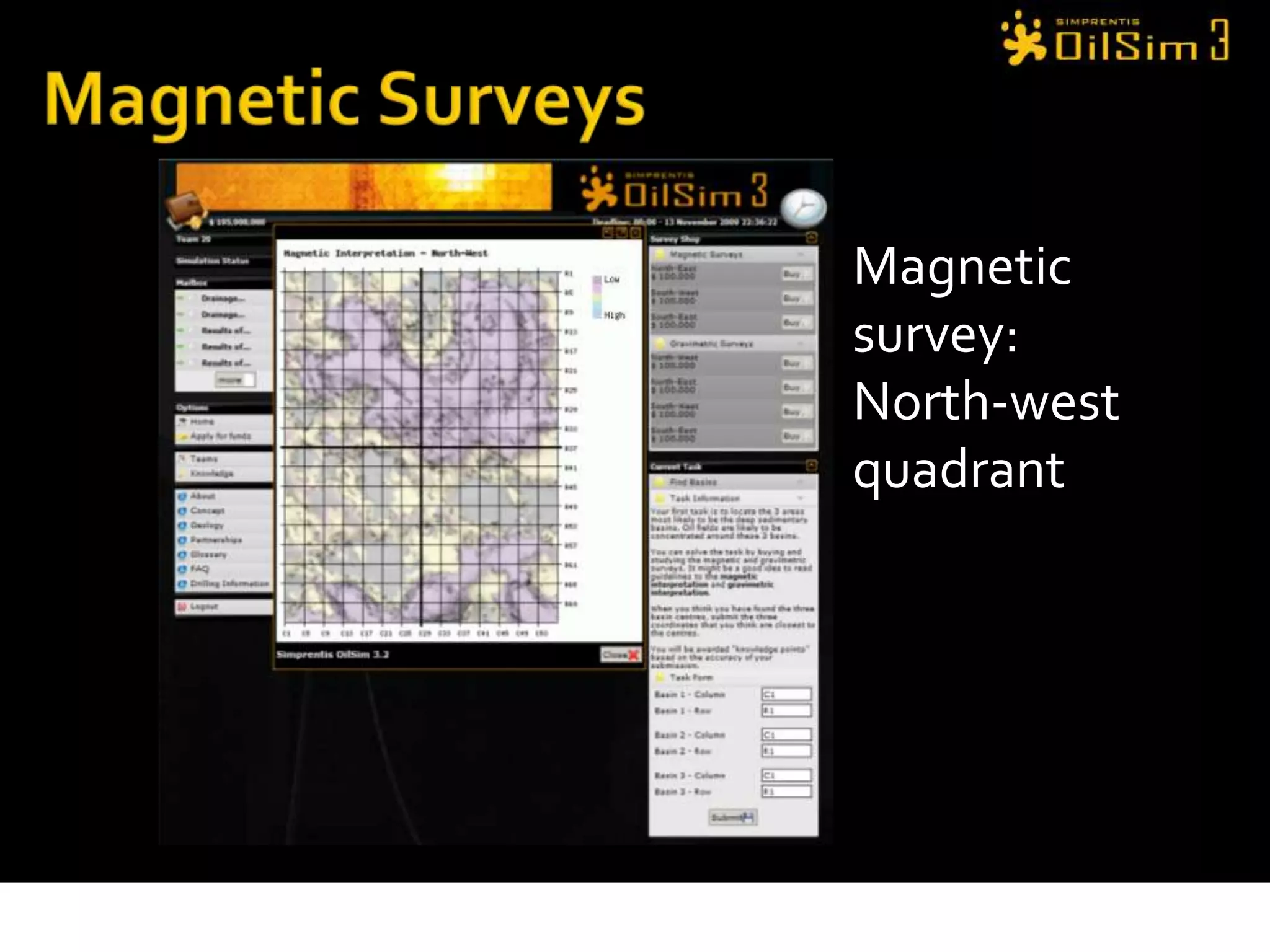
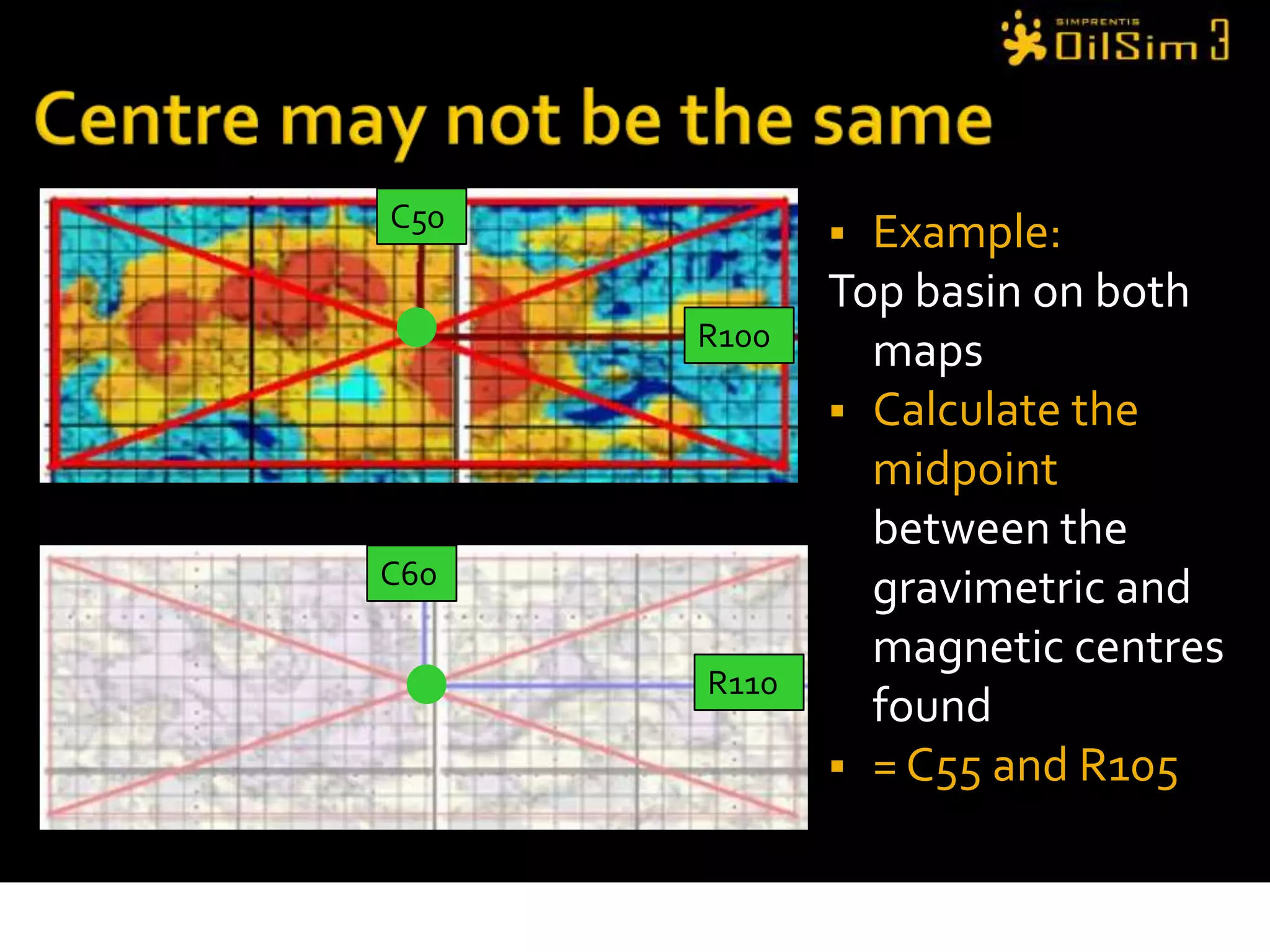
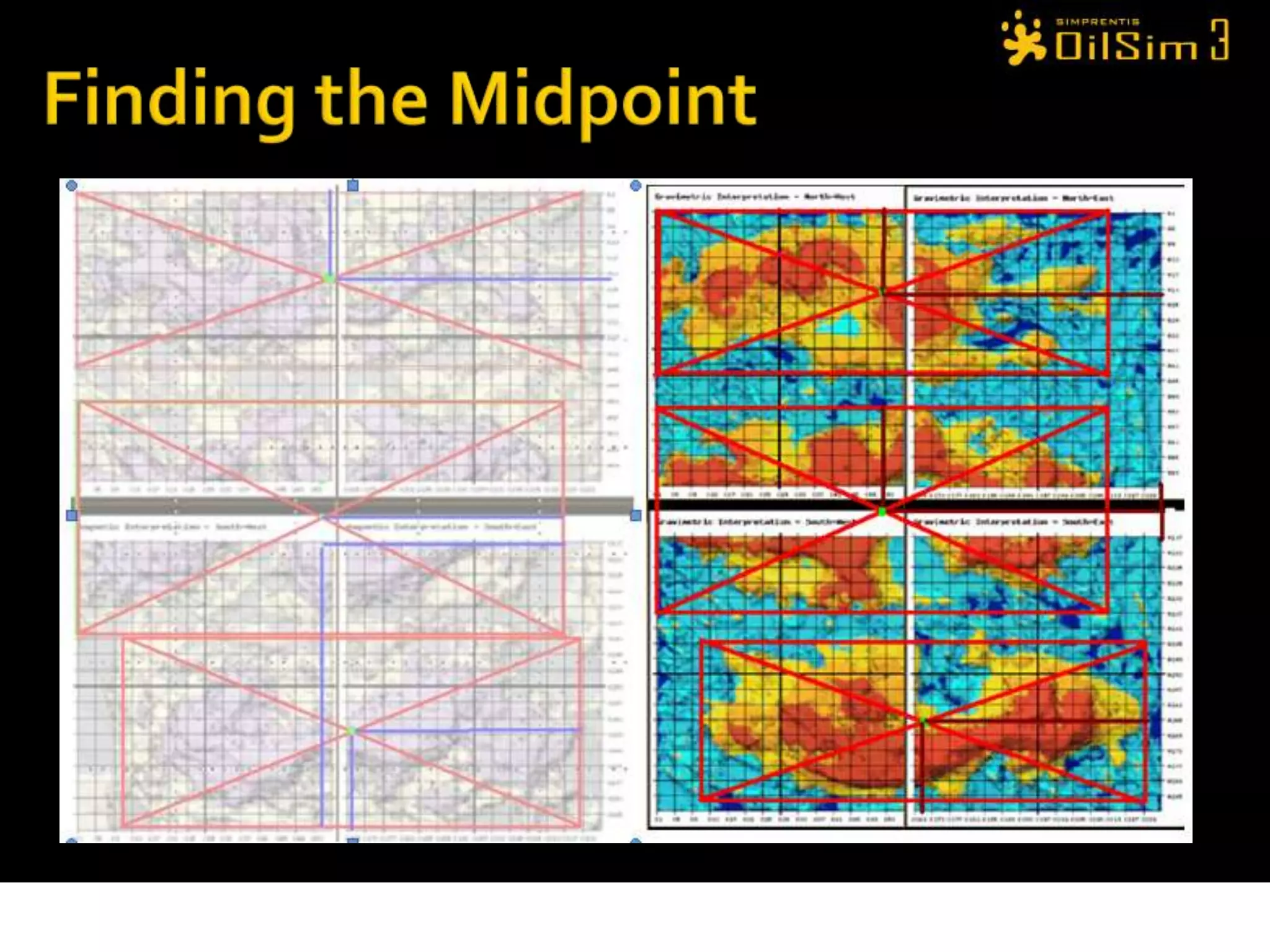
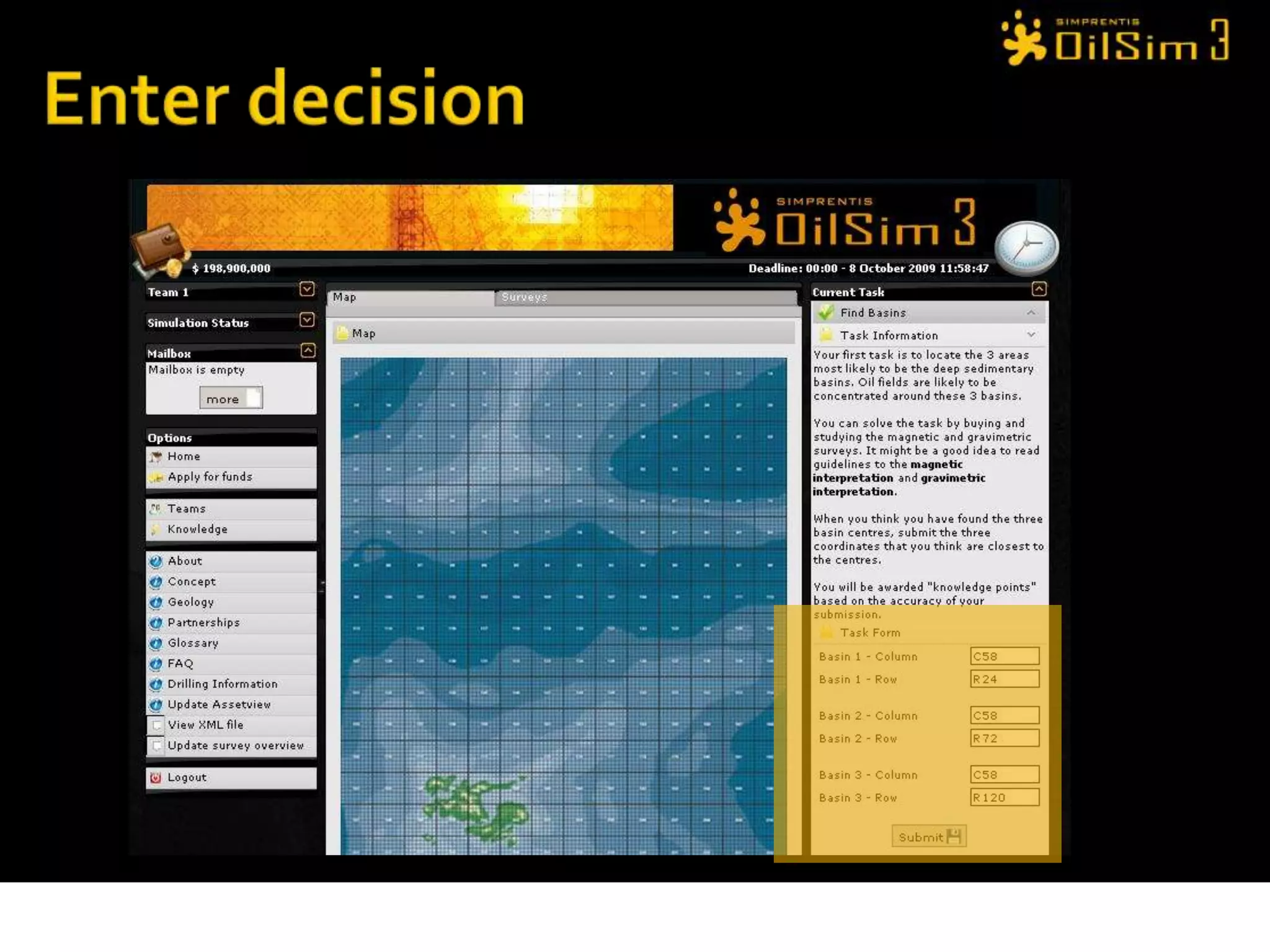
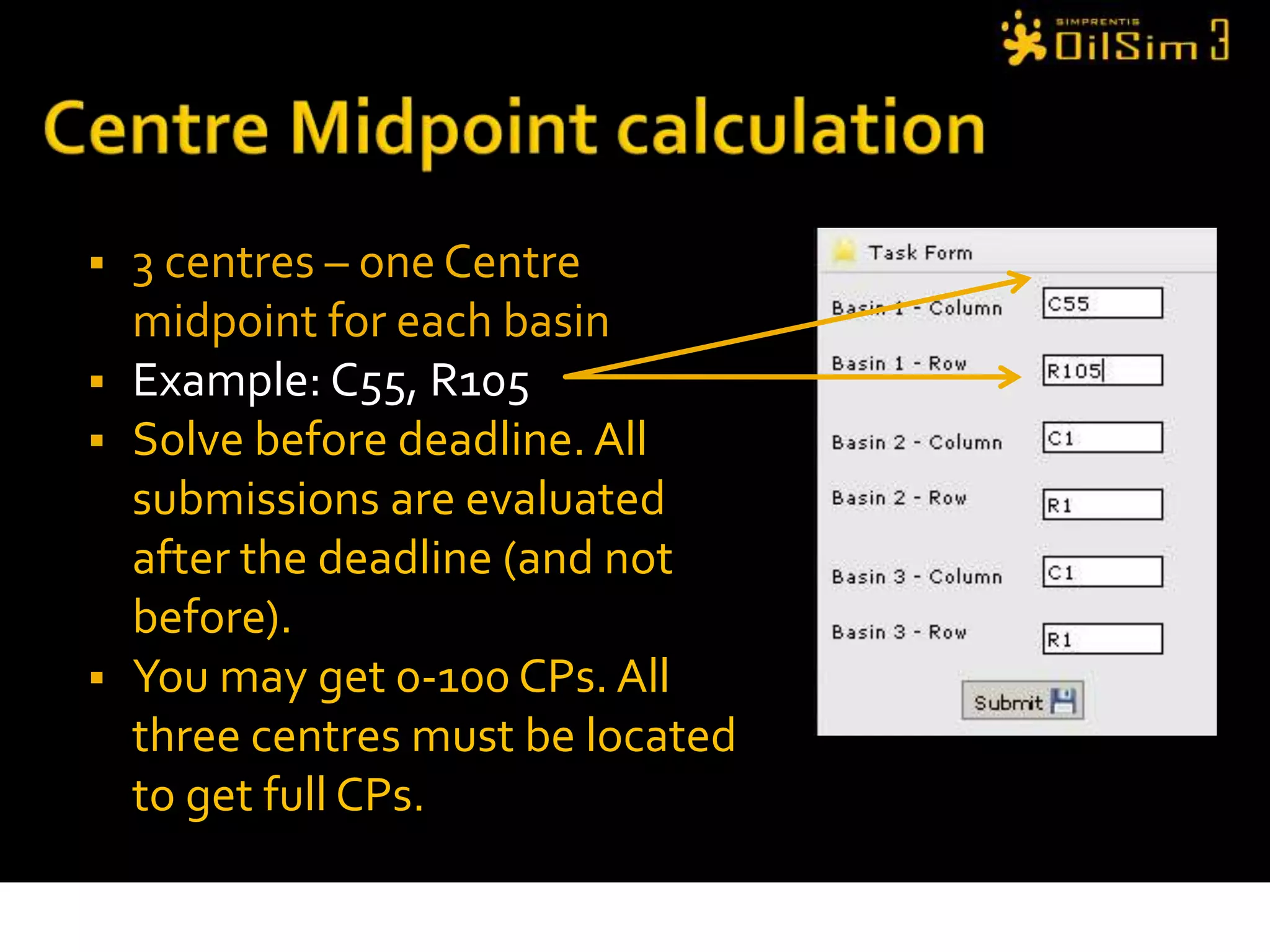
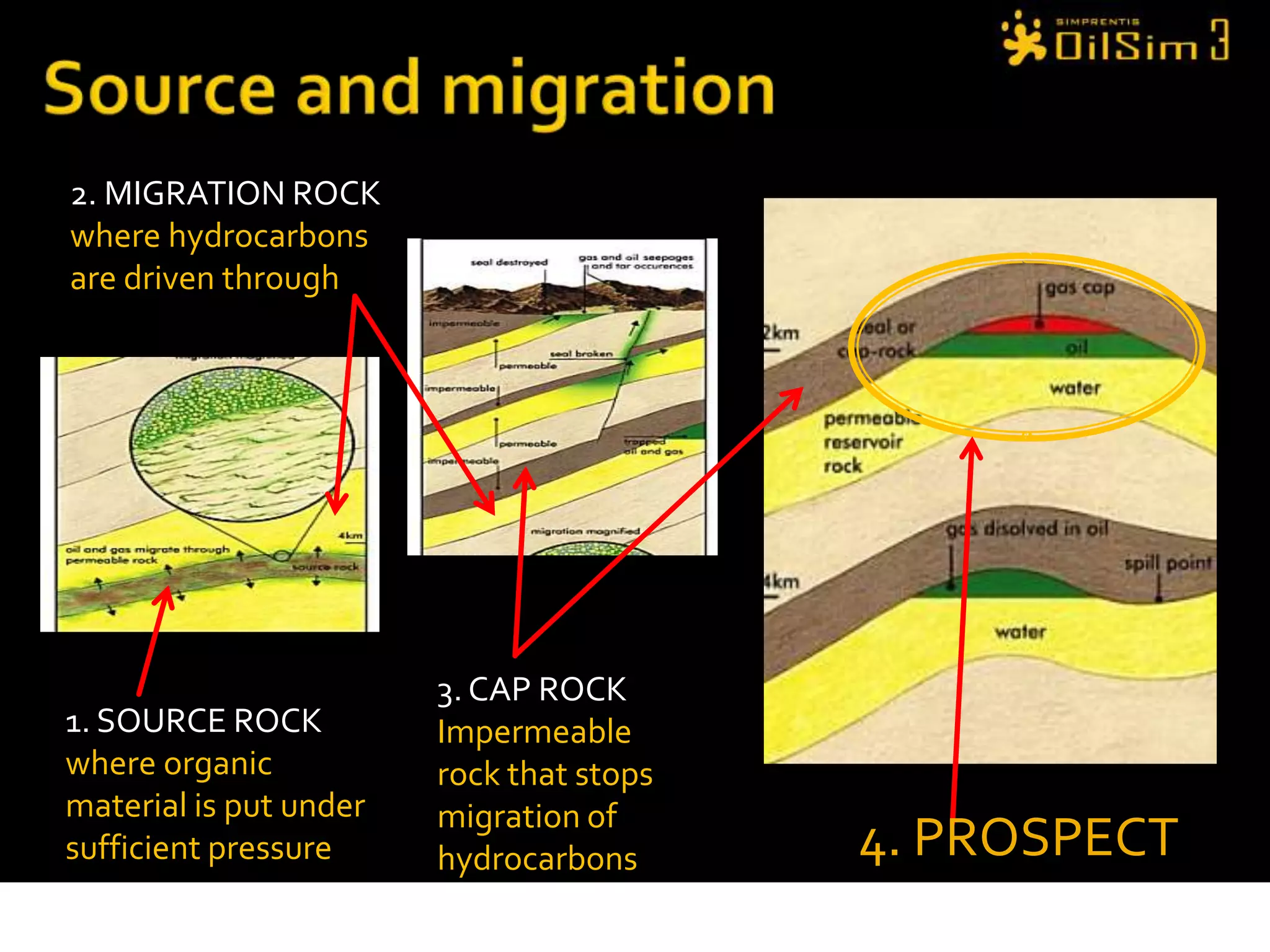
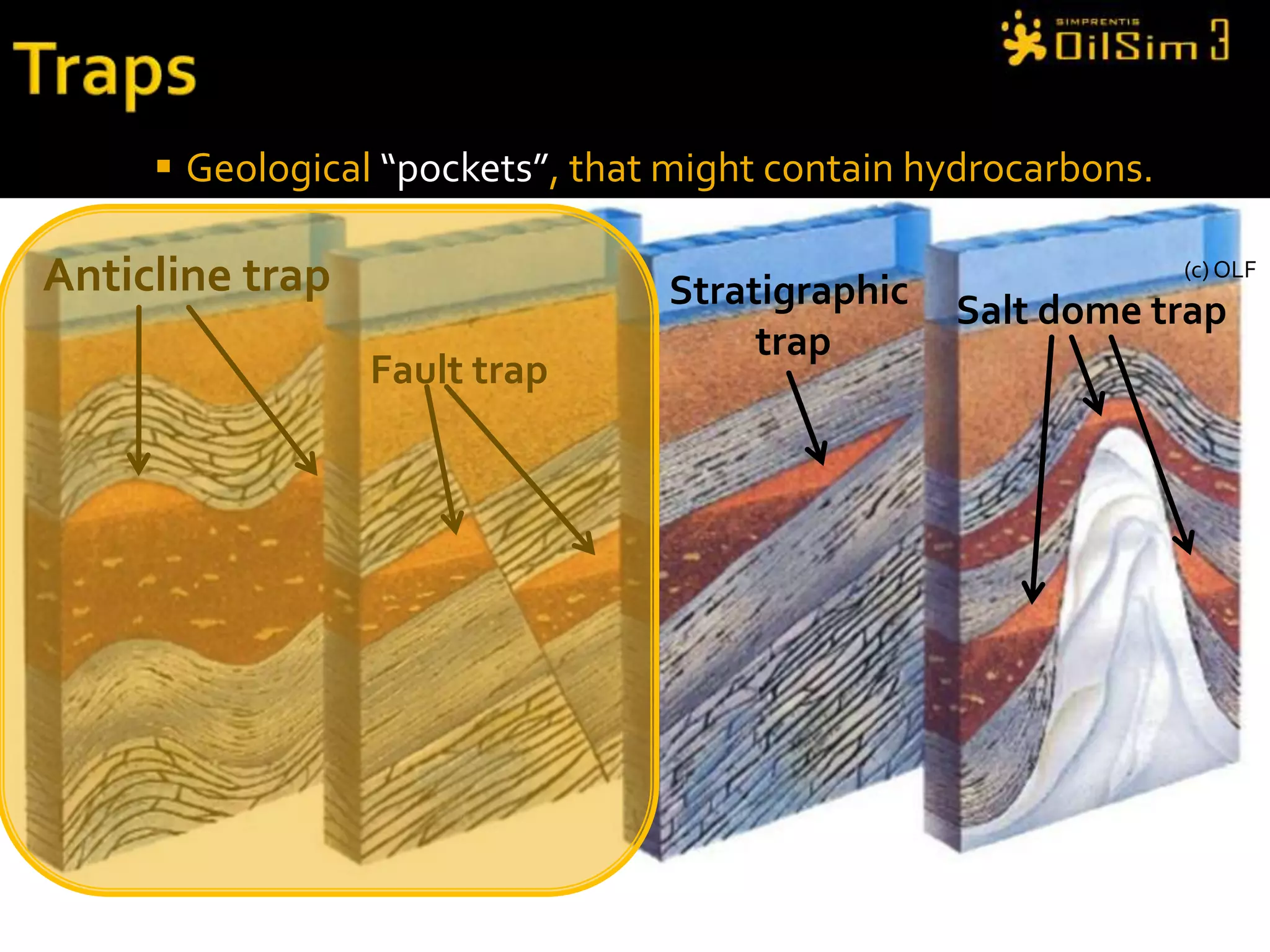
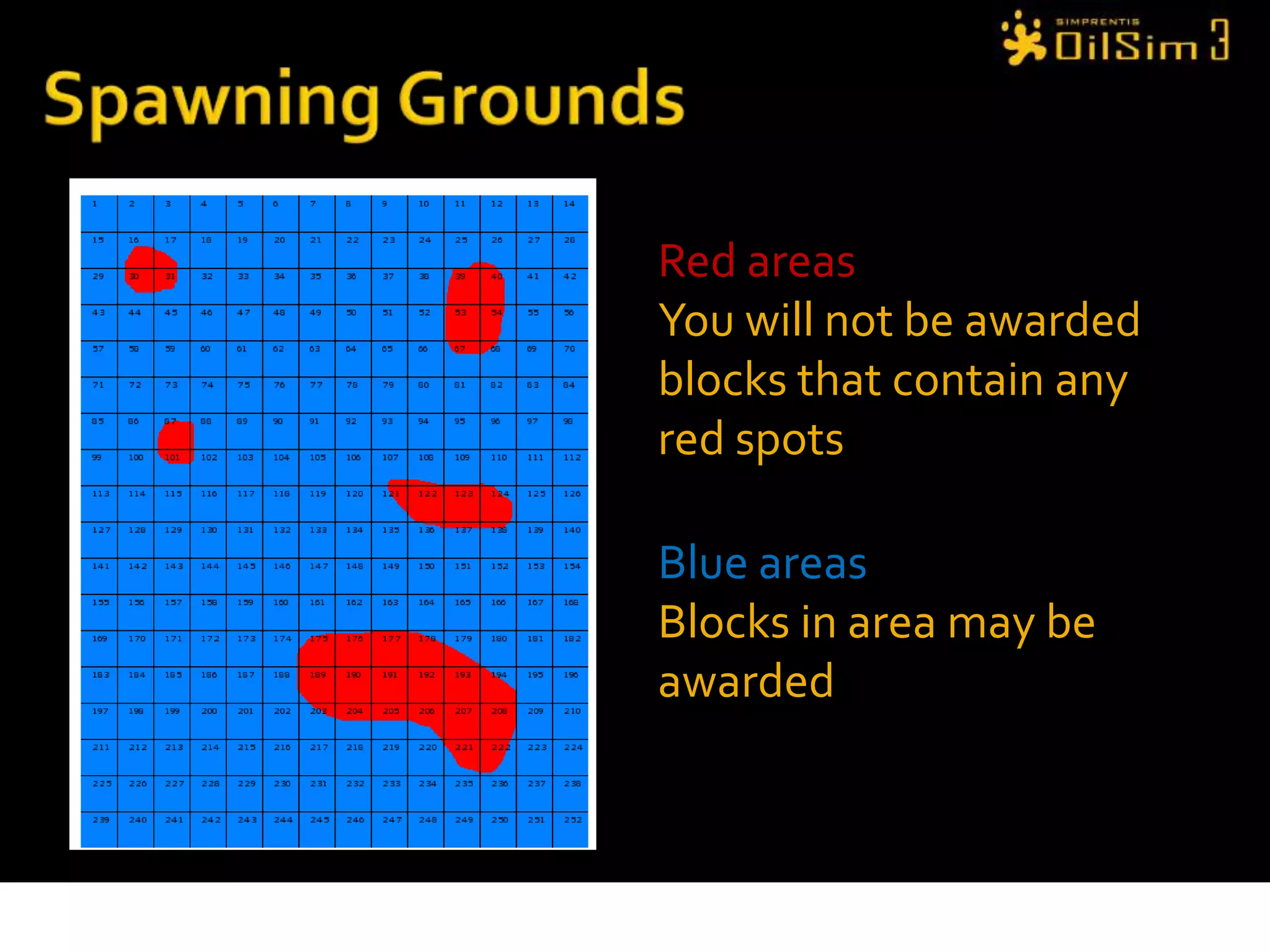
