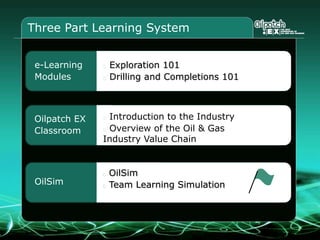
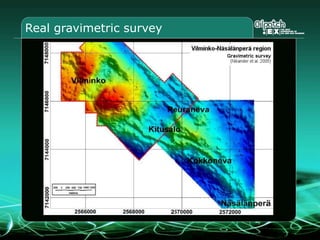
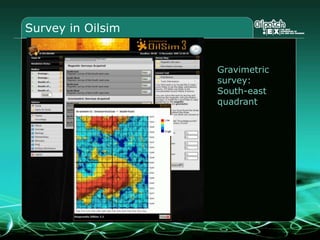
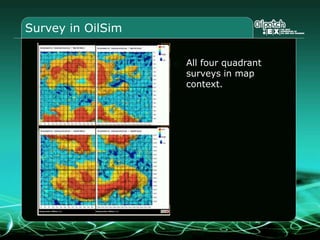
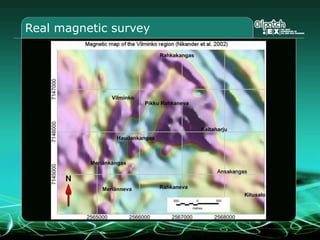
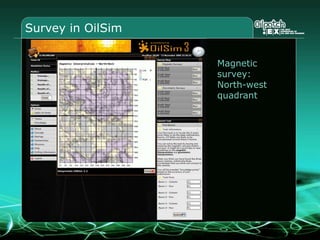
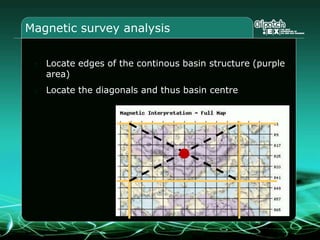
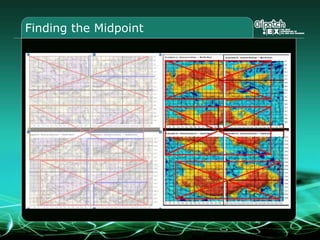
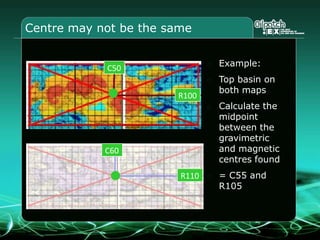
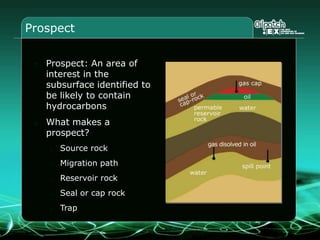
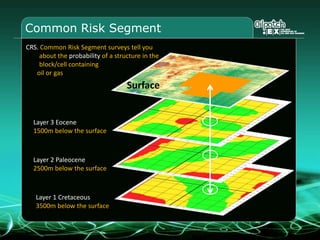
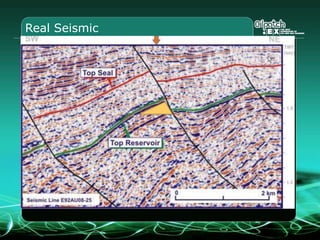
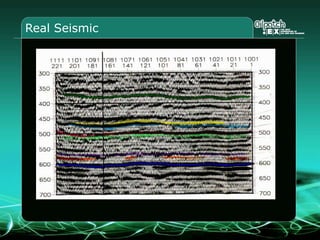
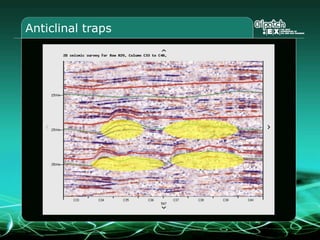
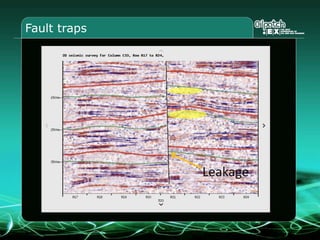
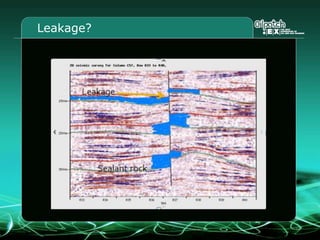
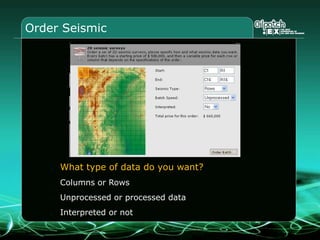
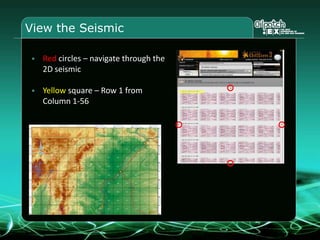
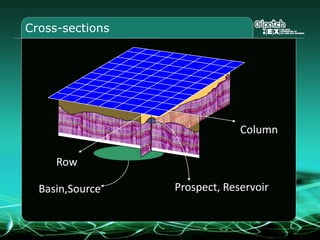
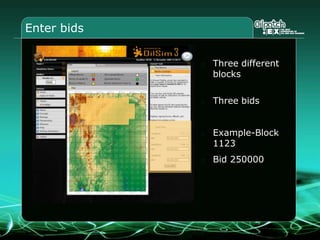
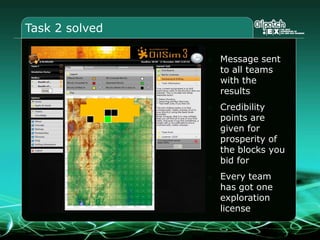
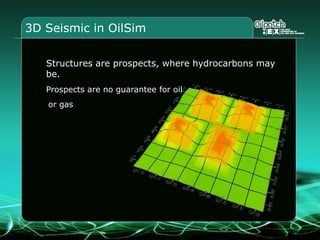
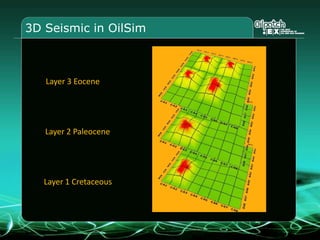
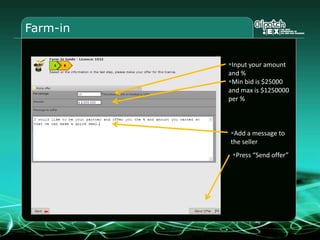
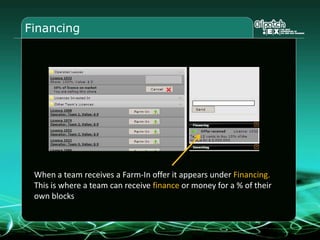
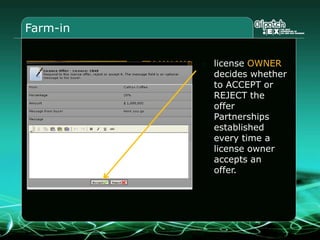
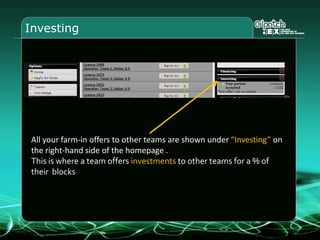
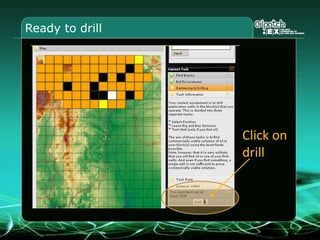
