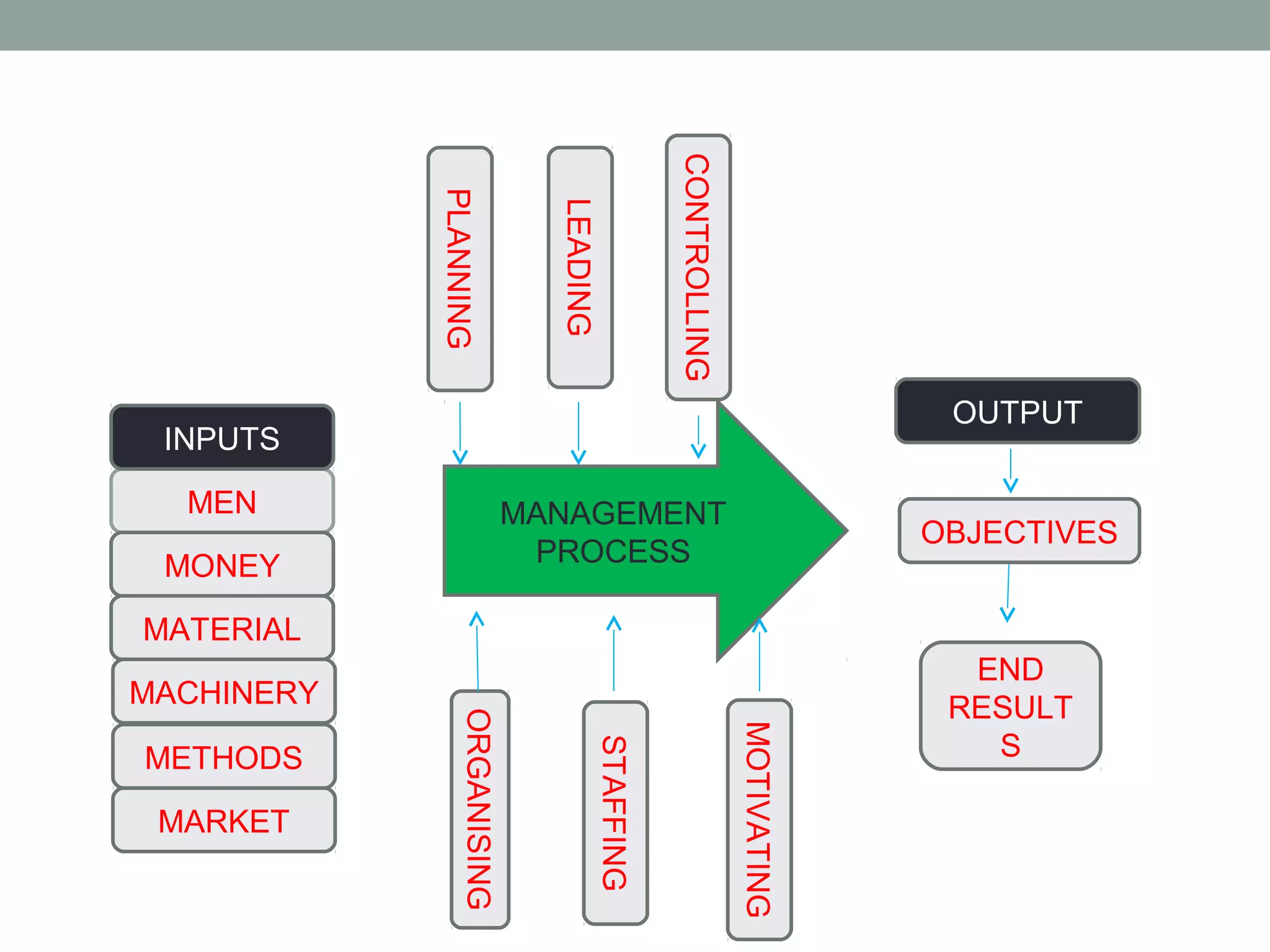
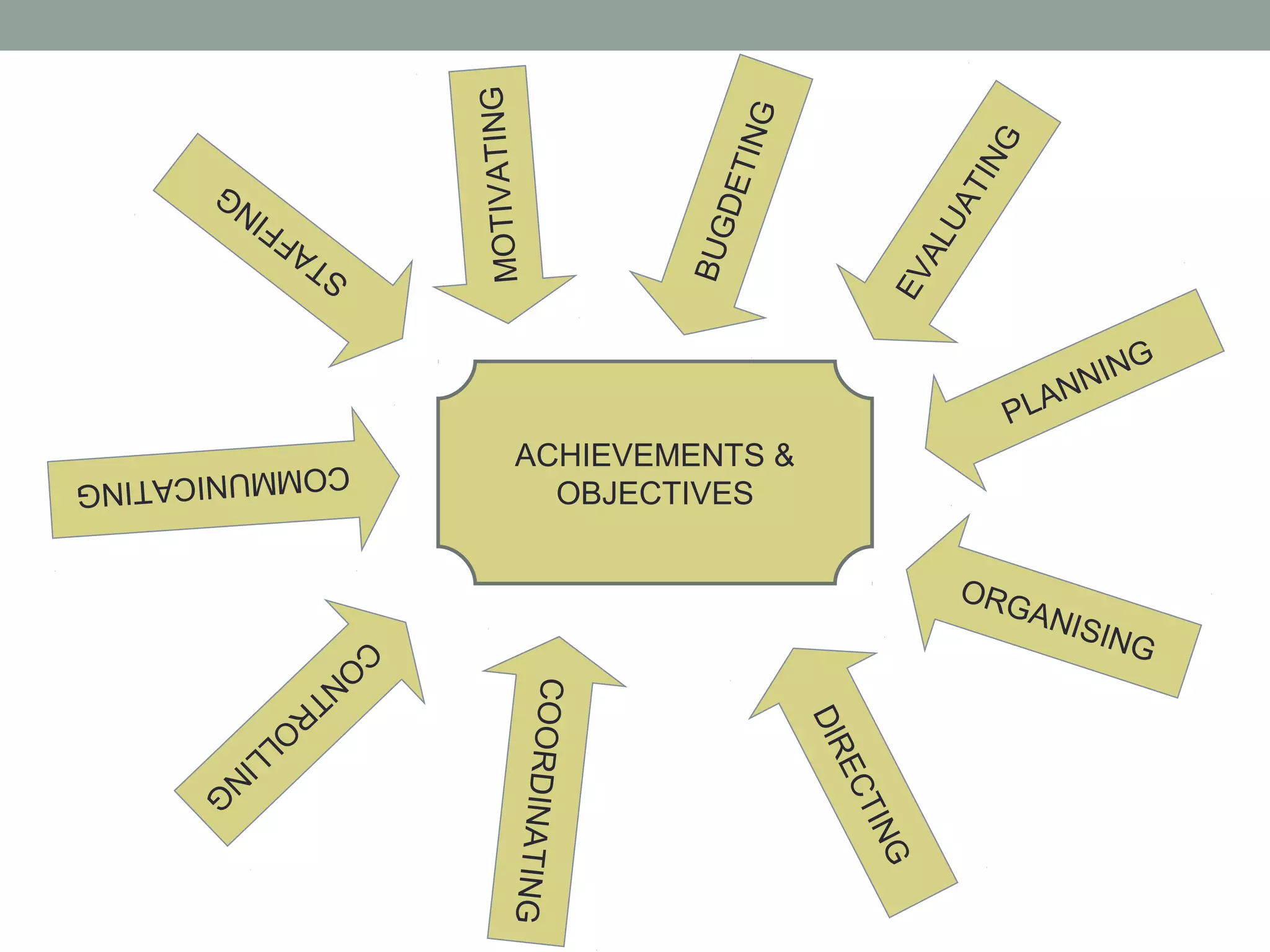
The document discusses office management and defines key related terms. It outlines the elements of management as planning, organizing, directing, controlling, motivating, coordinating, staffing, and communicating. Management involves handling human resources and physical/material resources. The summary also mentions the importance of management in getting maximum benefits with minimum effort and optimal utilization of resources.