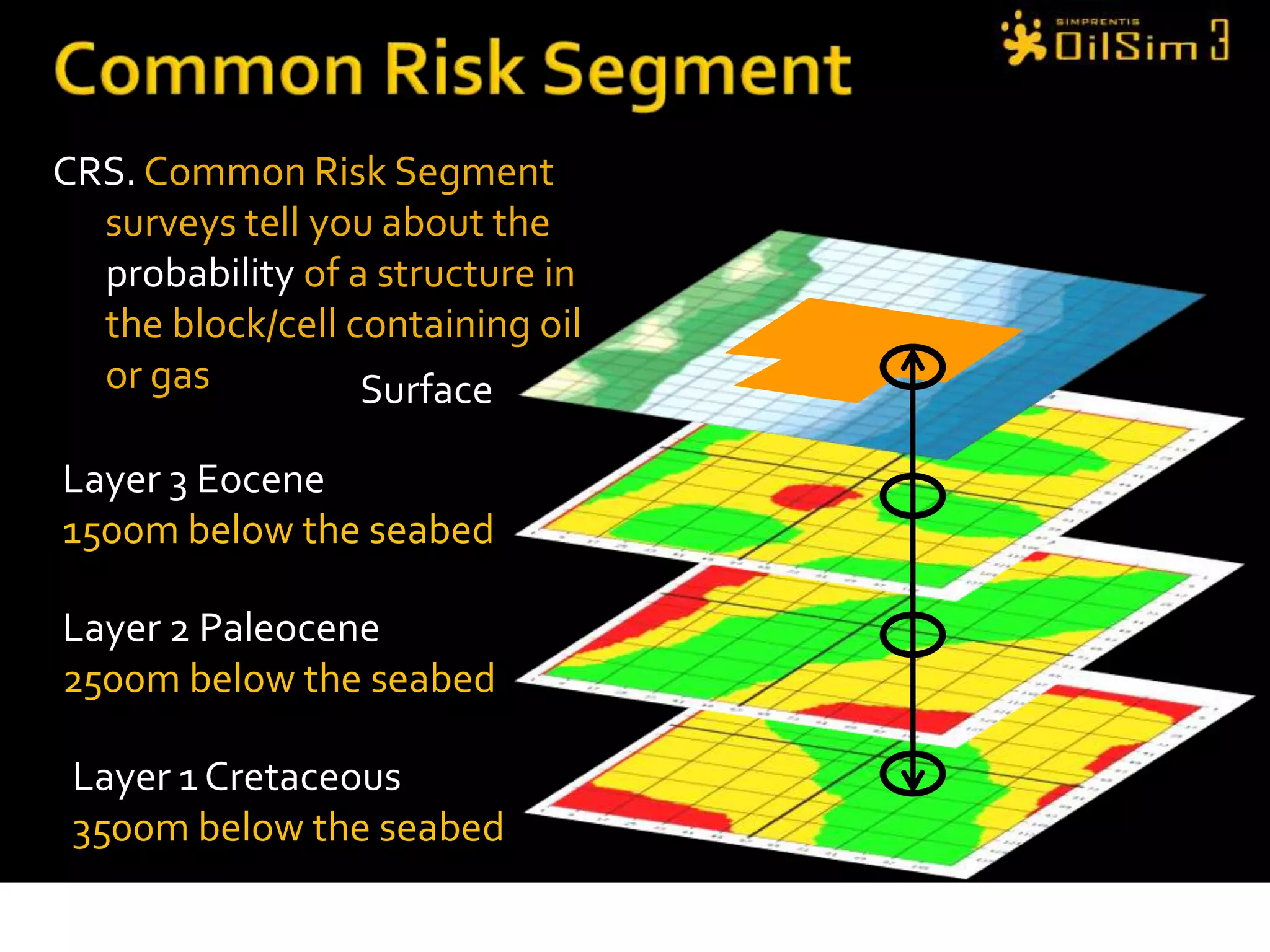
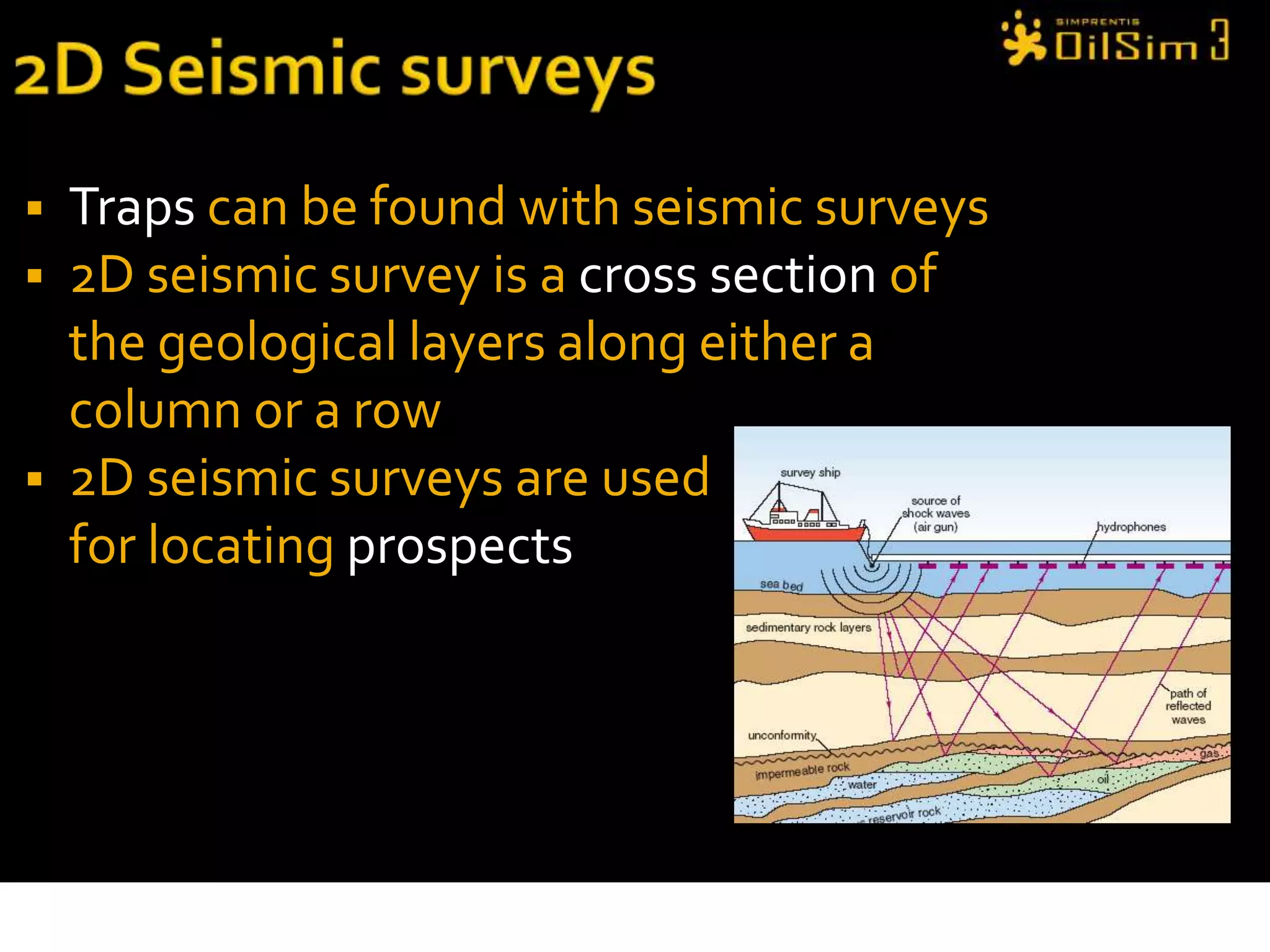
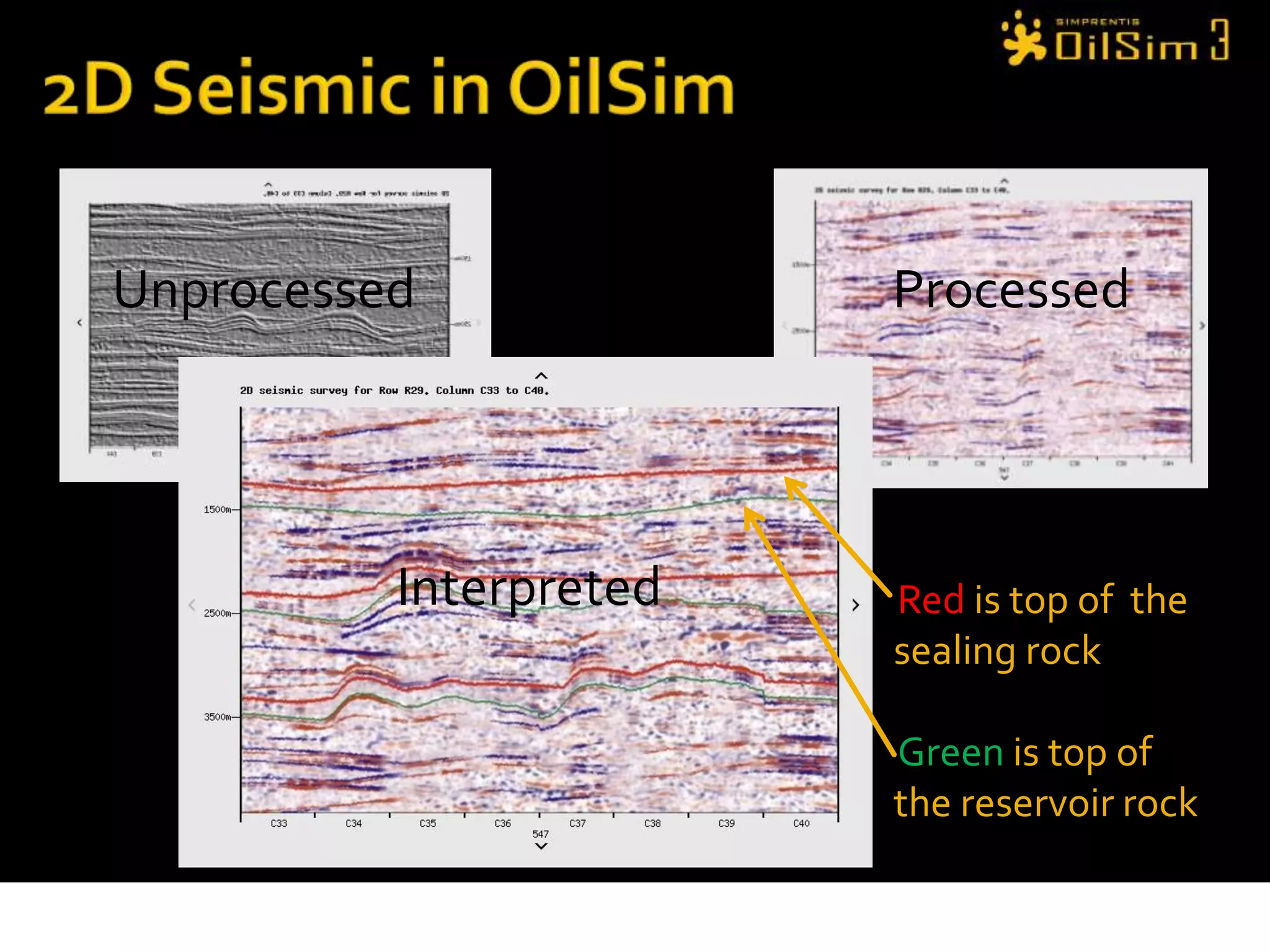
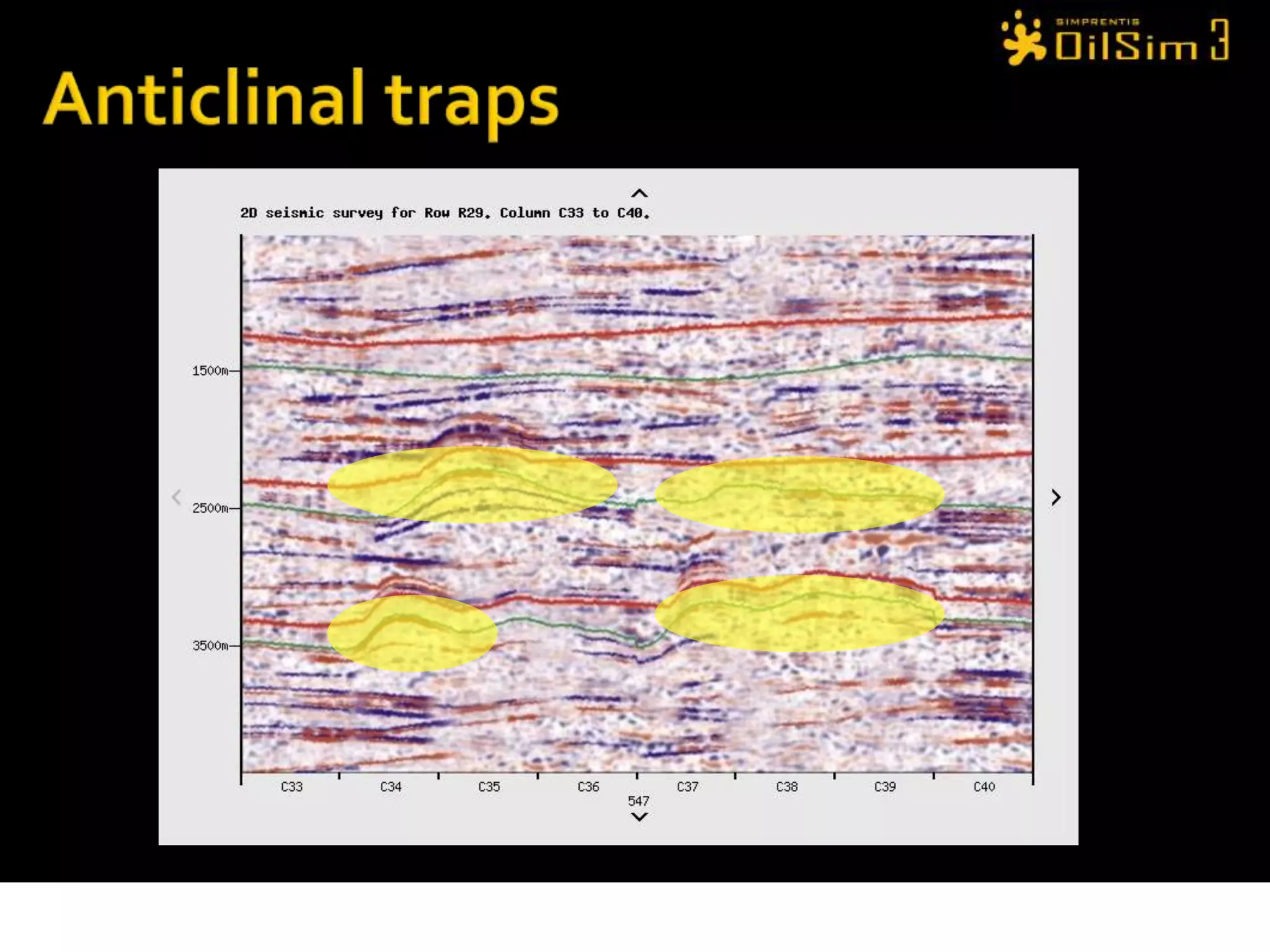
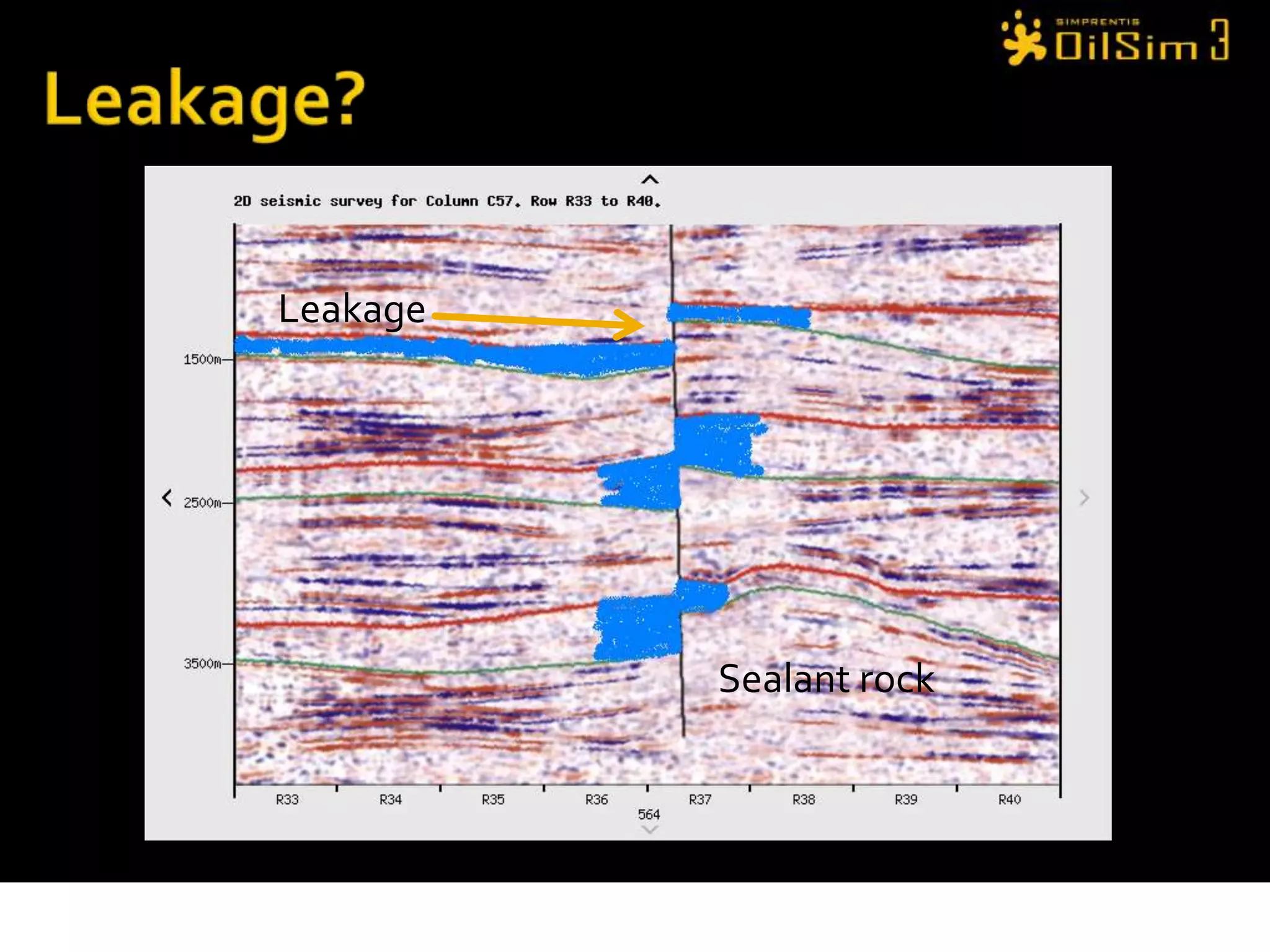
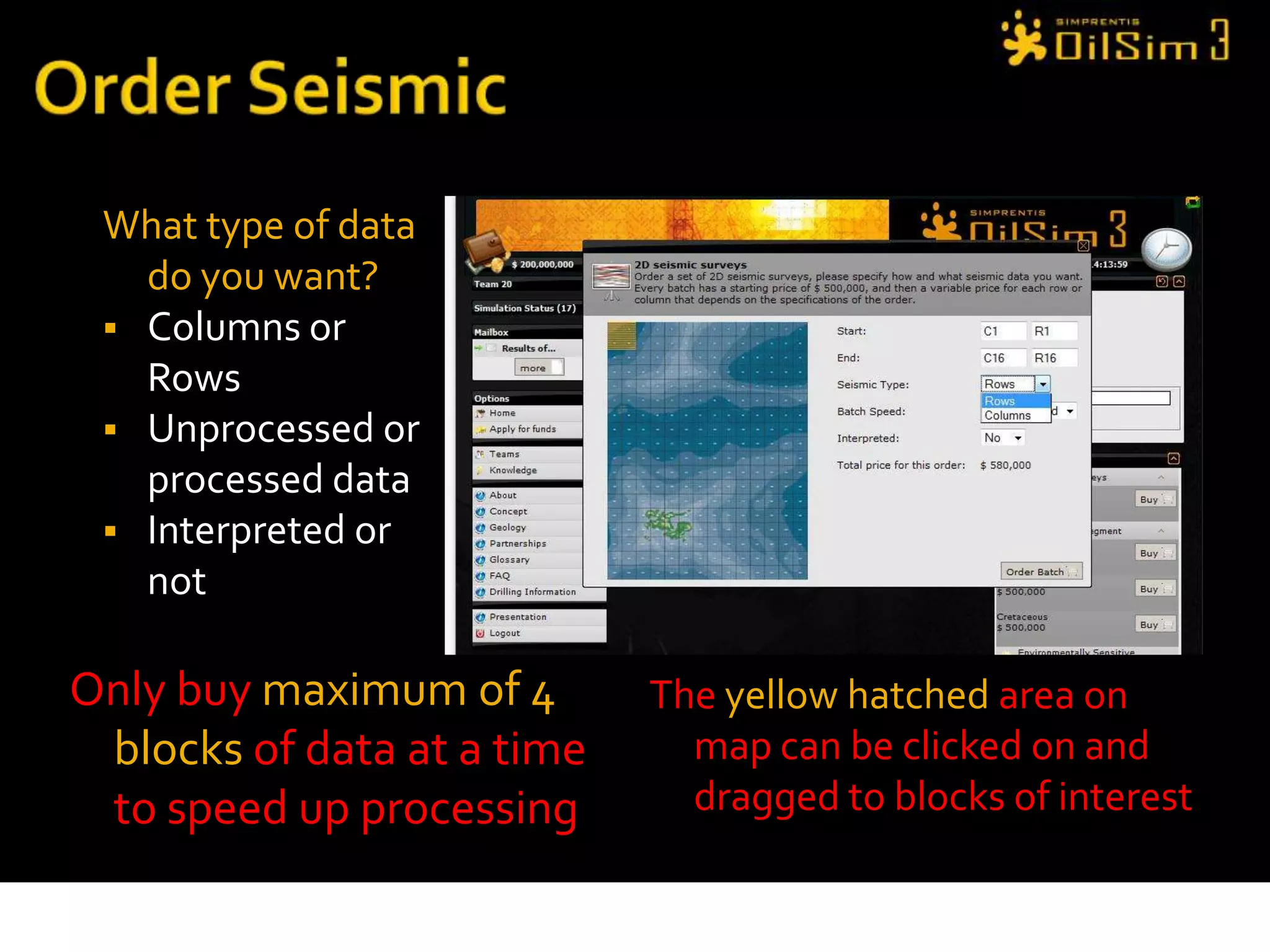
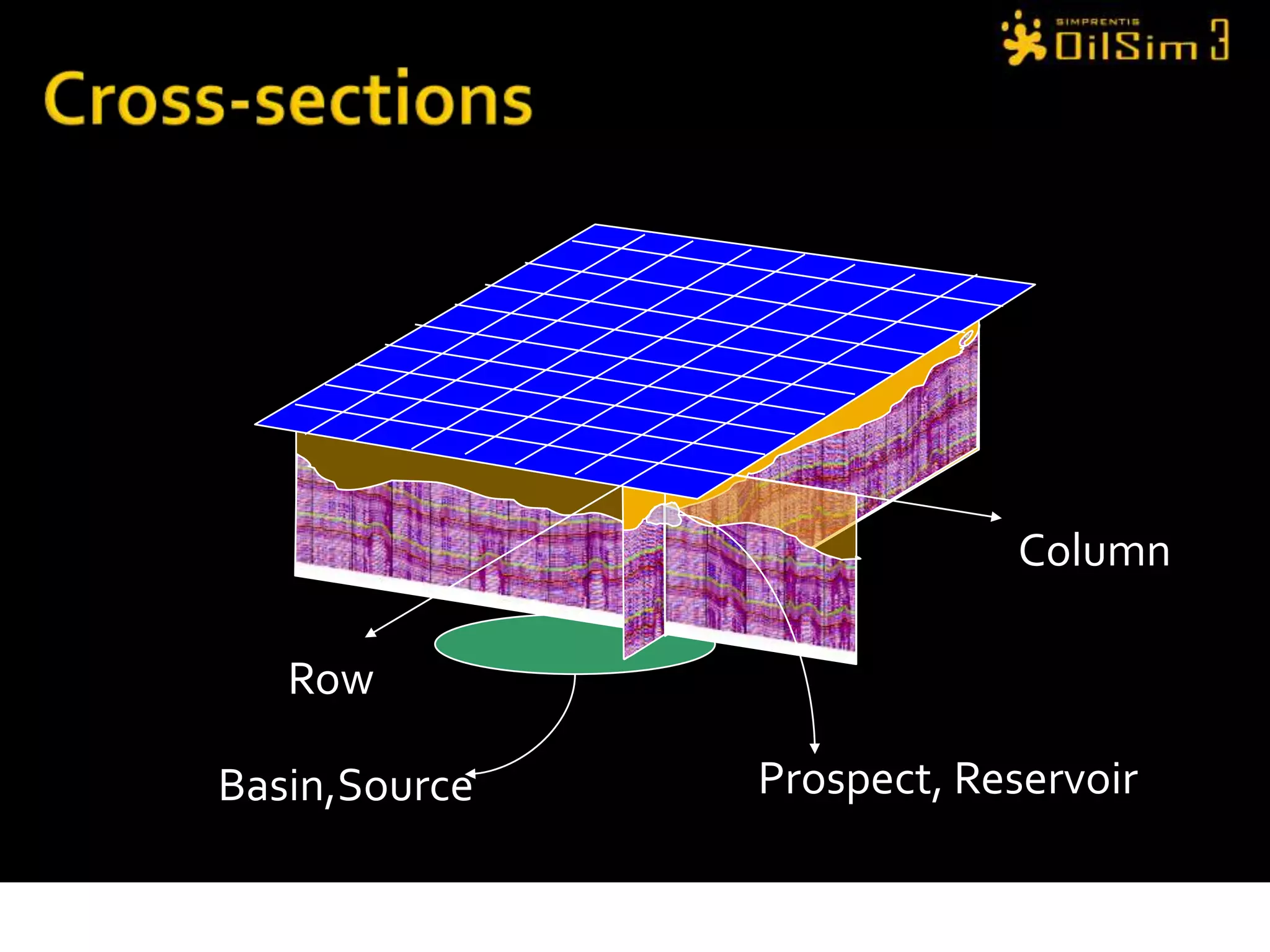
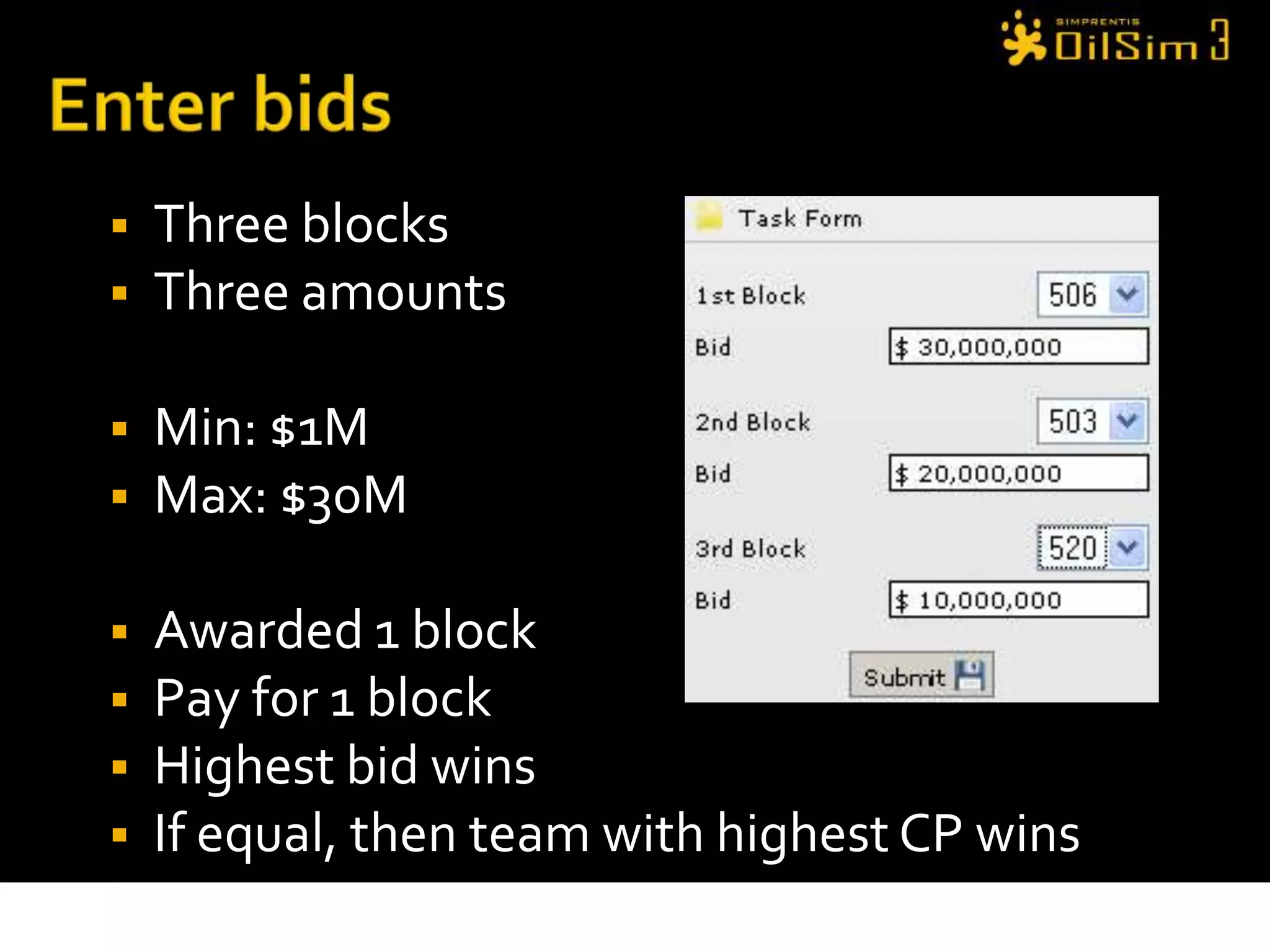
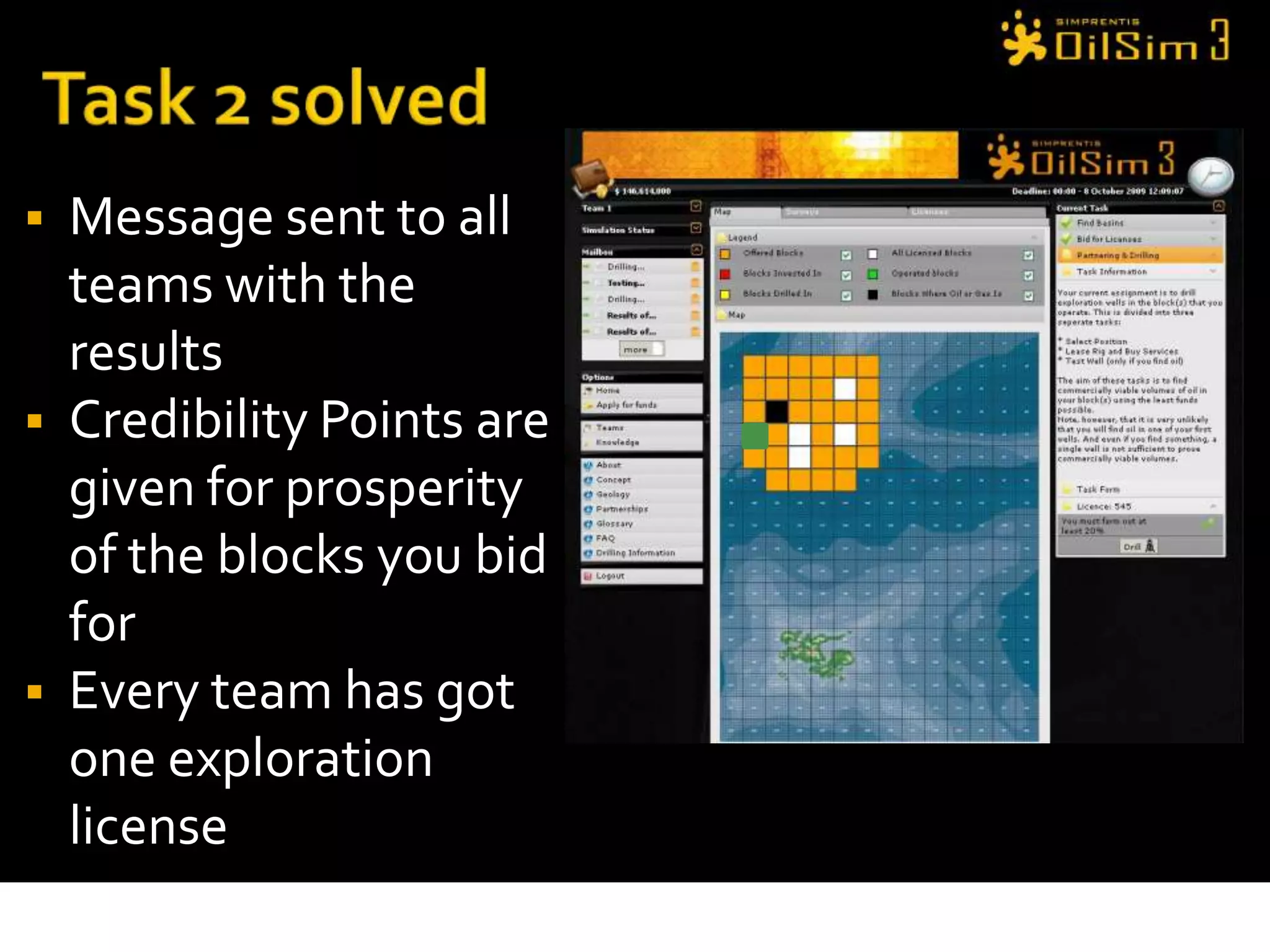