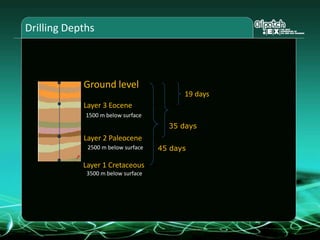
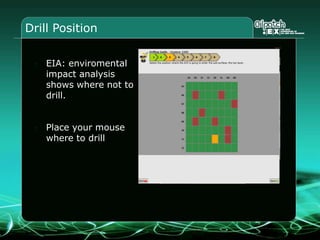
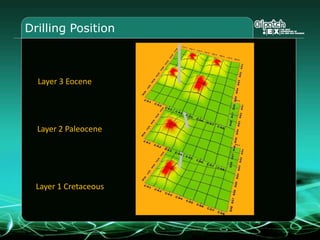
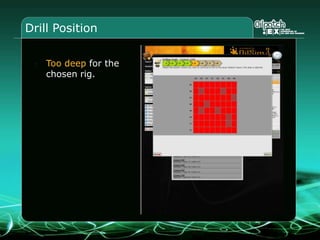
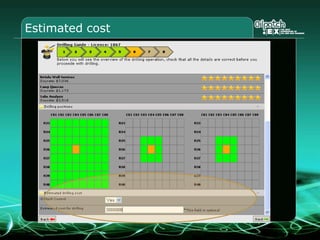
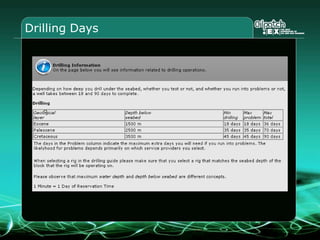
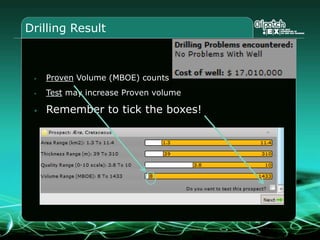
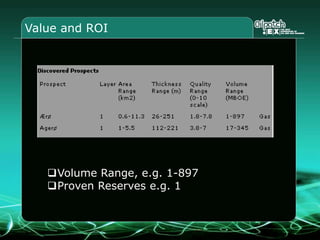
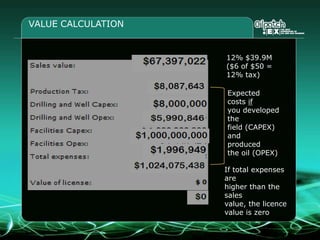
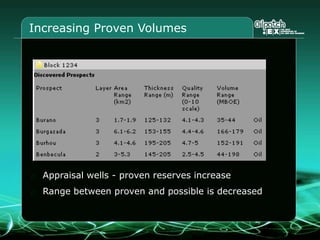
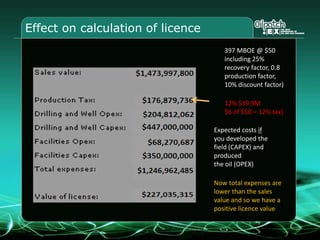
This document provides an overview and agenda for a three-part learning simulation about the oil and gas industry called OilSim. The simulation uses a team-based challenge where participants take on the role of an exploration team tasked with finding and drilling for new oil reserves. It outlines the objectives to learn about exploration, drilling, partnerships, licensing rounds, and applying business strategies. The agenda includes challenges to find sedimentary basins, identify promising blocks, form partnerships, conduct drilling, and participate in additional licensing rounds. It describes the evaluation of teams based on return on investment and credibility points awarded for correct decisions.