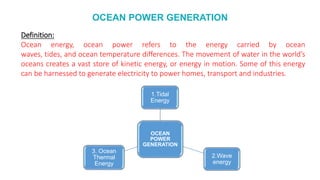
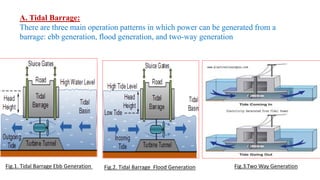
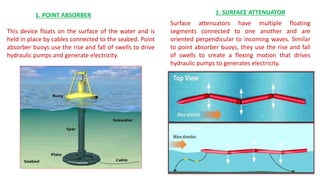
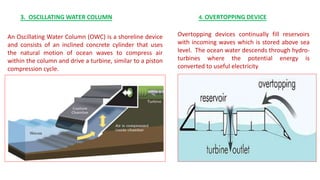
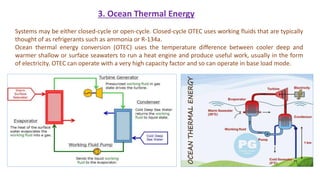
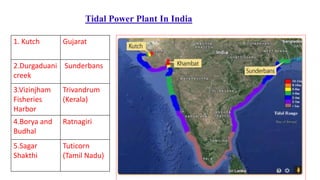
The document discusses ocean power generation as a form of renewable energy derived from ocean waves, tides, and temperature differences. It details different types of non-conventional energy sources, specifically focusing on tidal and wave energy generation methods, as well as ocean thermal energy conversion. Additionally, it outlines the advantages and disadvantages of tidal energy and emphasizes its potential for predictable and sustainable power generation.