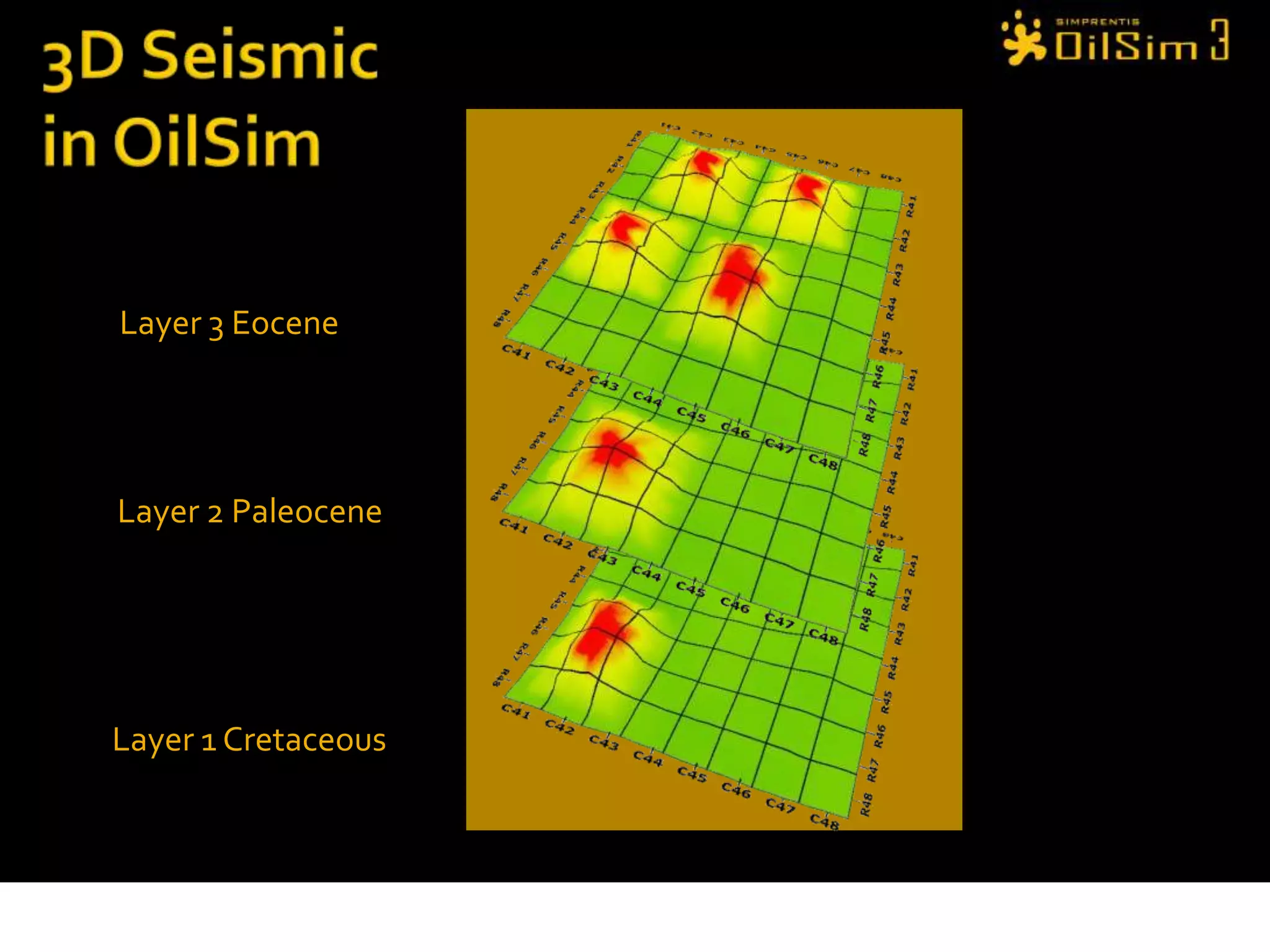
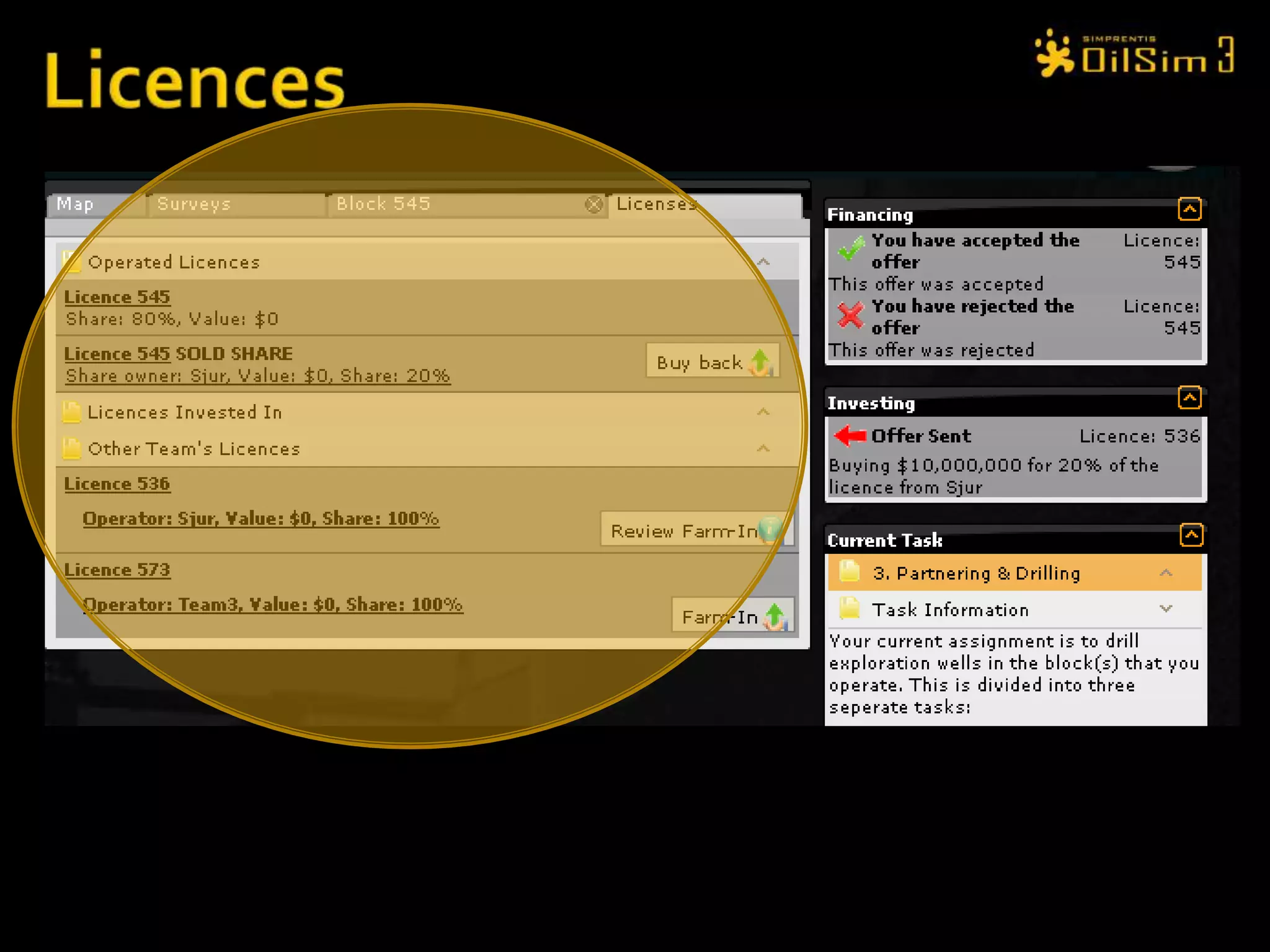
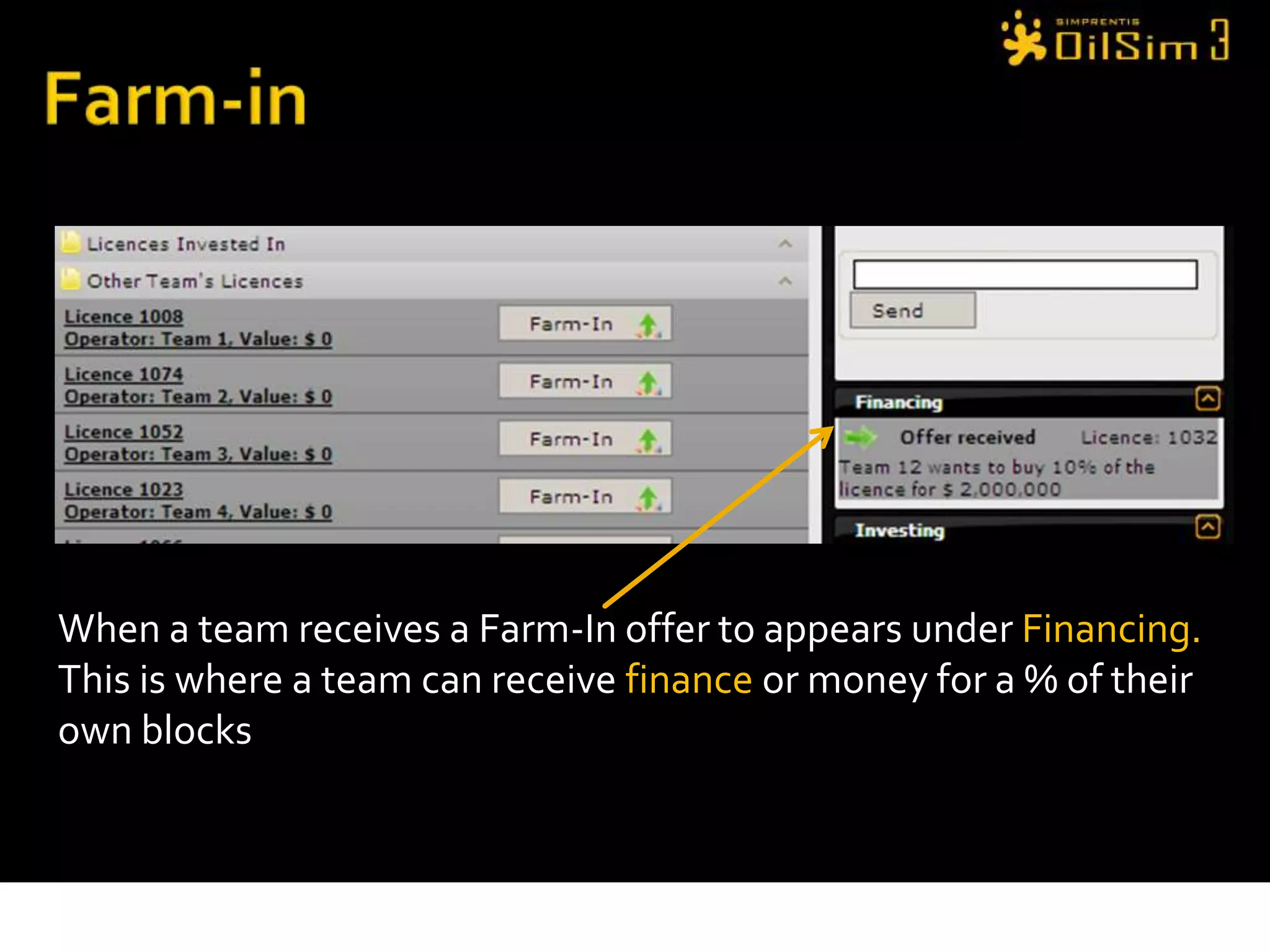
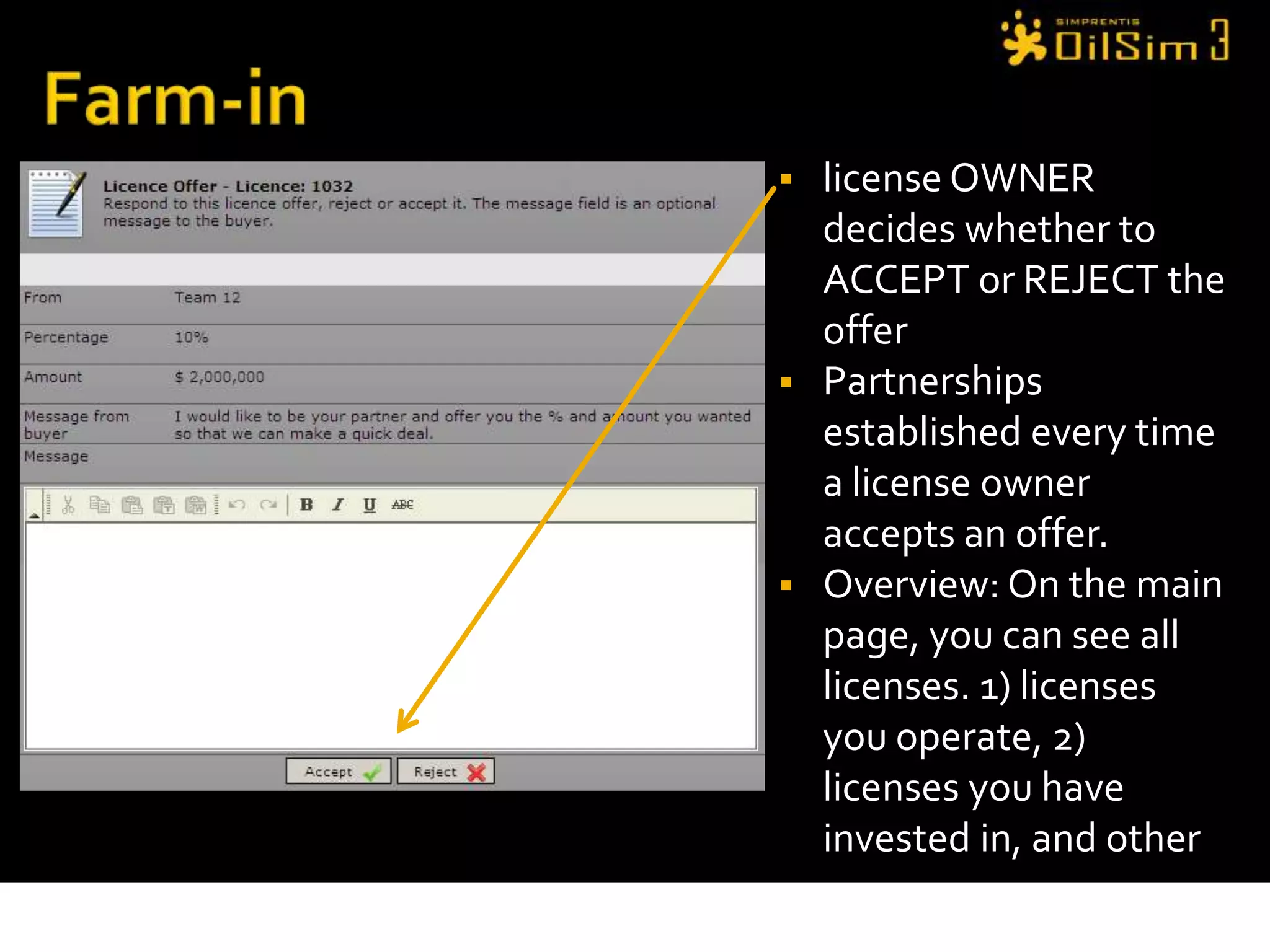
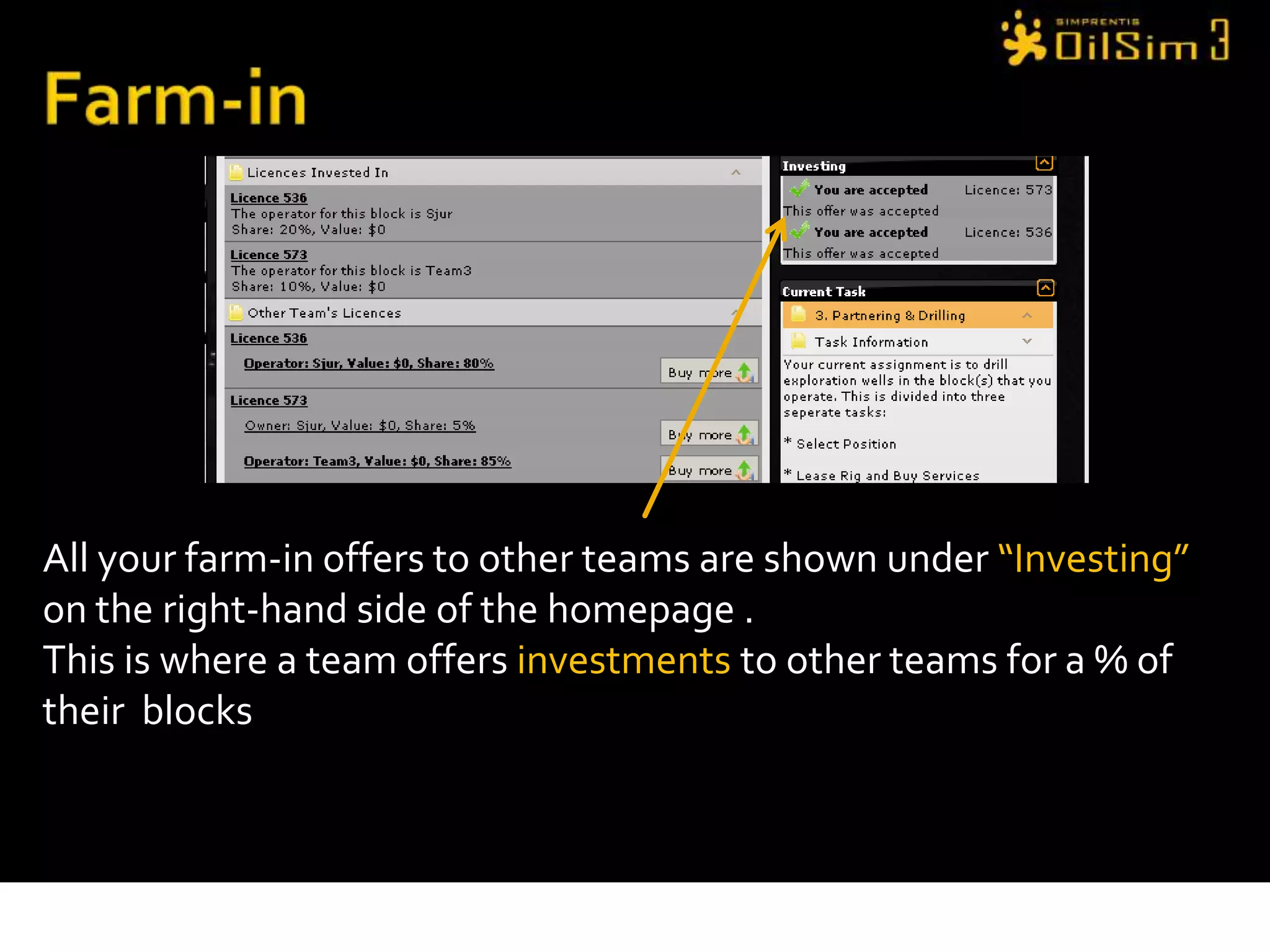
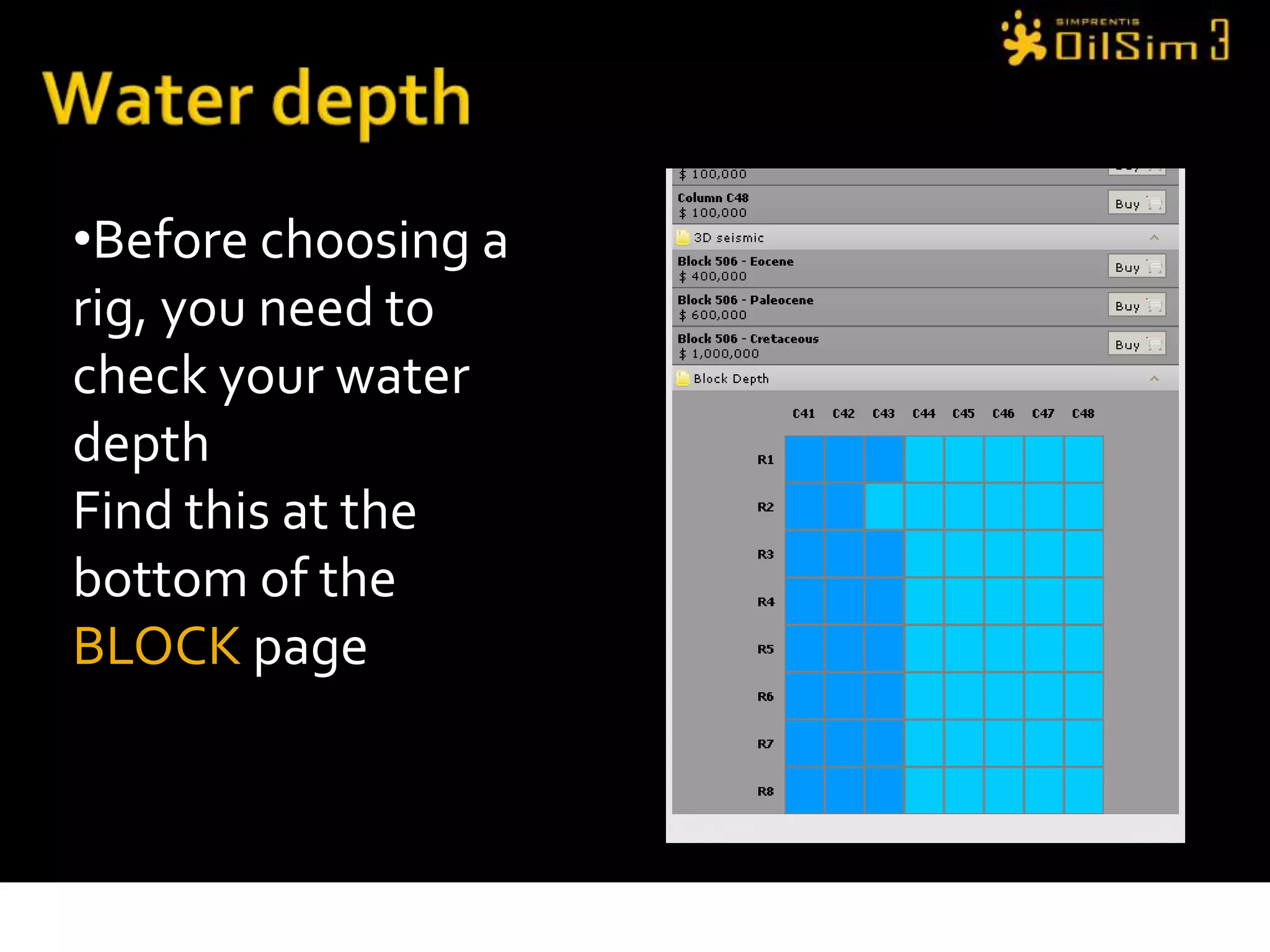
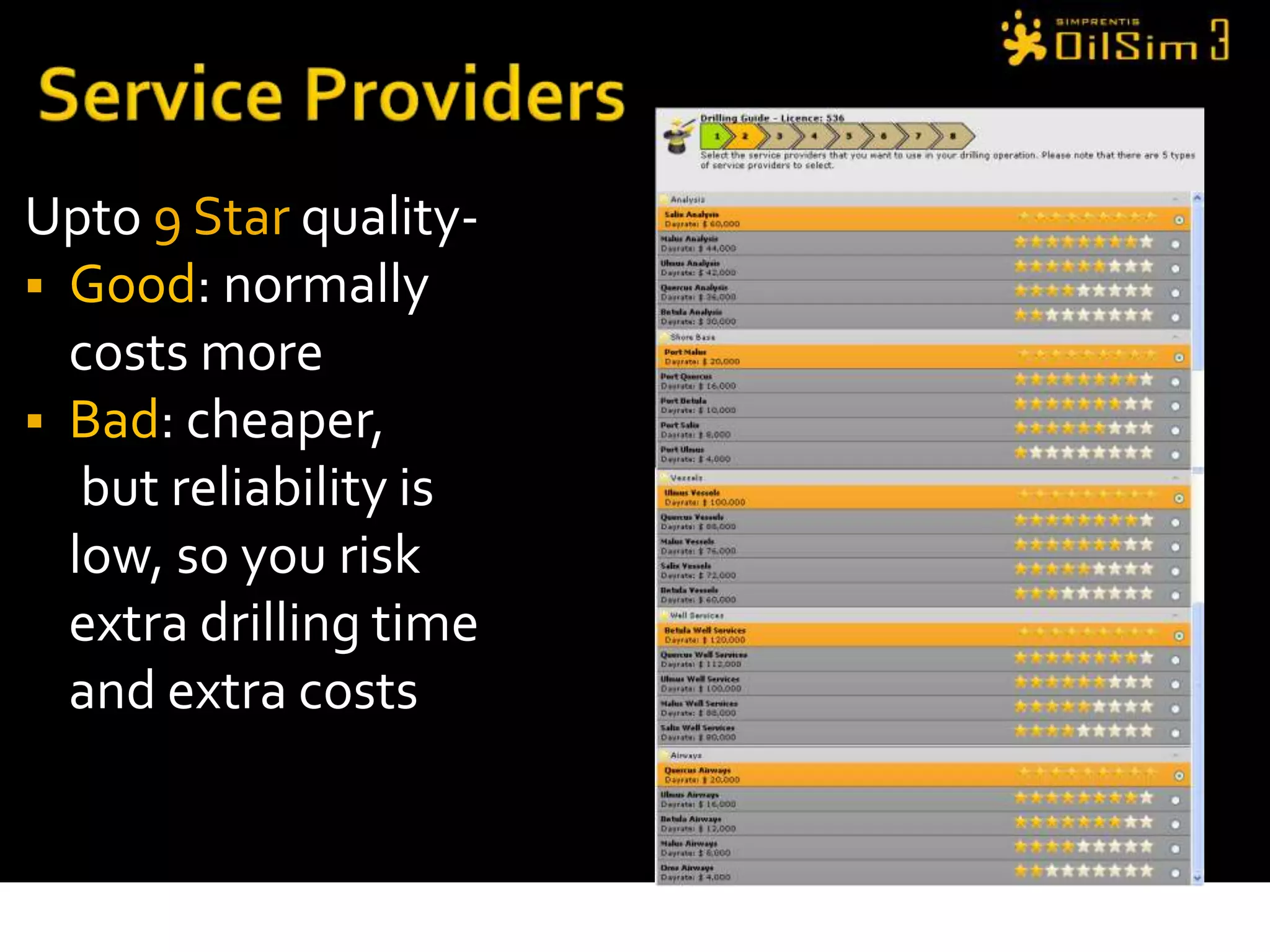
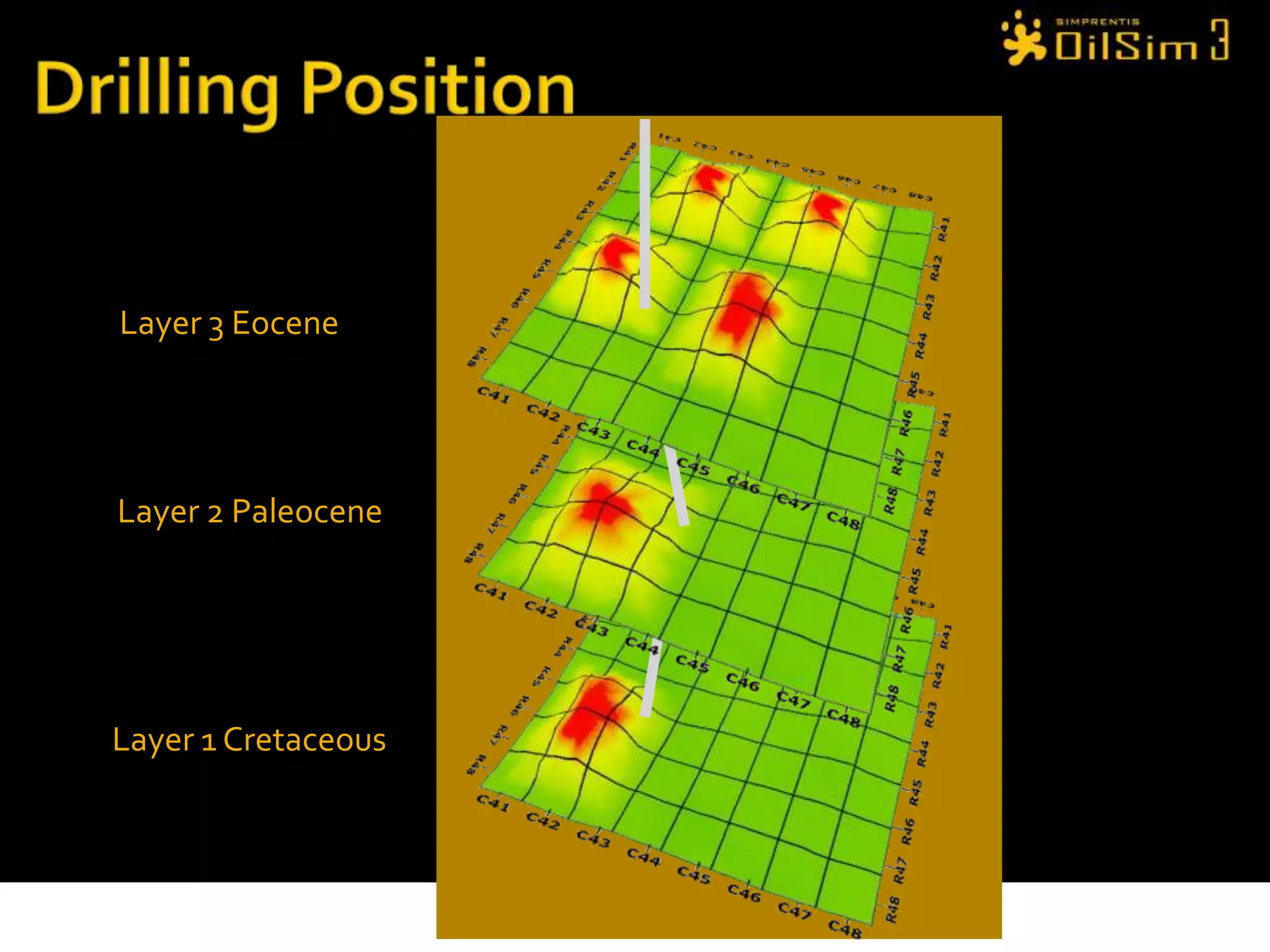
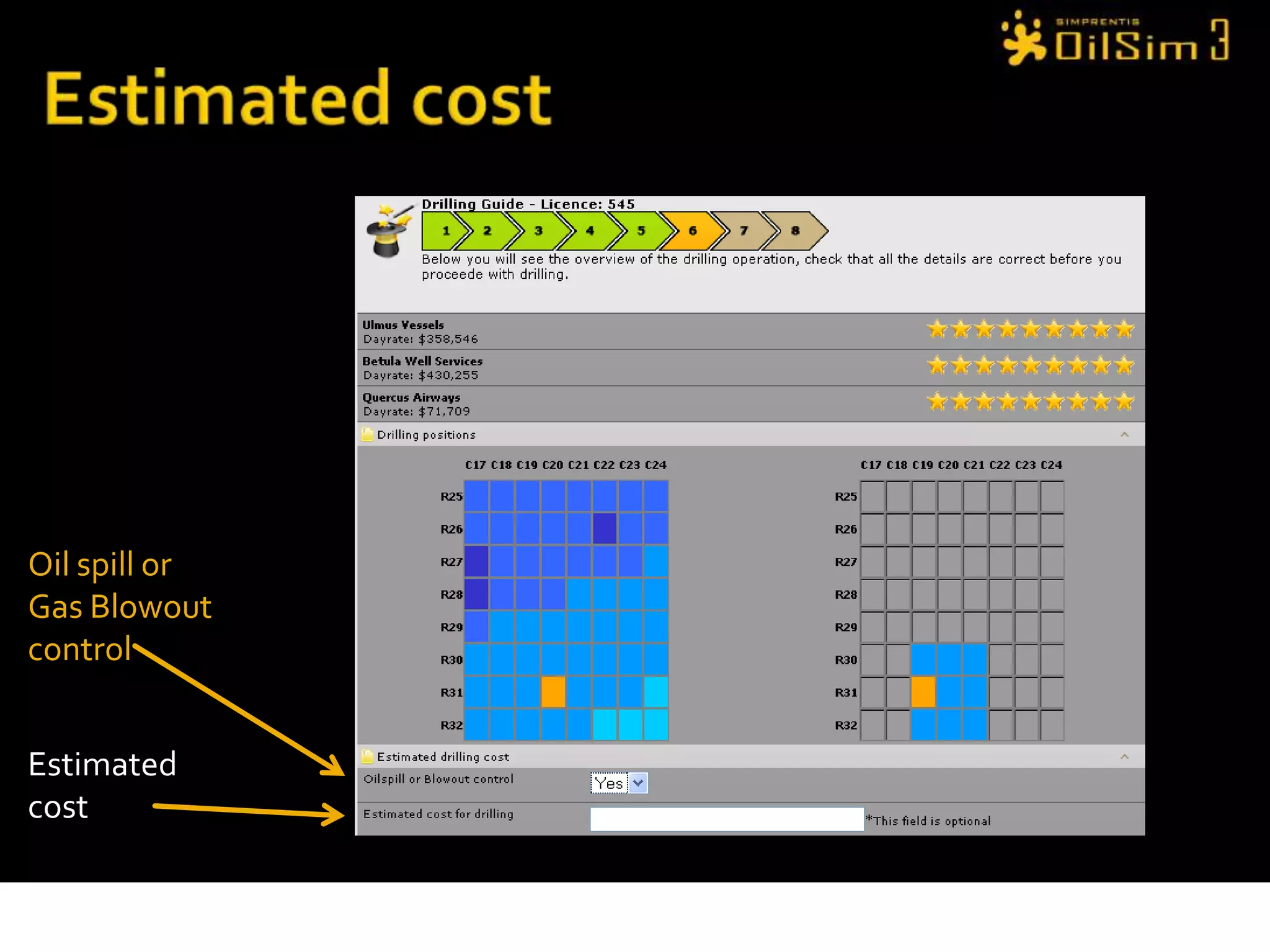
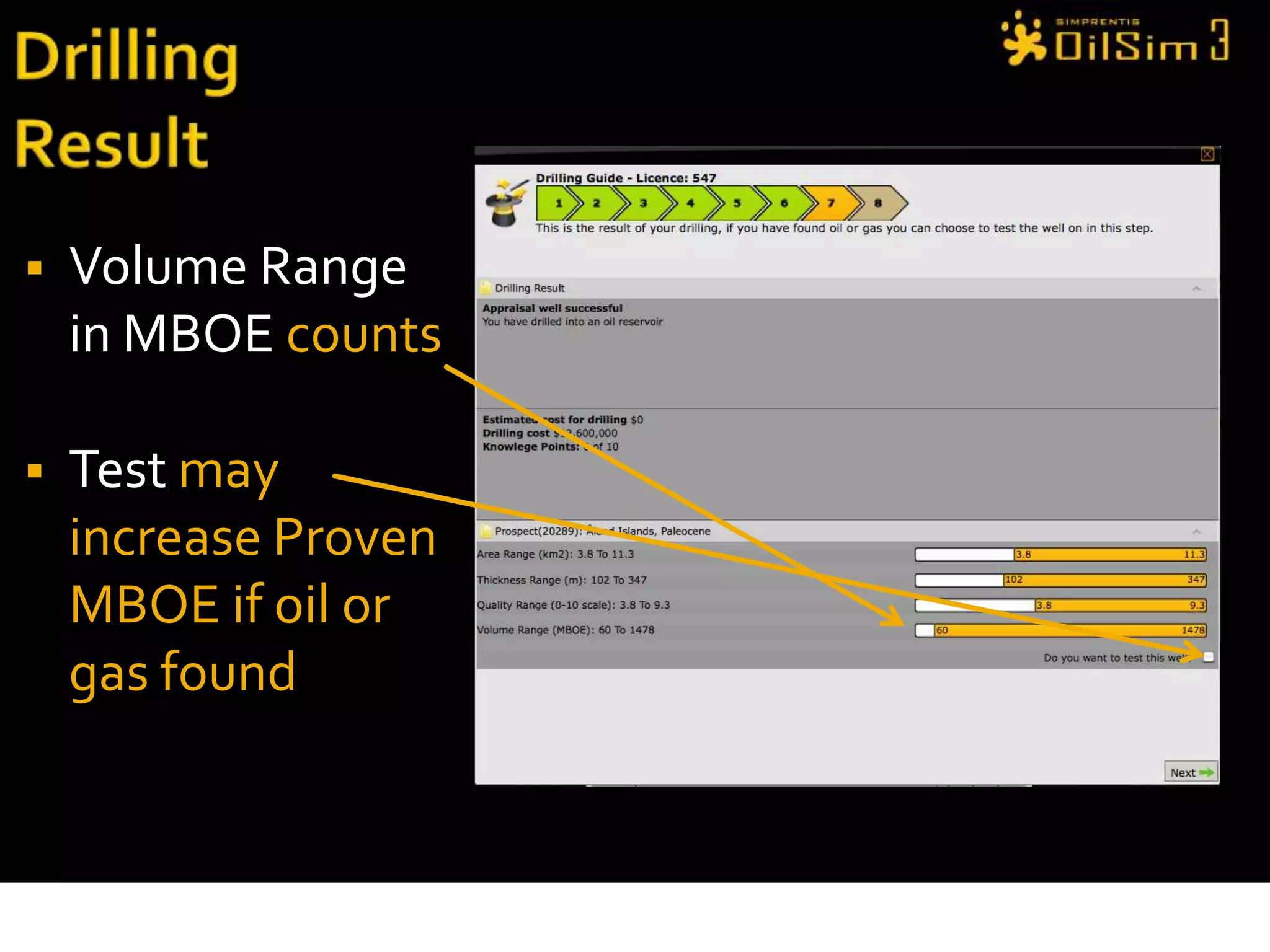
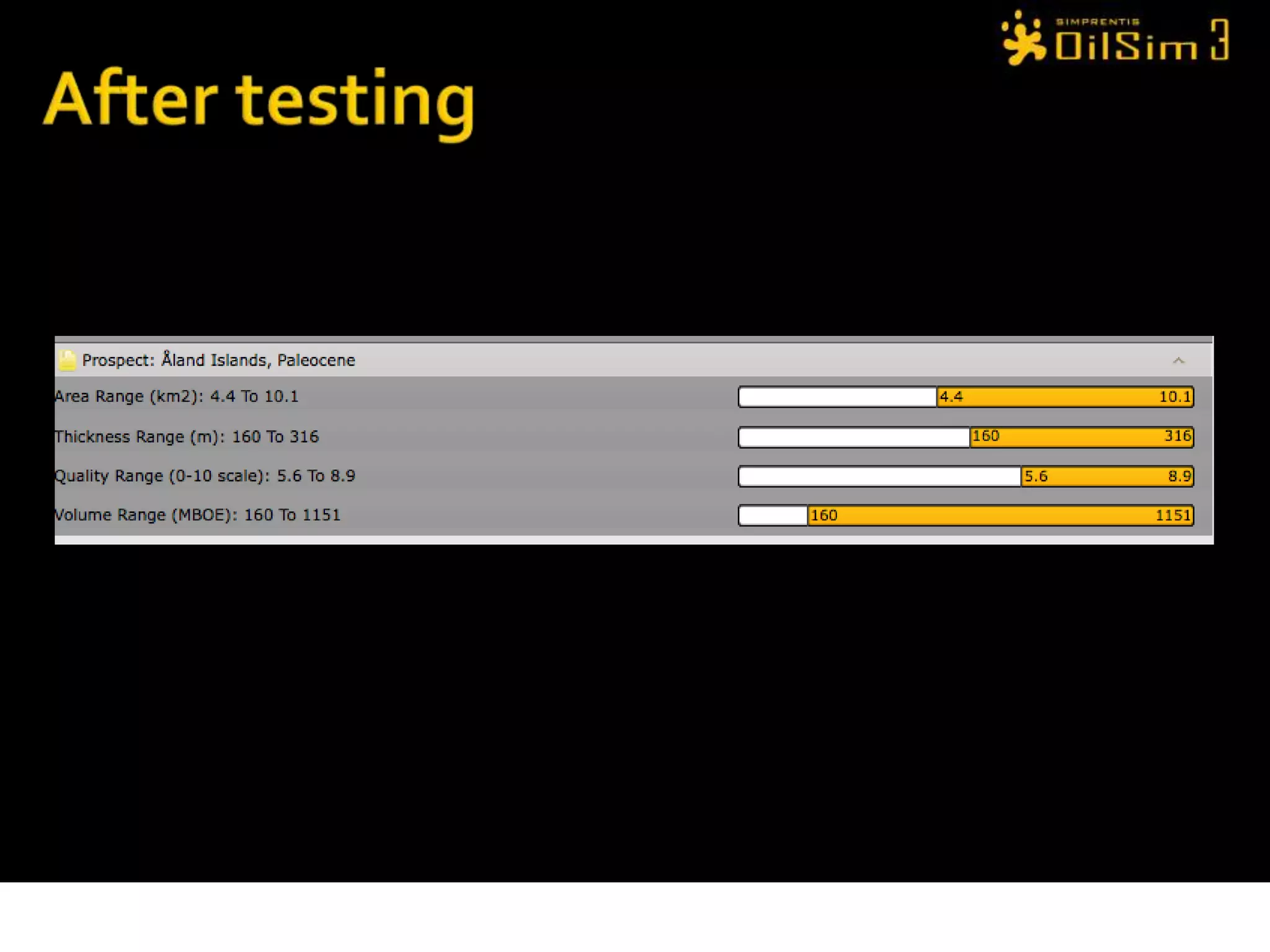
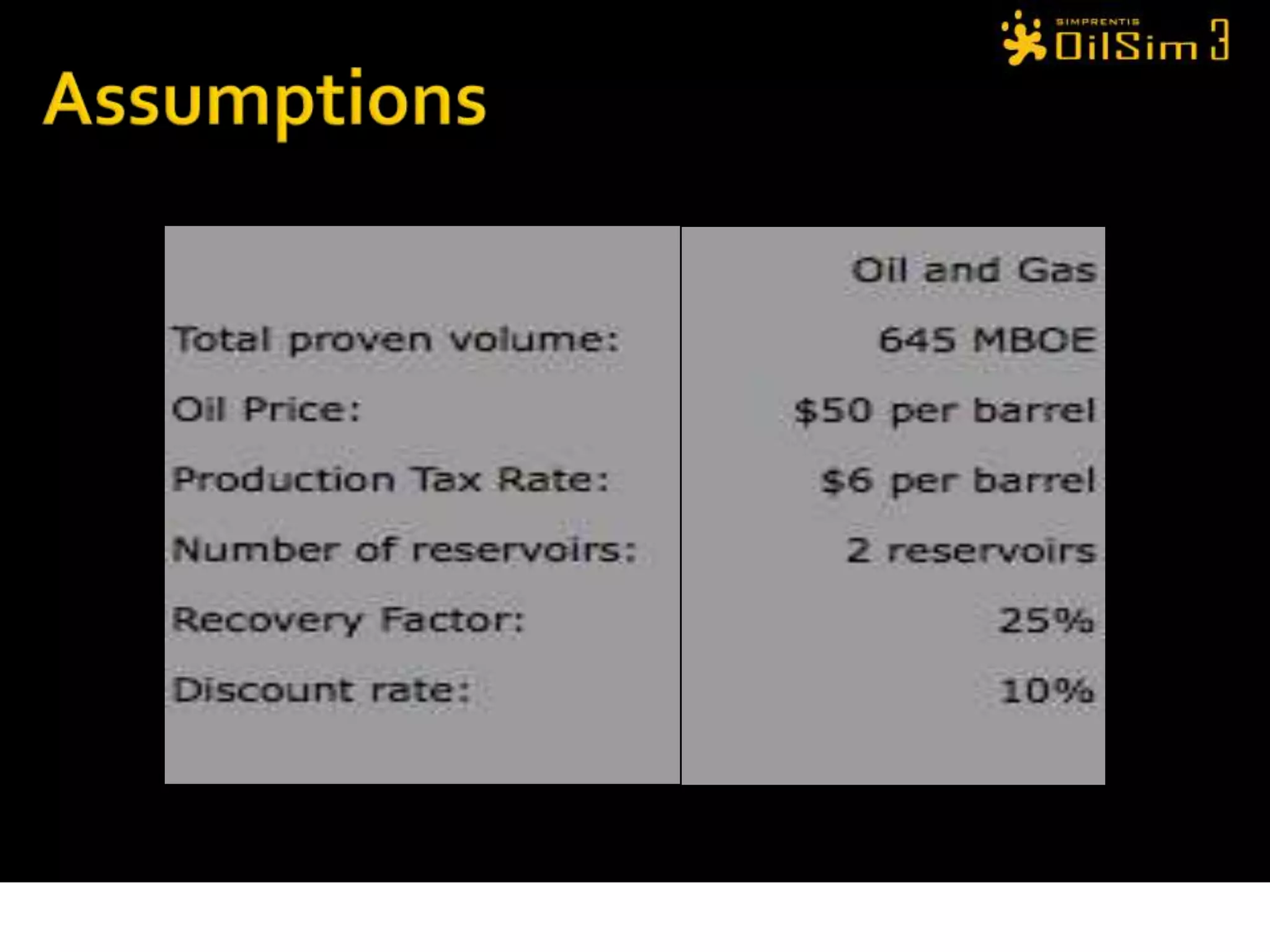
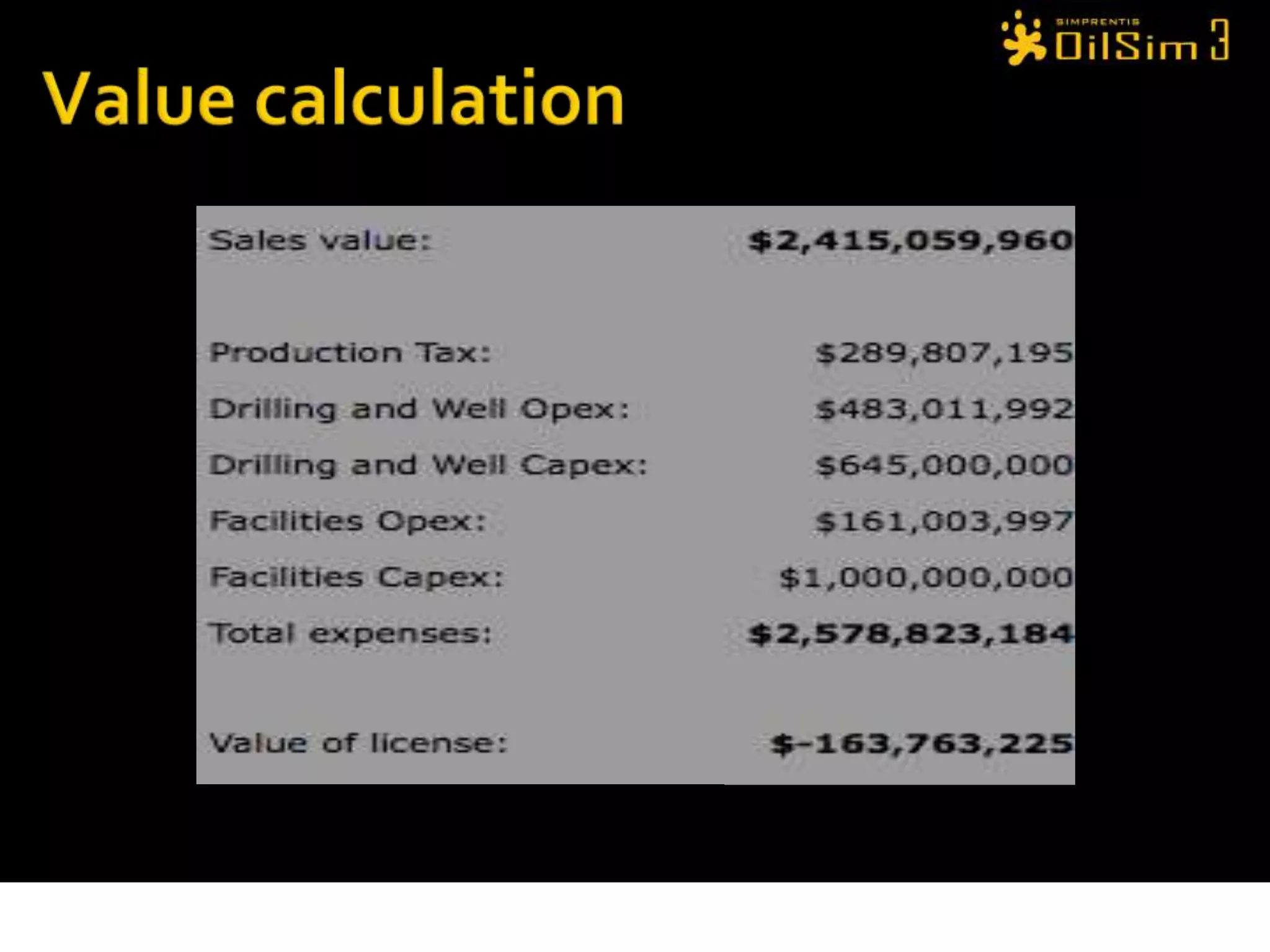
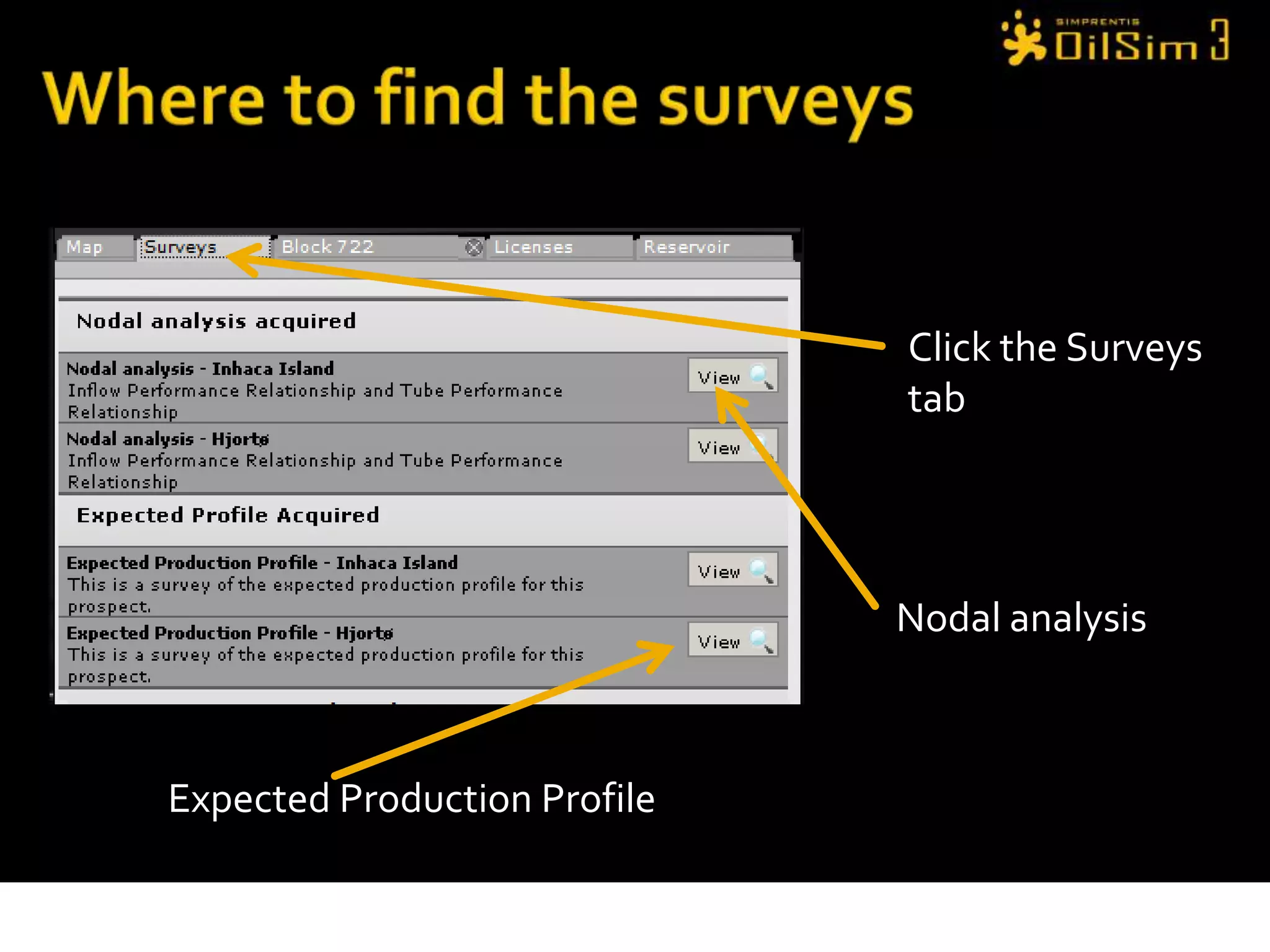
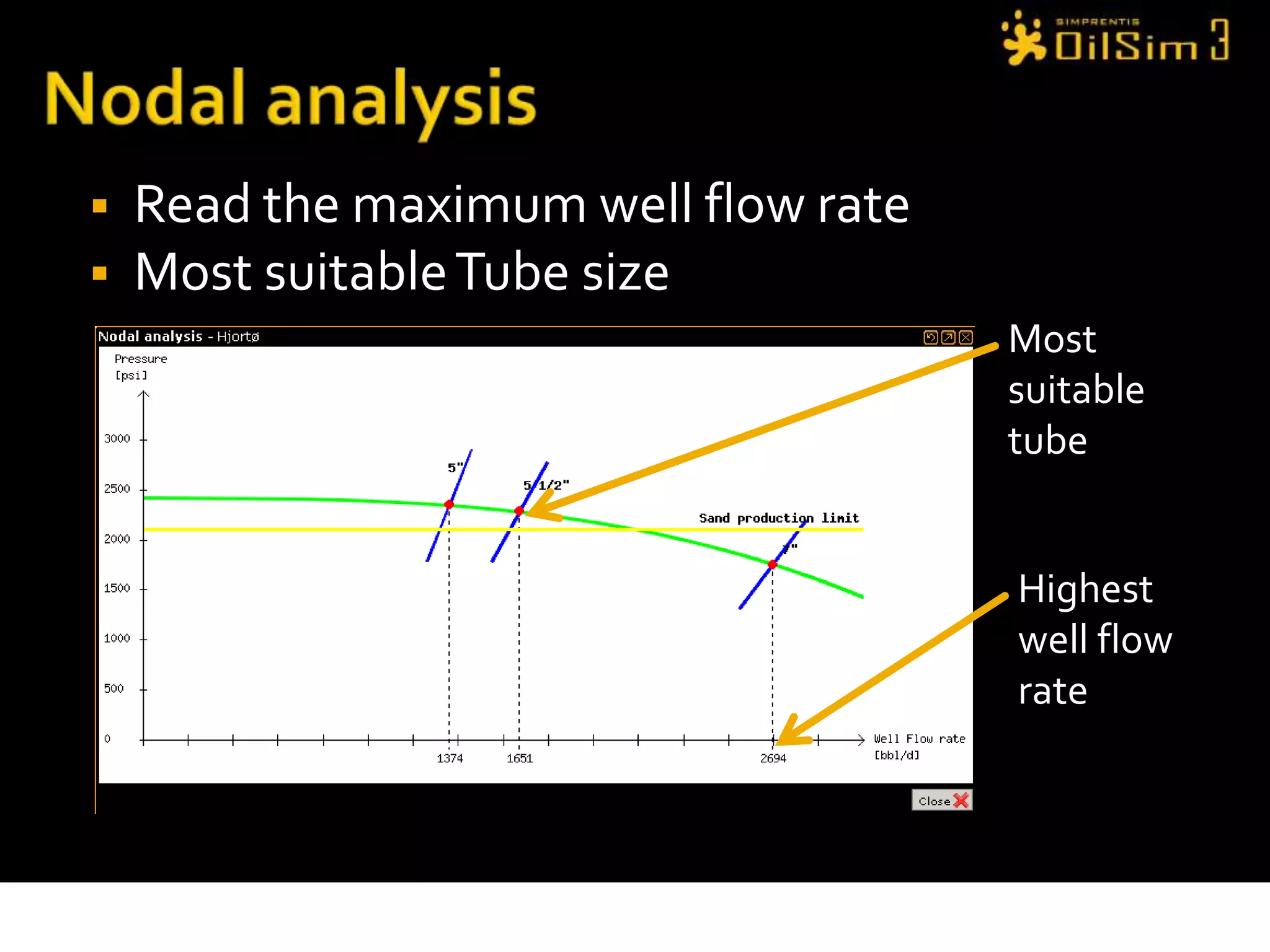
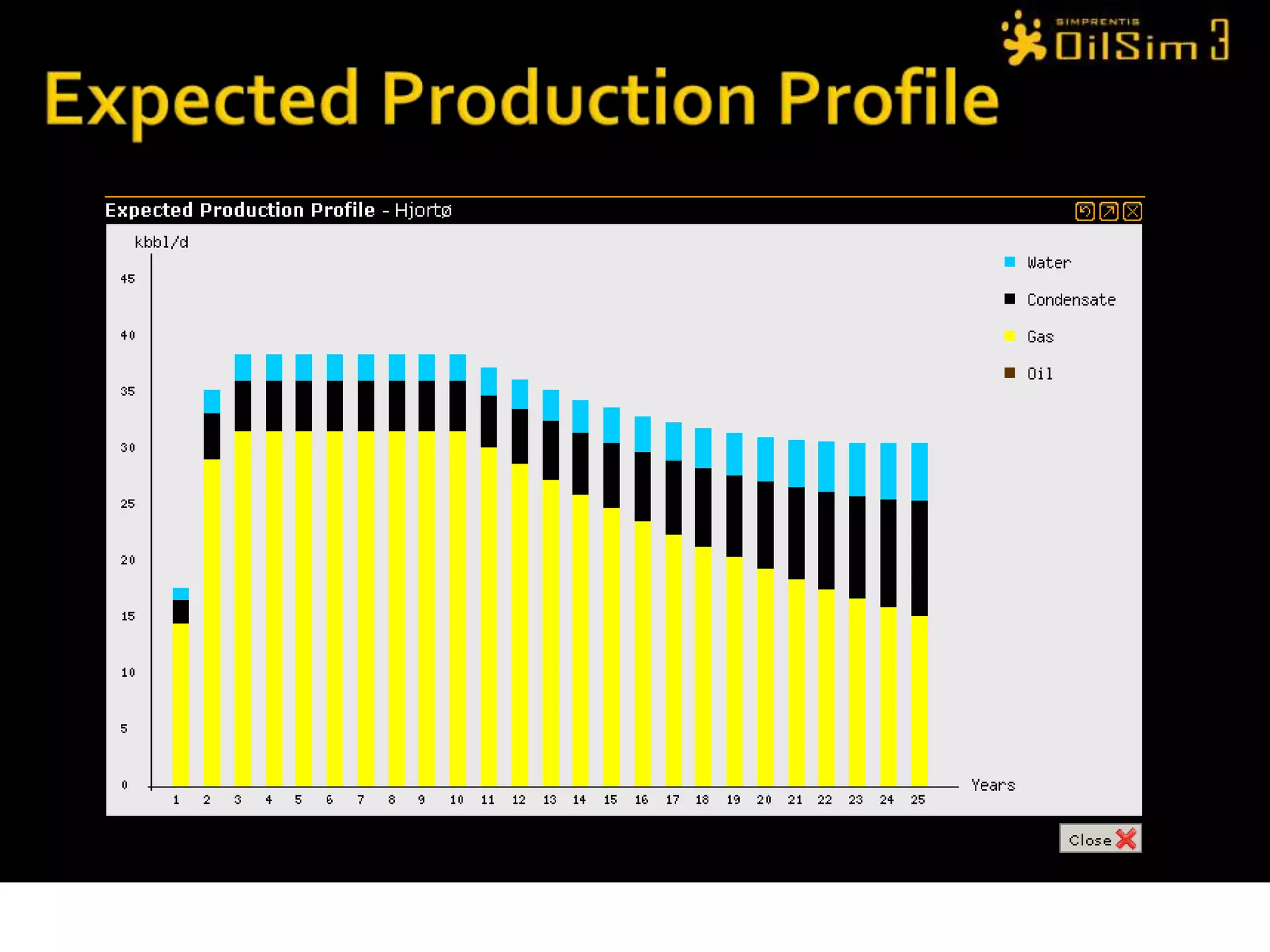
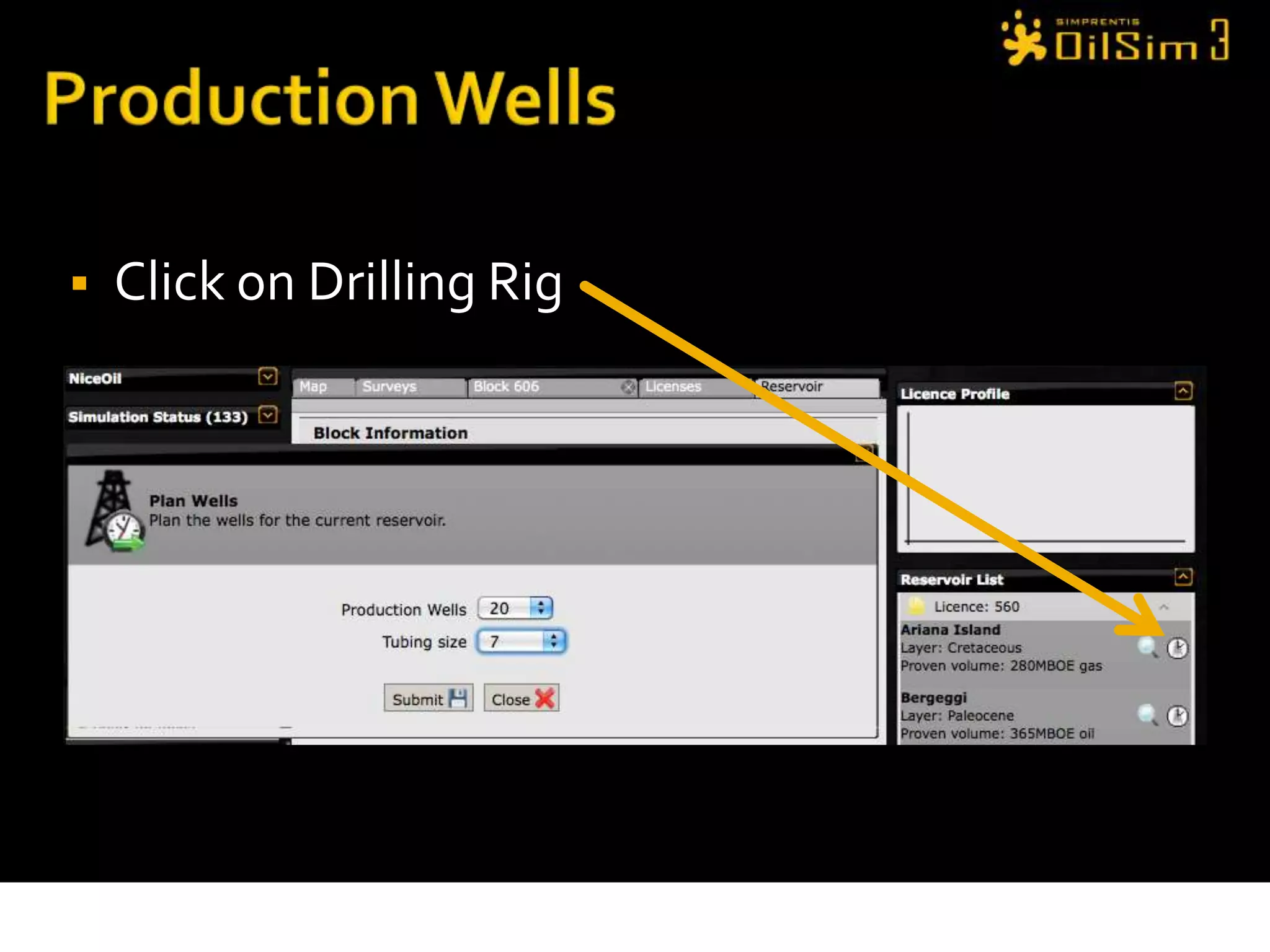
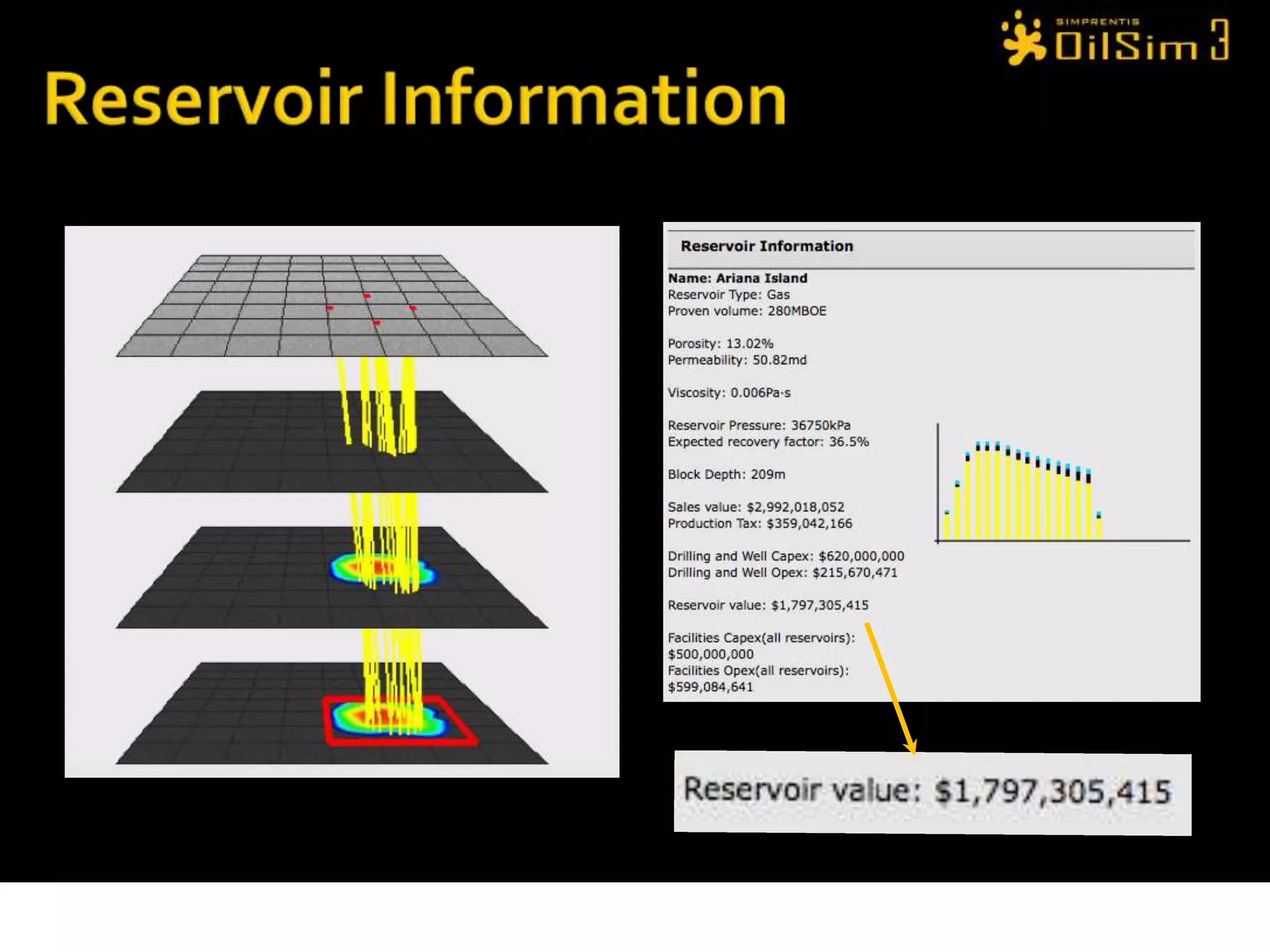
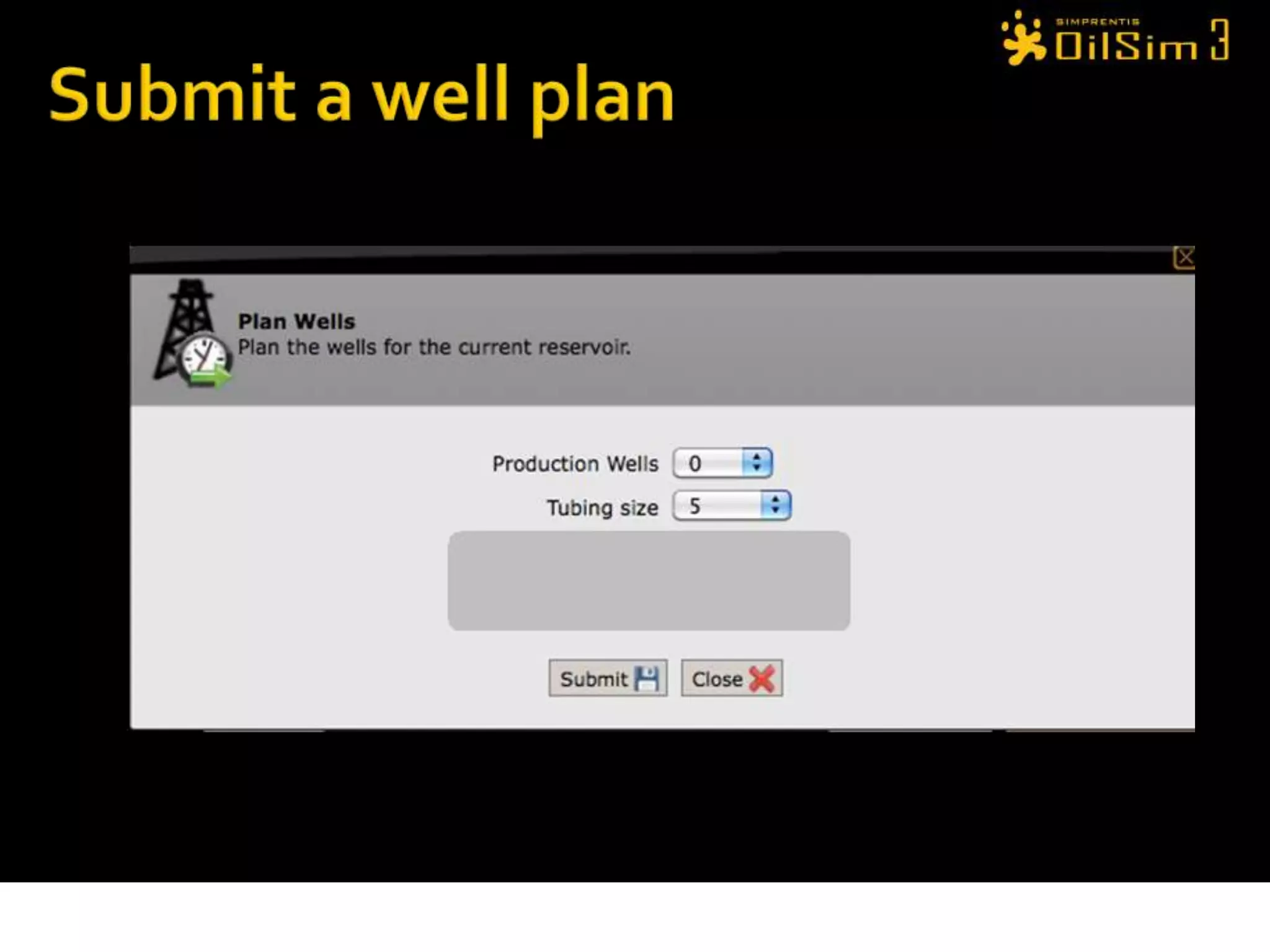
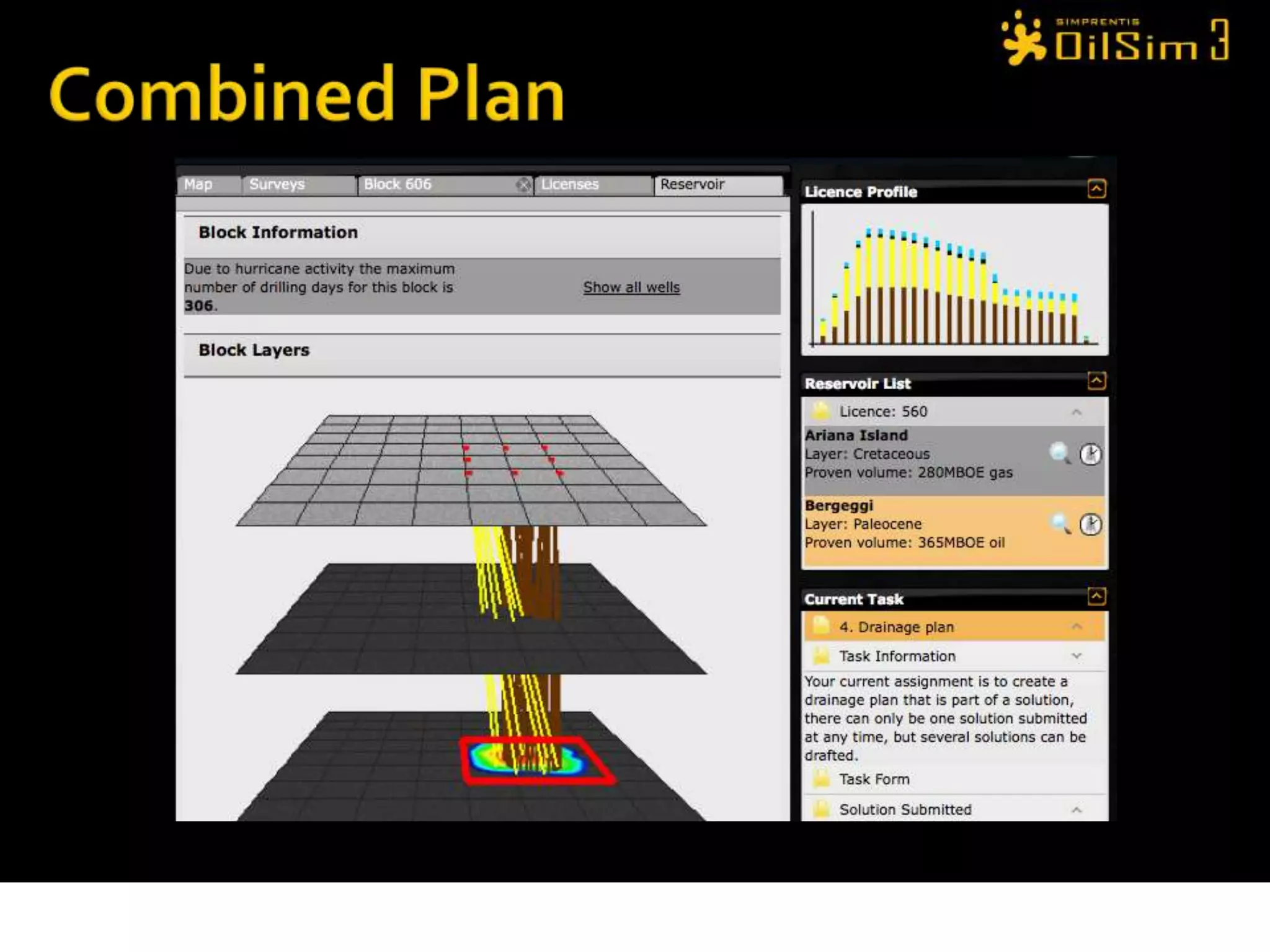
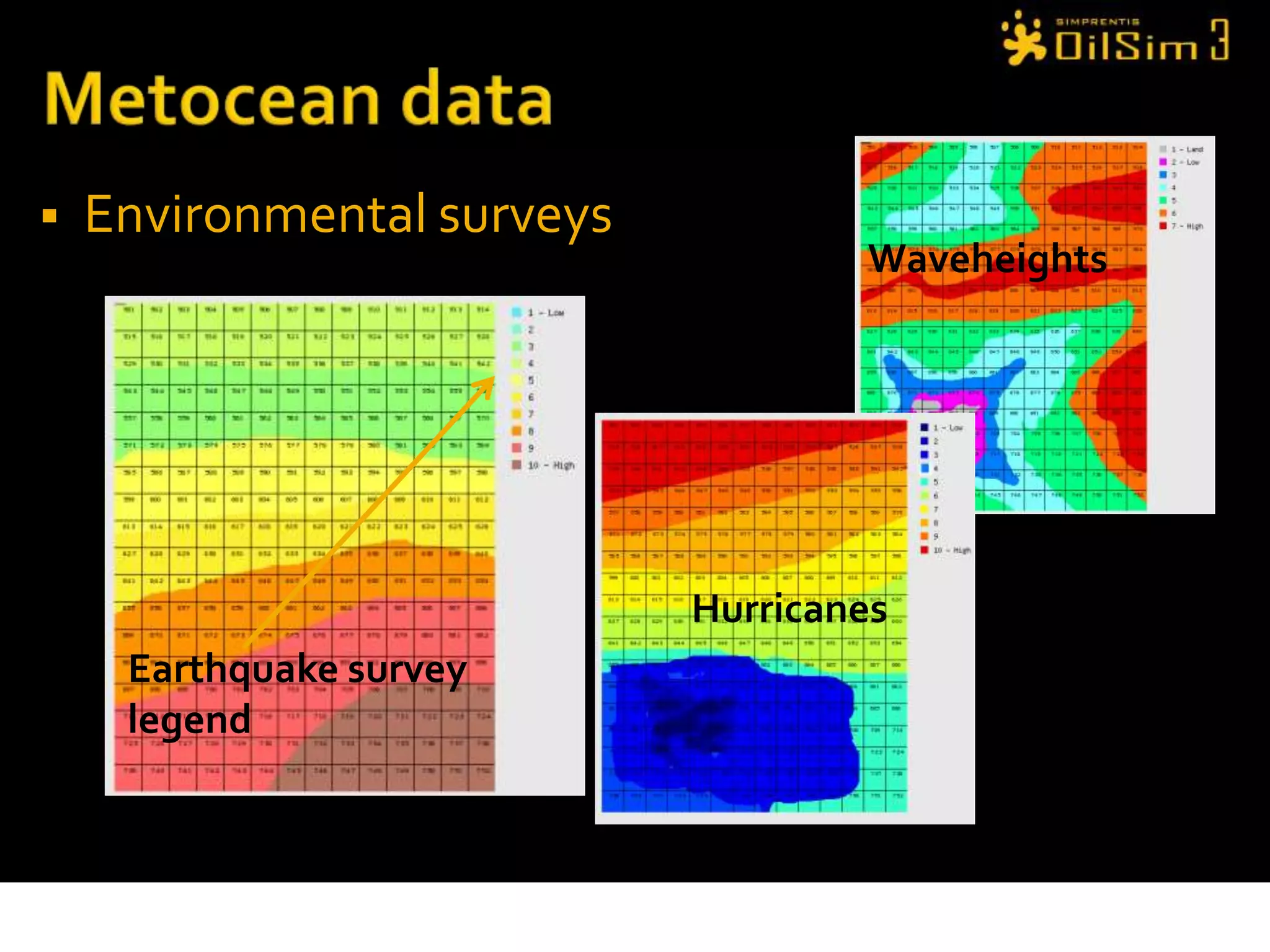
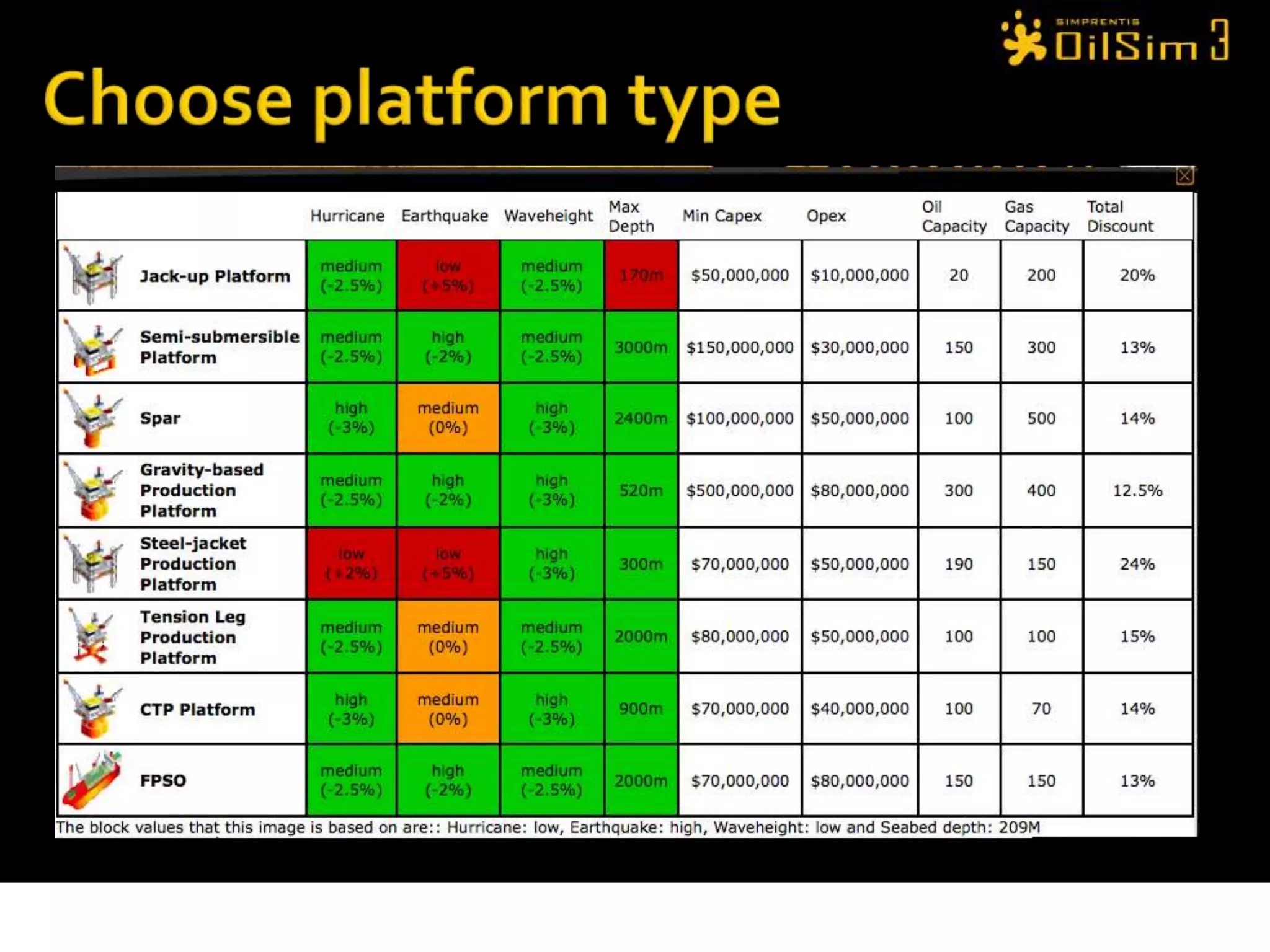
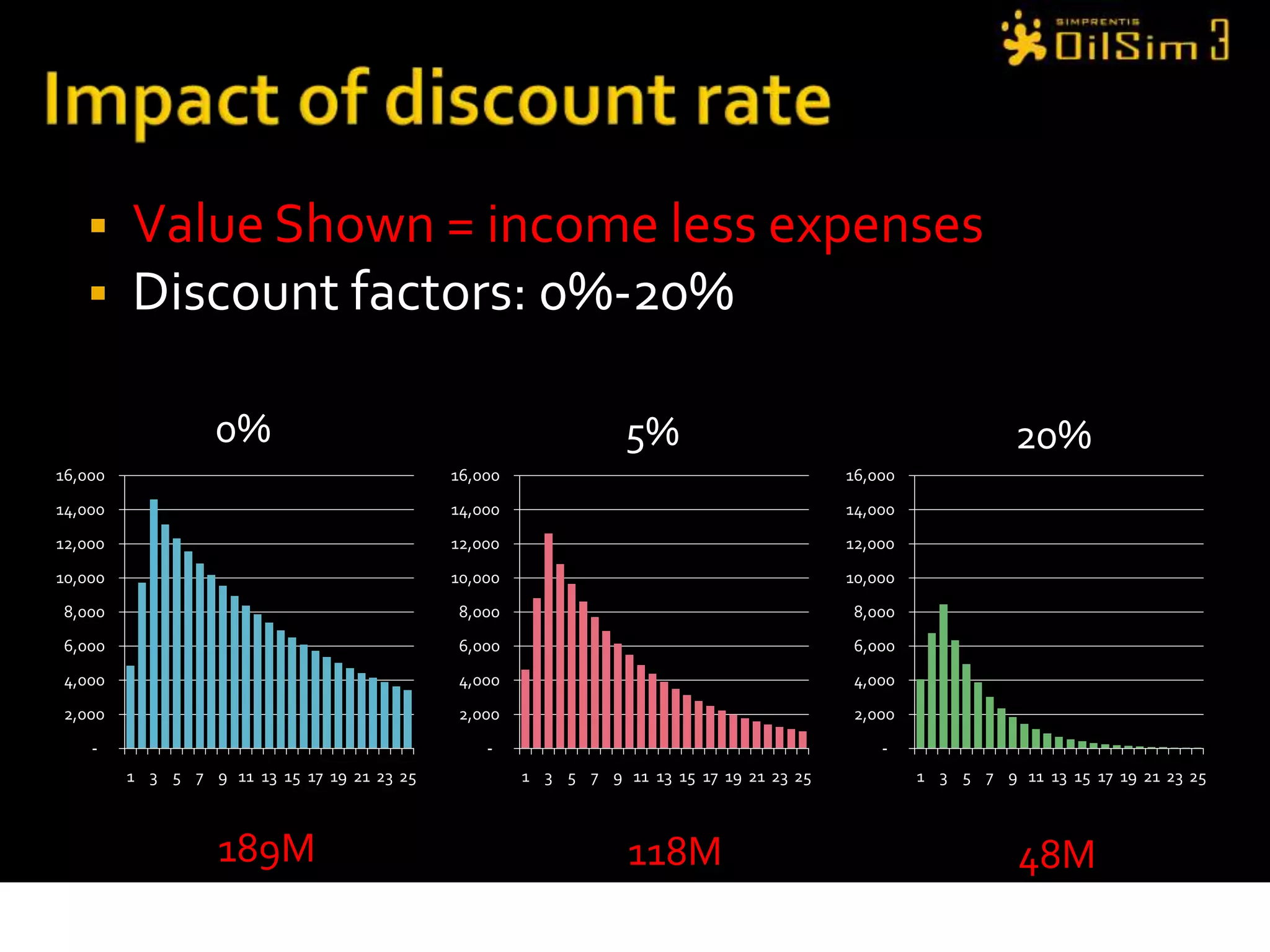
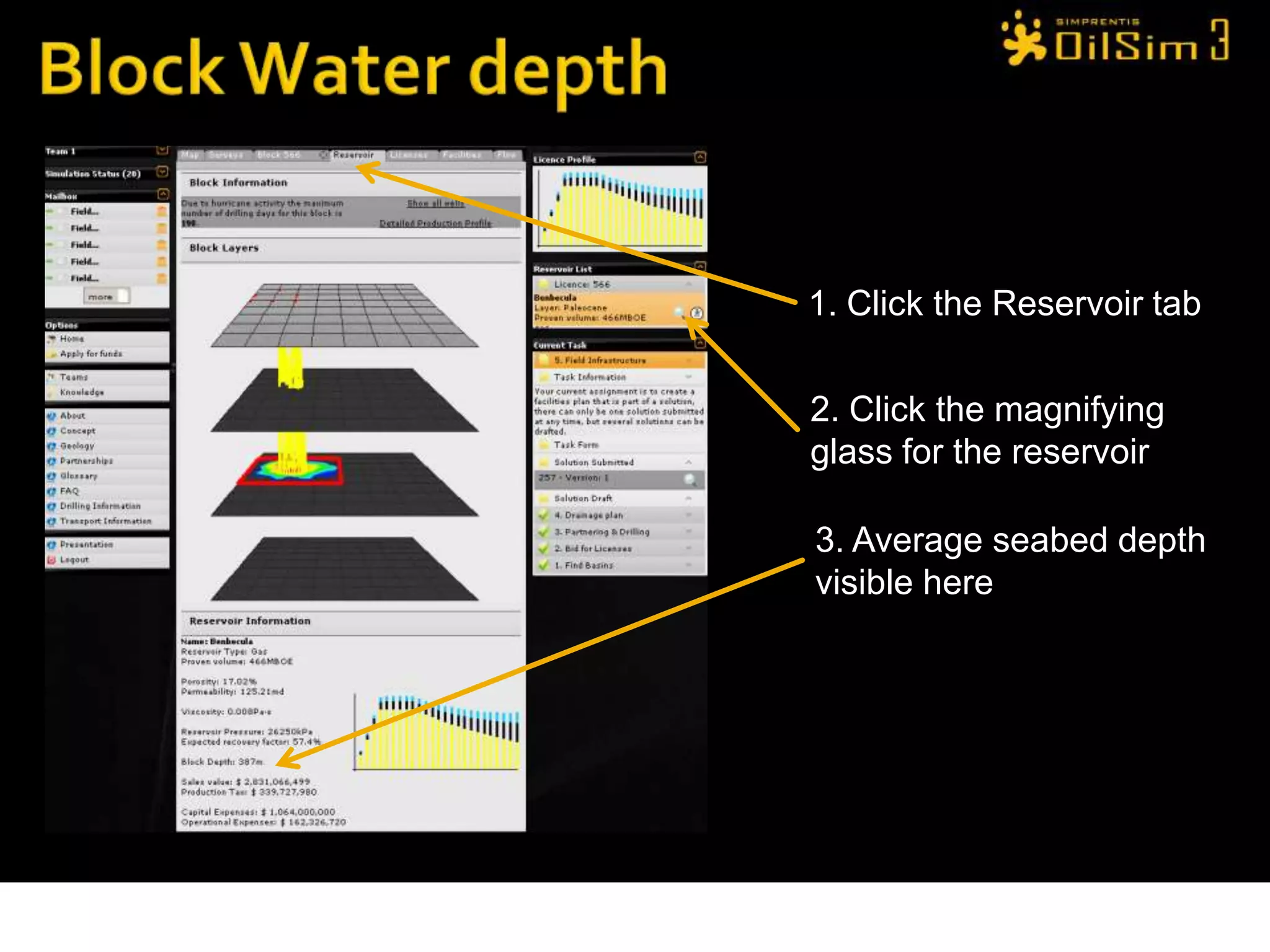
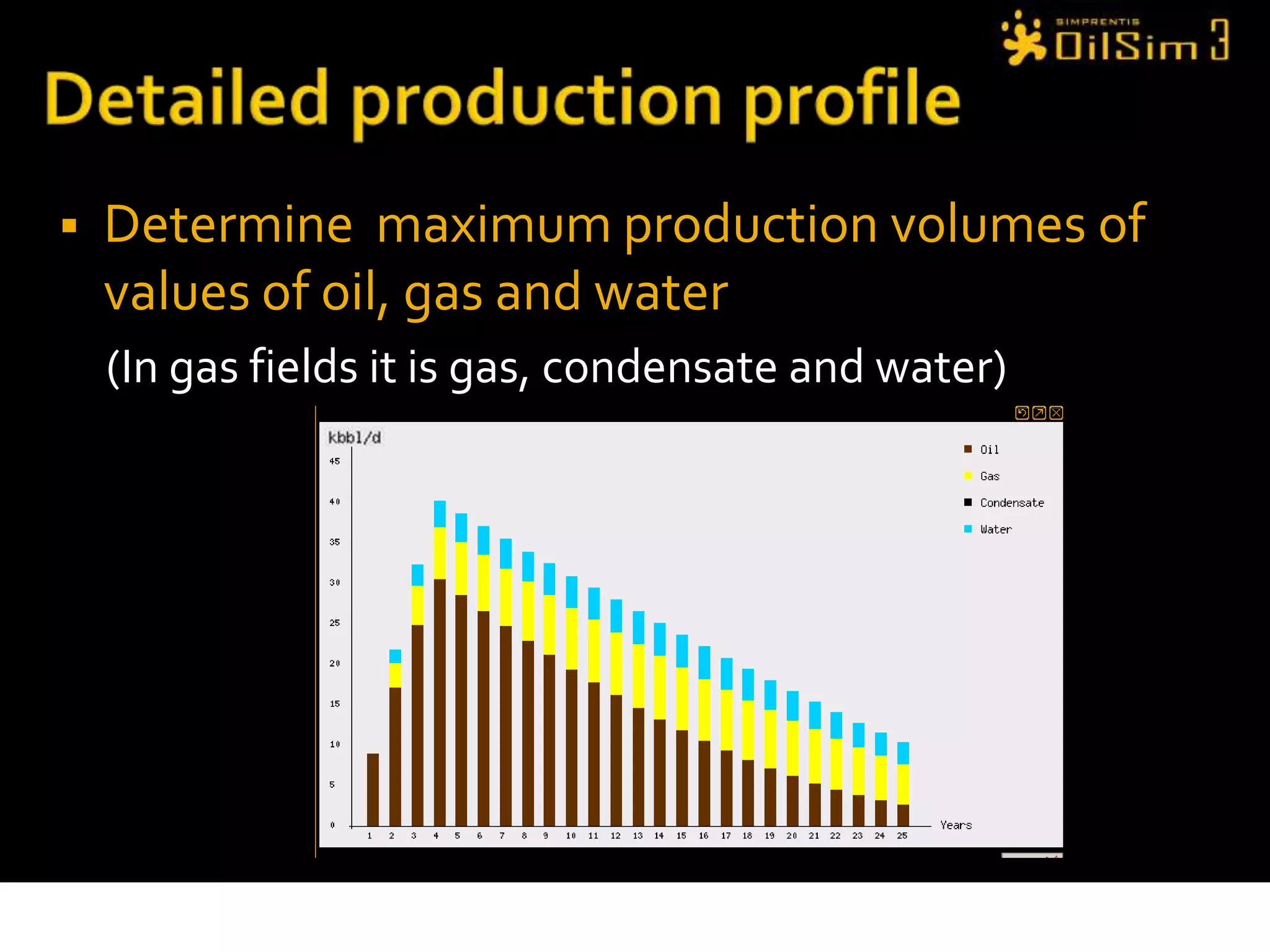
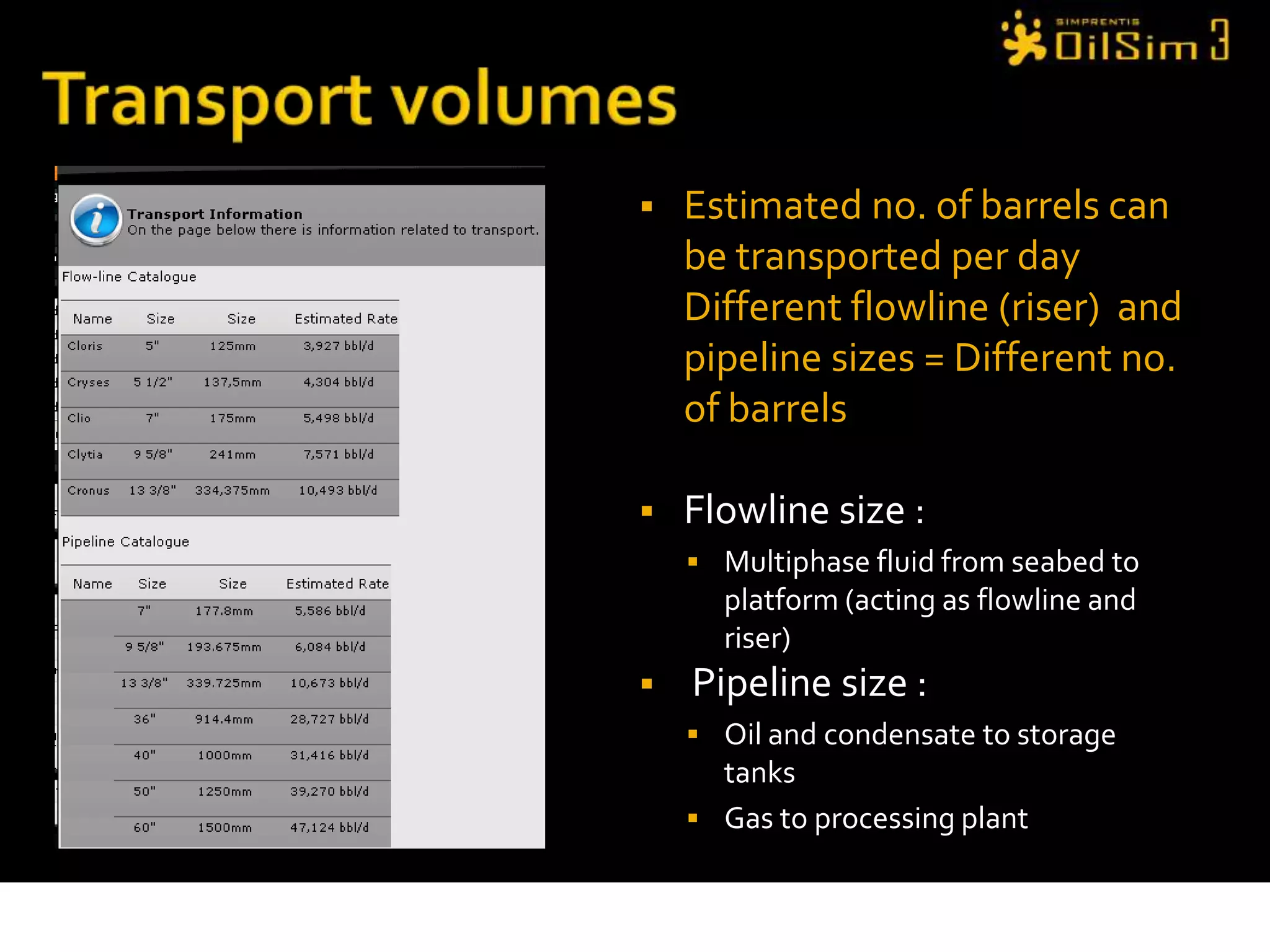
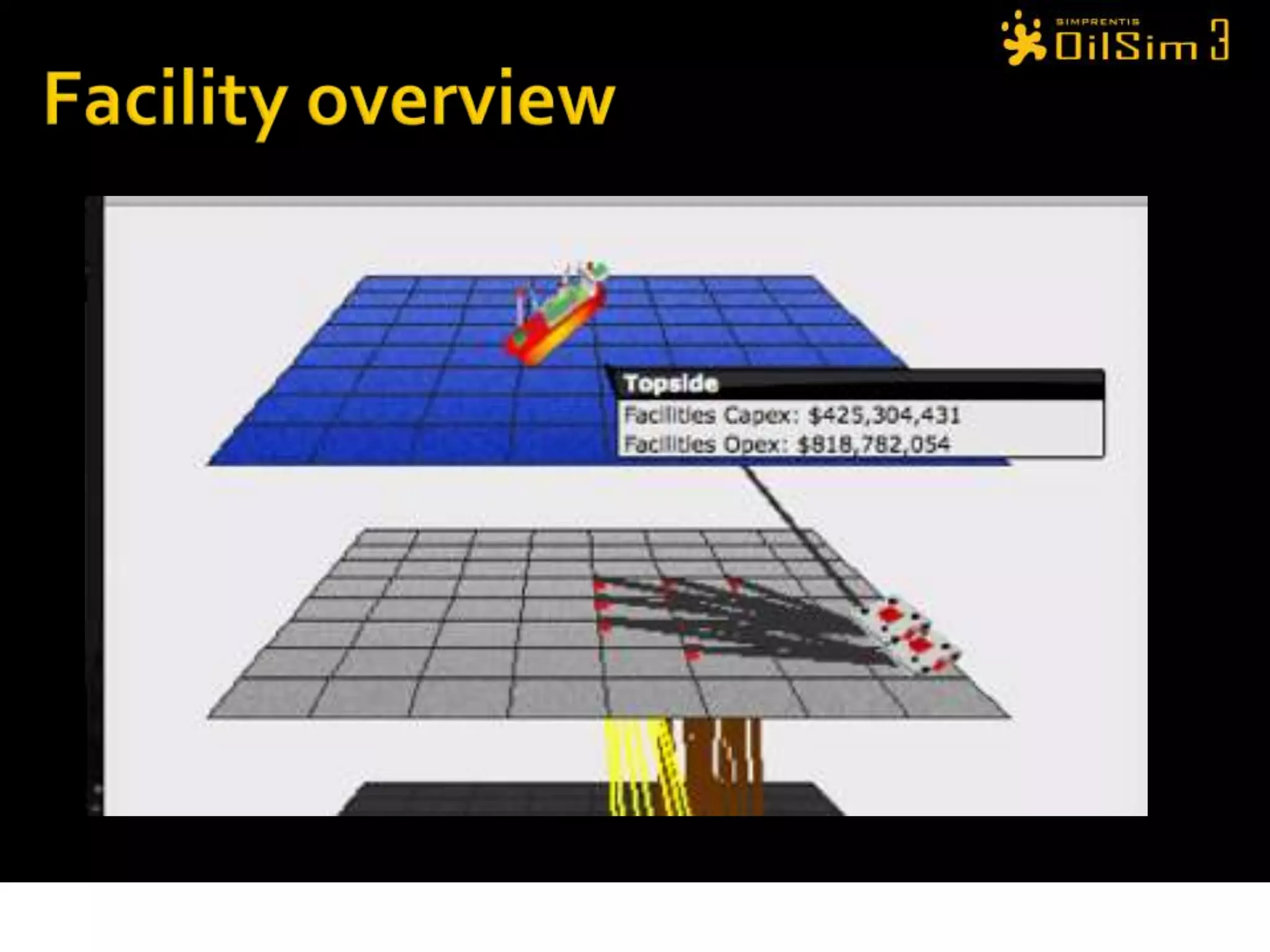
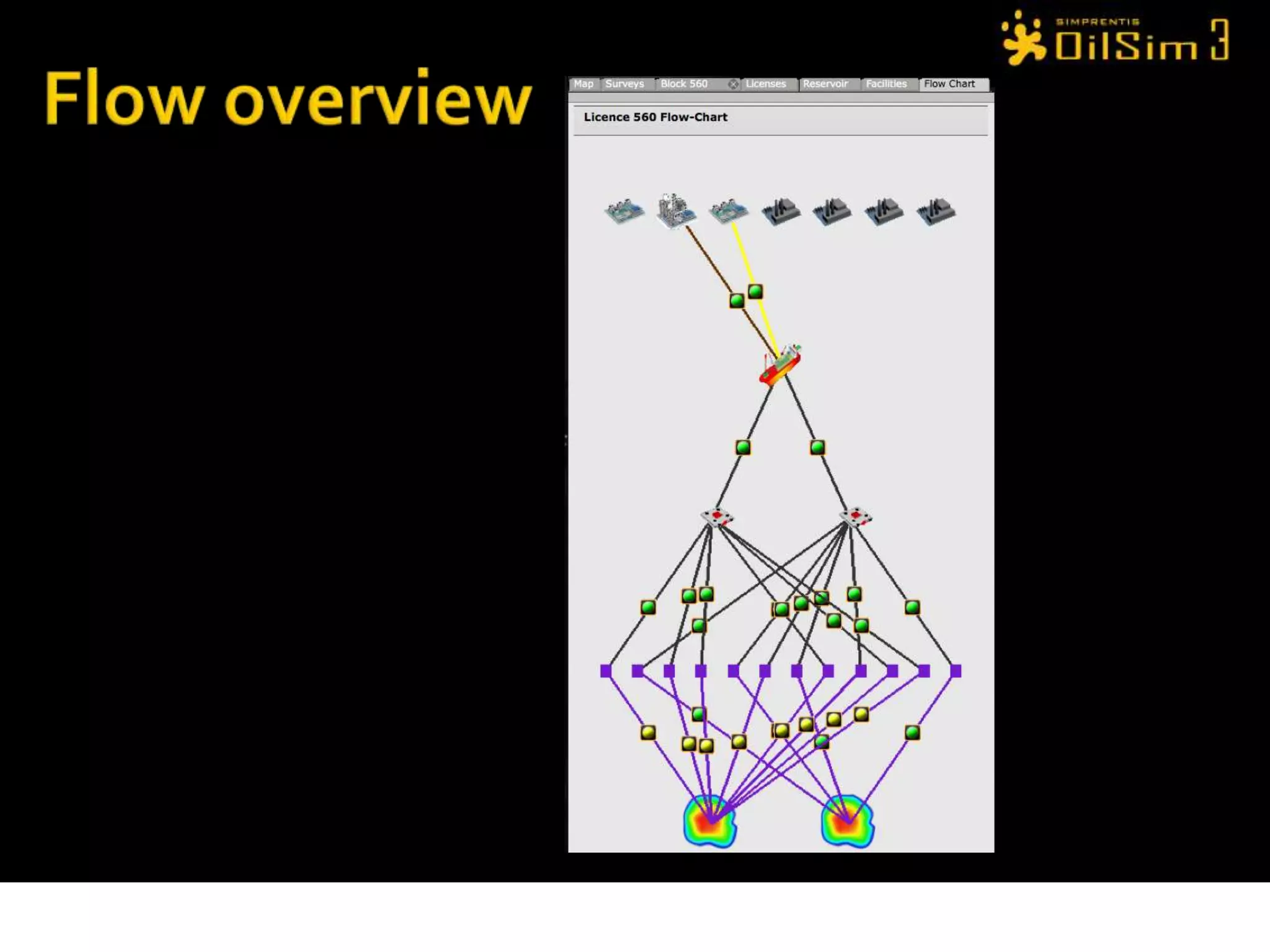
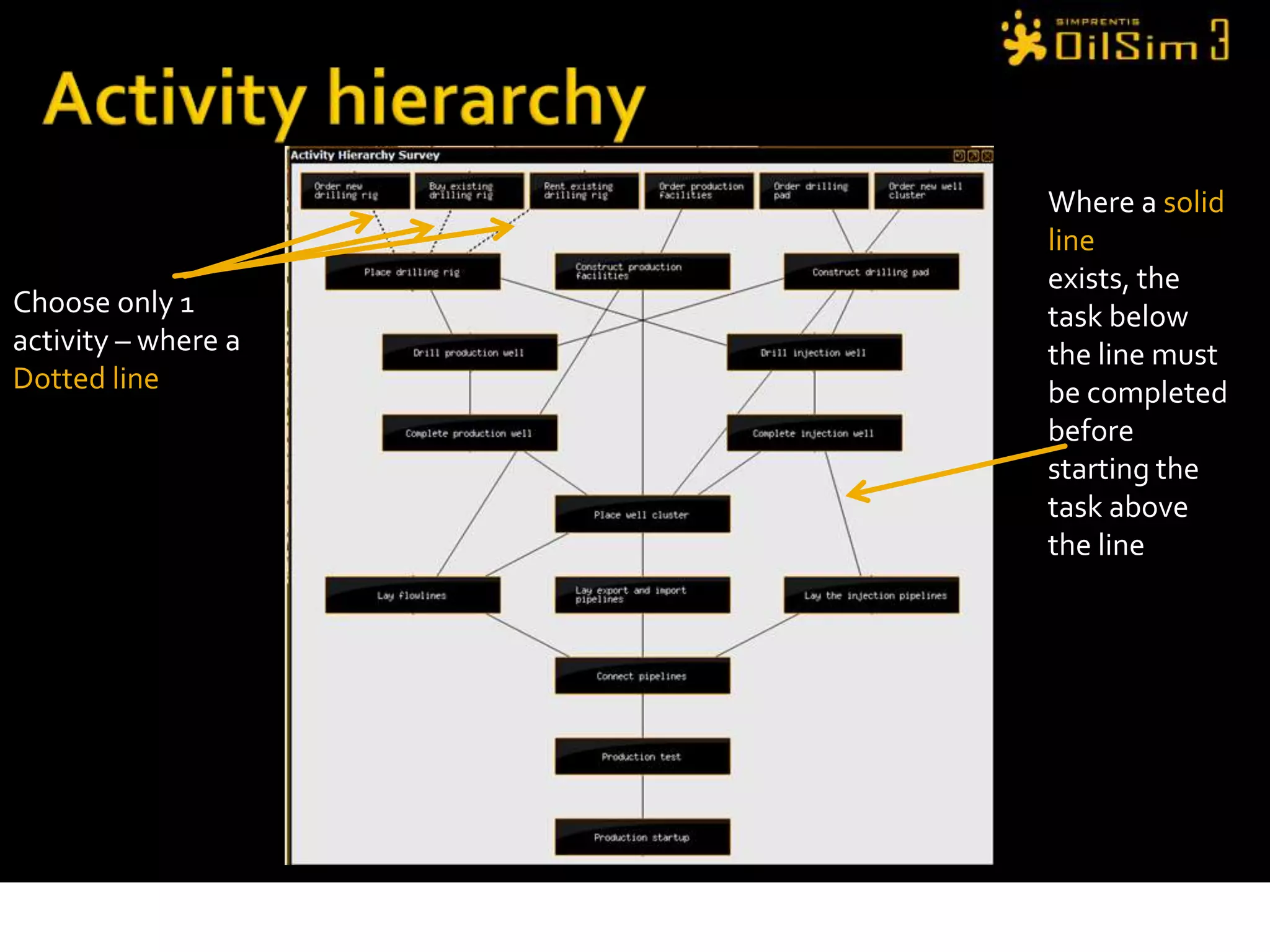
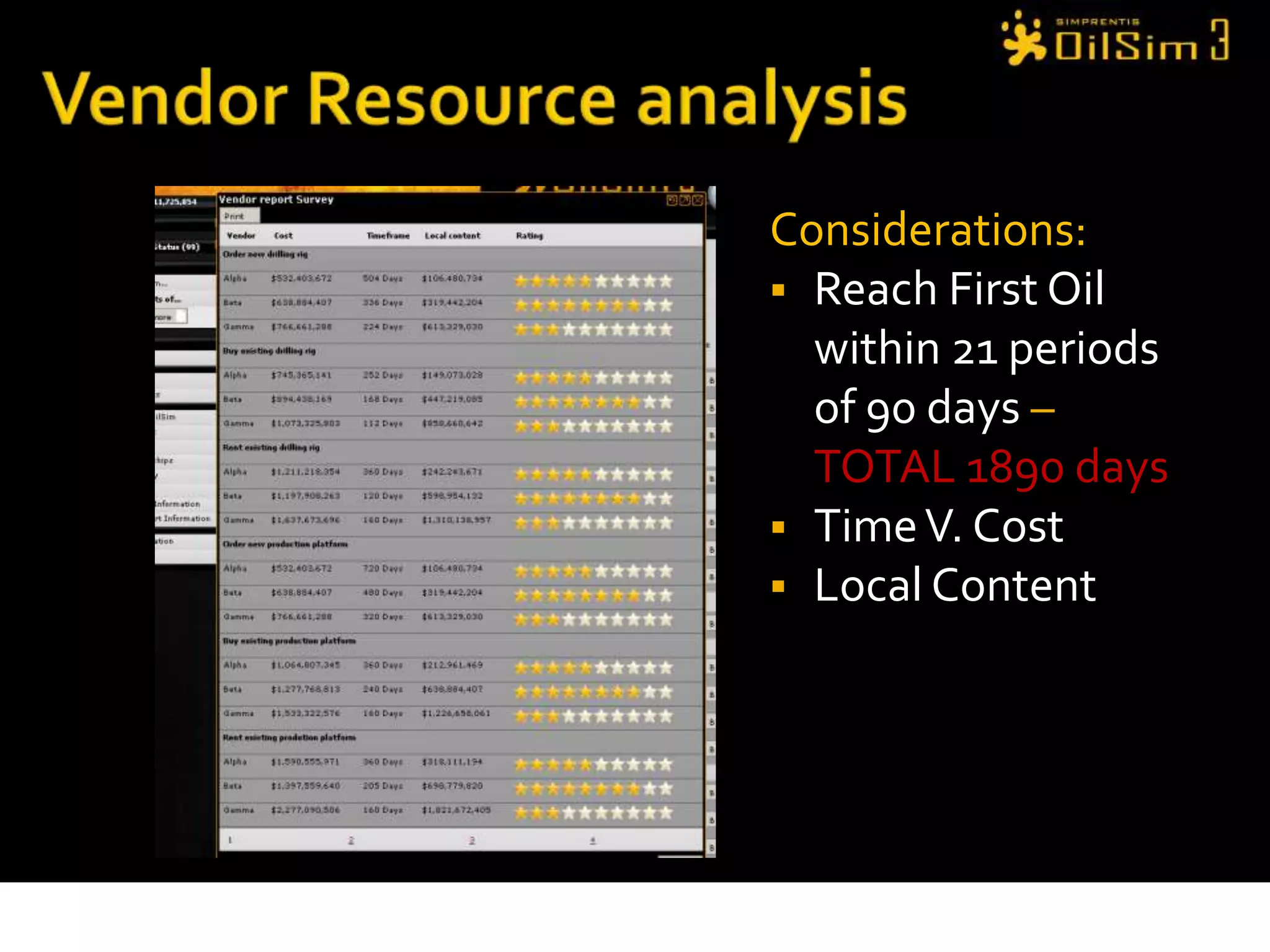
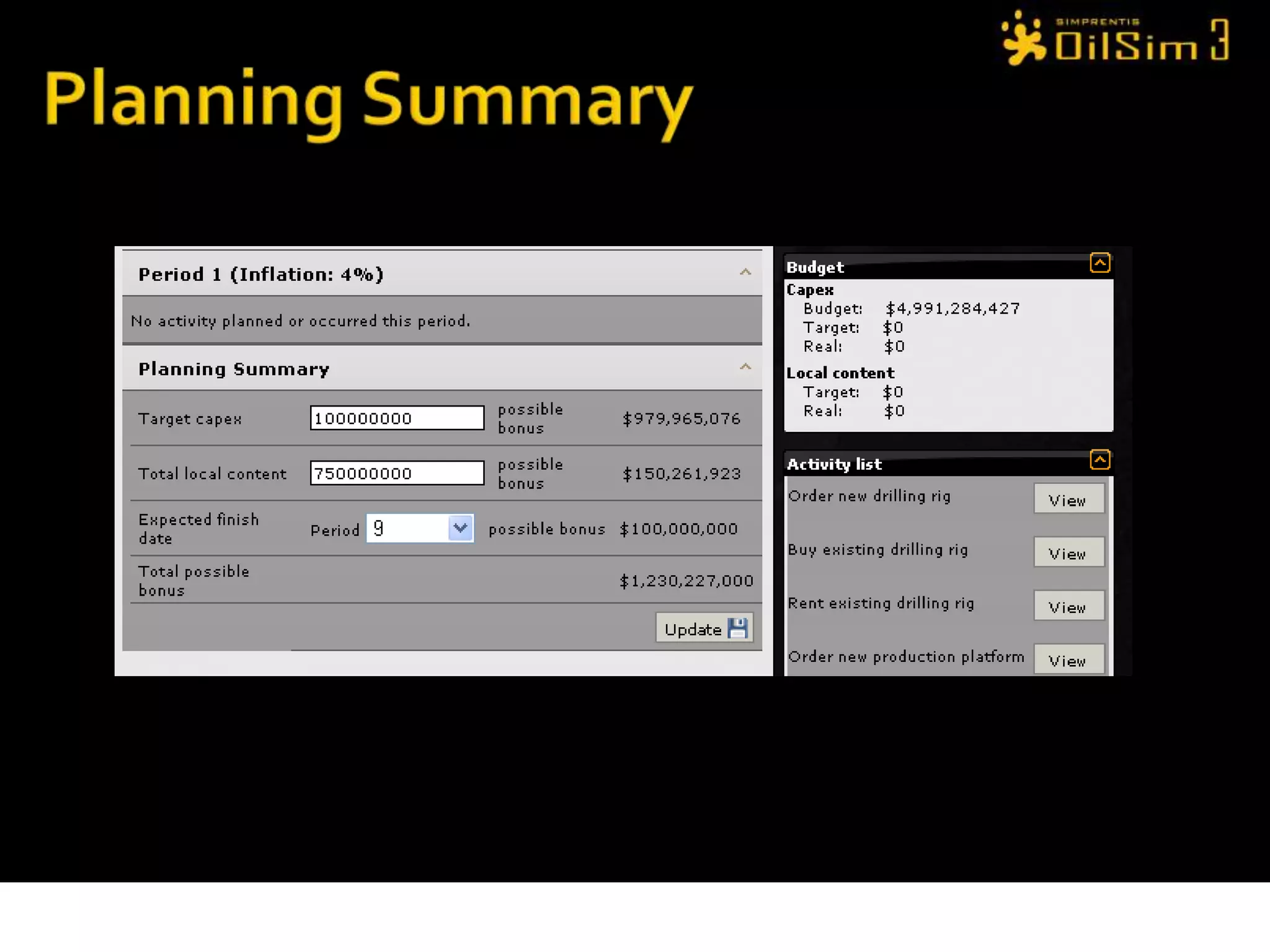
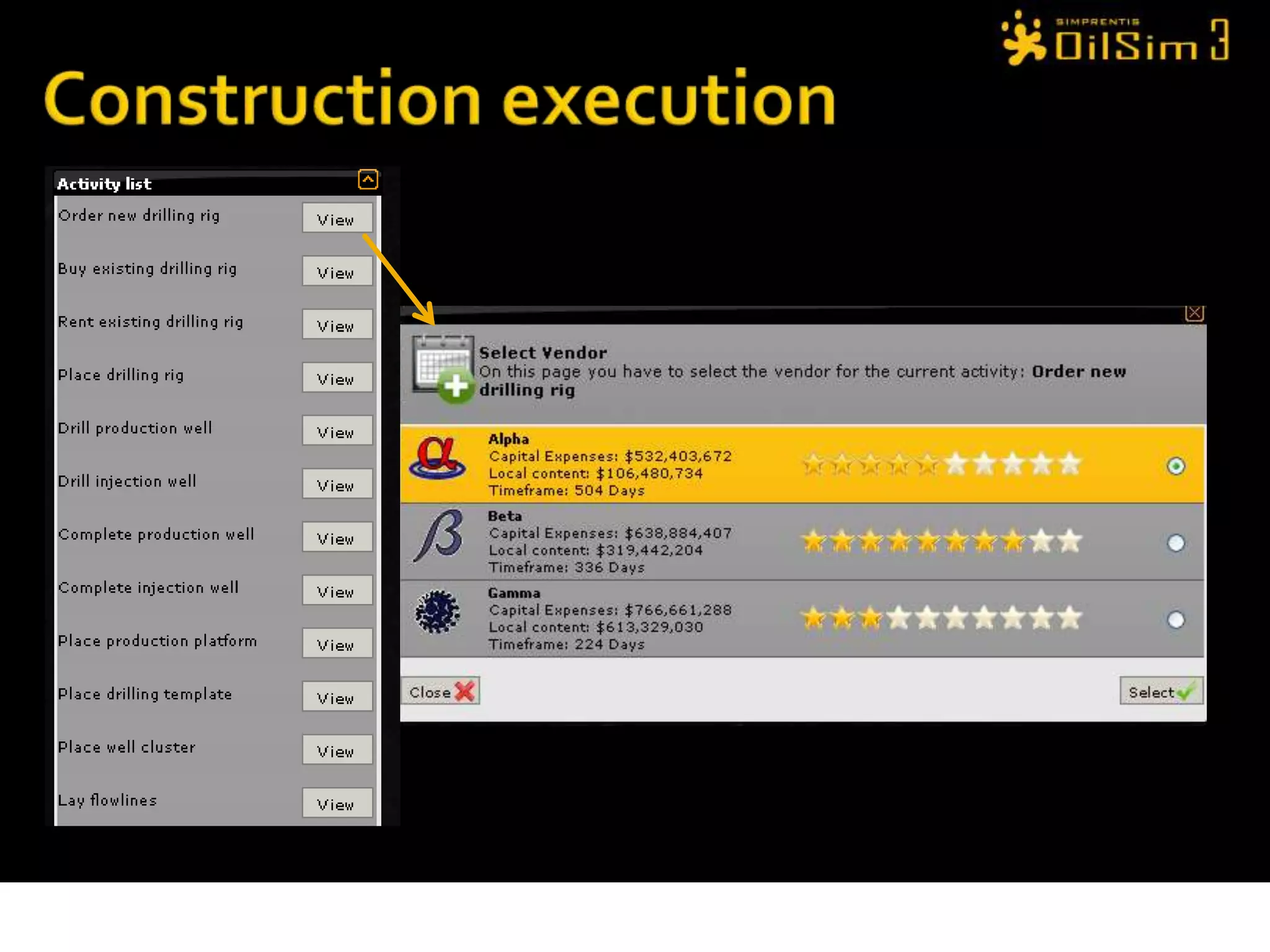
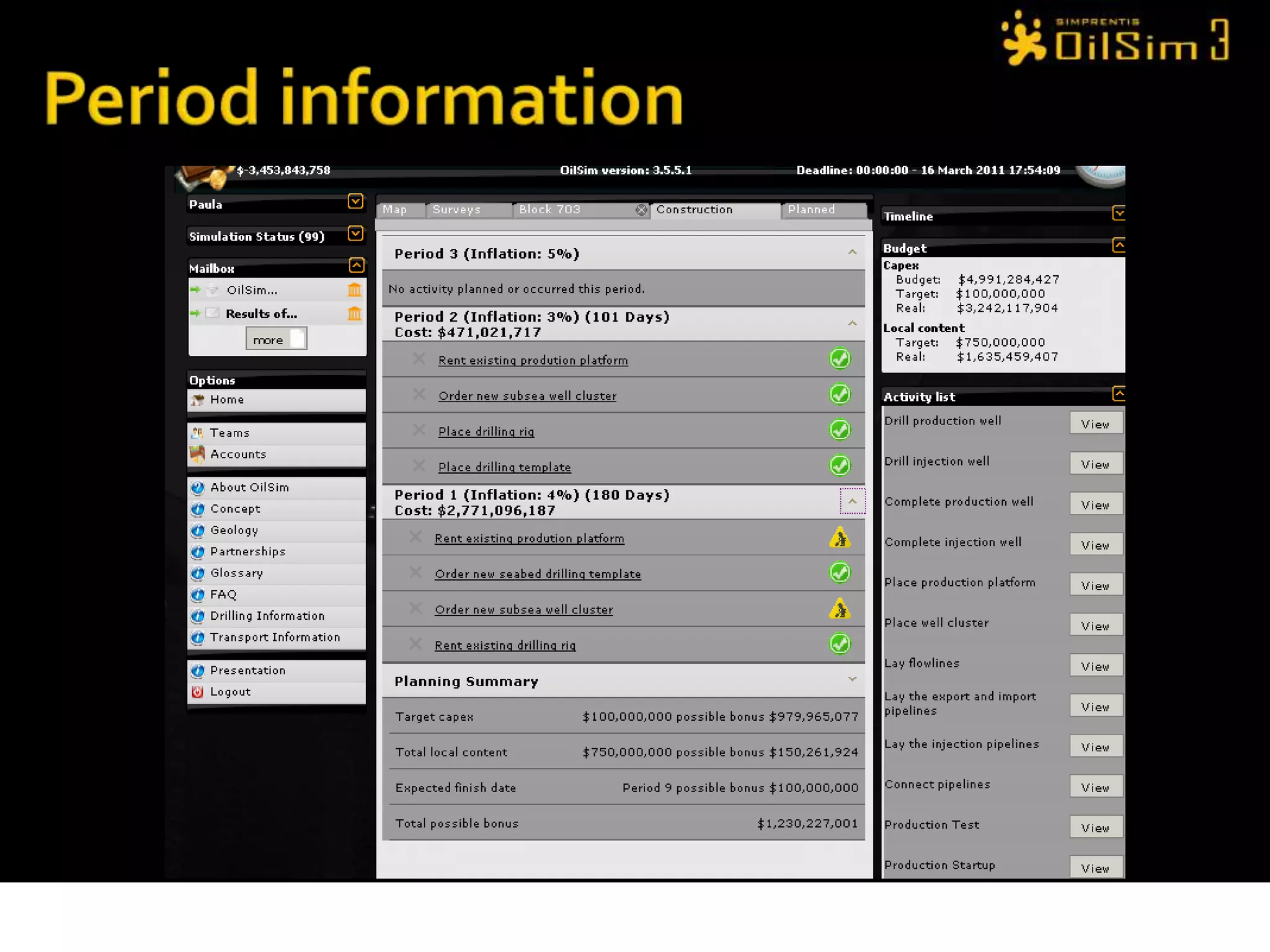
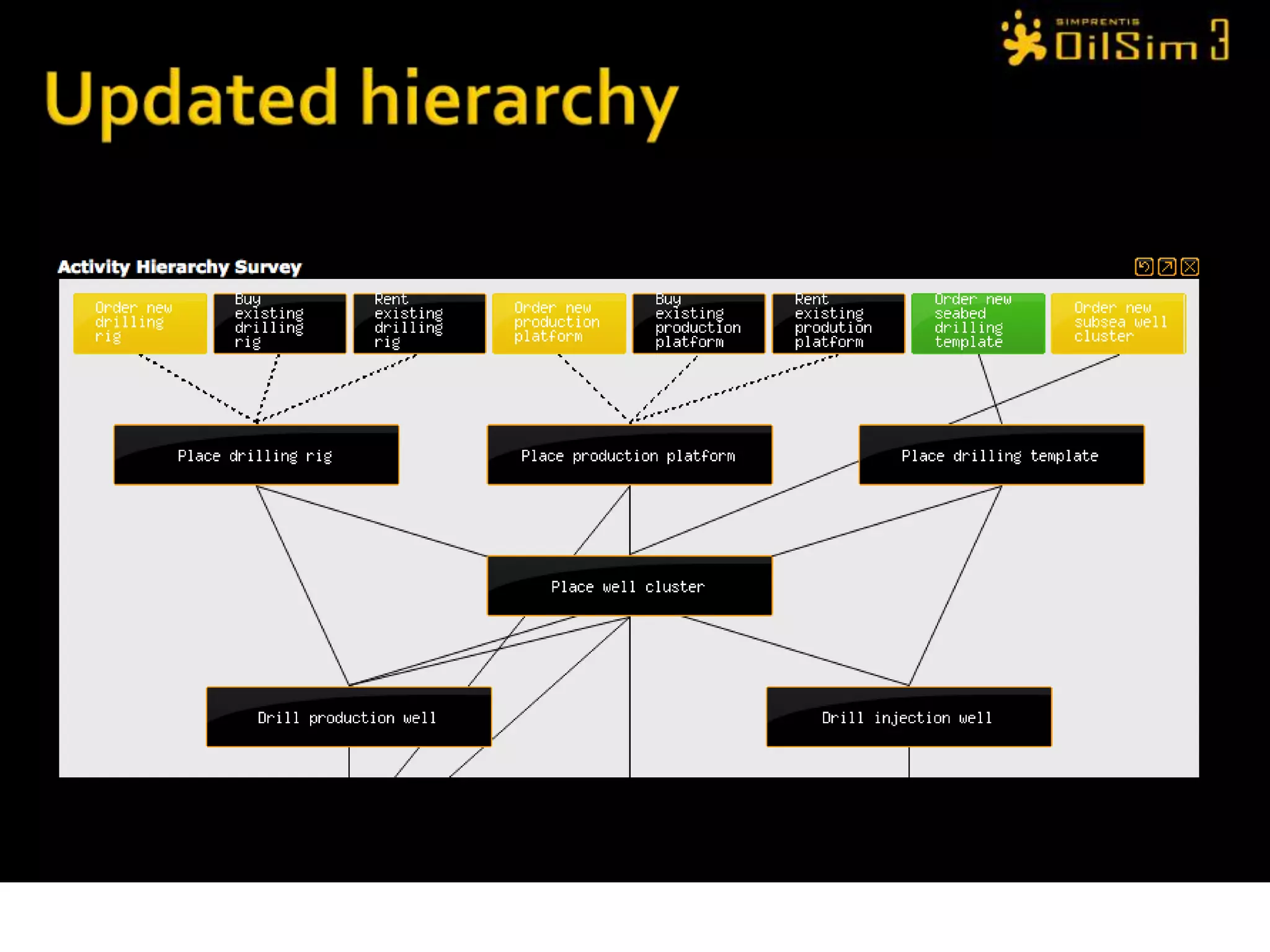
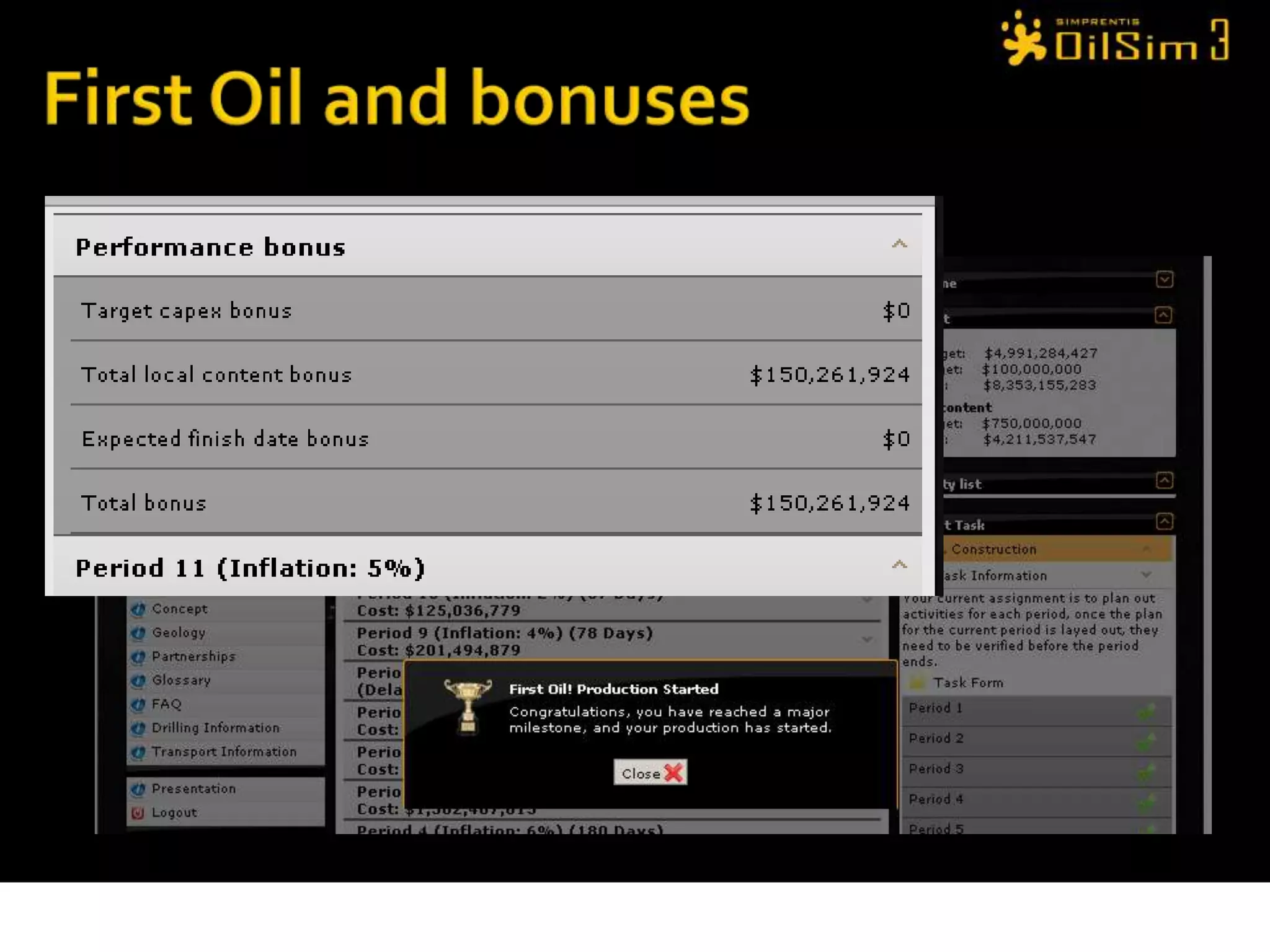
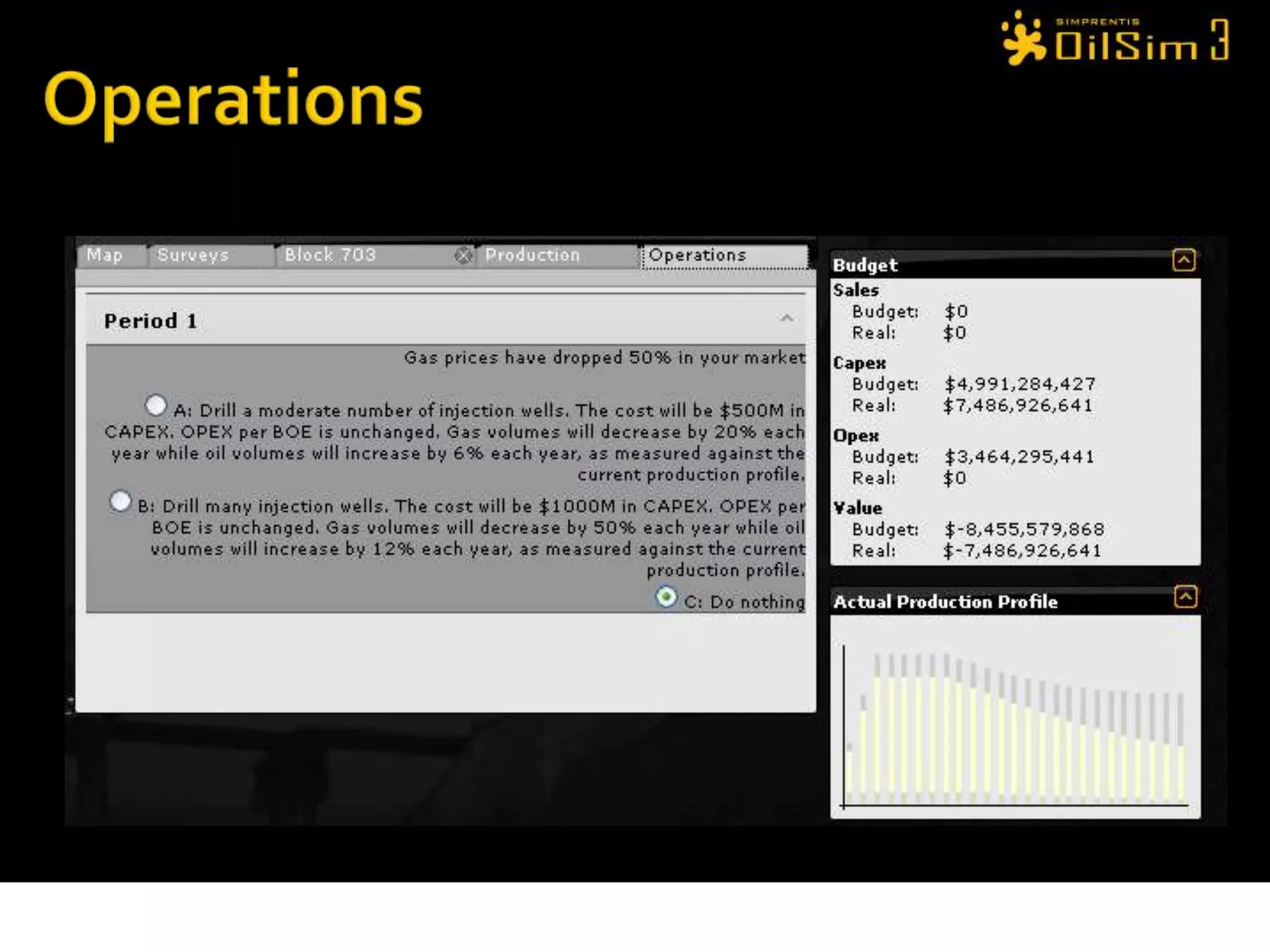
This document provides an overview of OilSim, a simulation for the oil and gas upstream value chain. It describes the learning objectives, challenges, and tasks involved in exploring for and developing oil and gas resources. The tasks include identifying sedimentary basins from surveys, bidding on exploration licenses, acquiring seismic data, drilling exploration and appraisal wells to evaluate discoveries, and developing field production plans to maximize resource recovery. The goal is to make economically viable decisions that consider costs, risks, environmental factors, and partnerships with other teams.