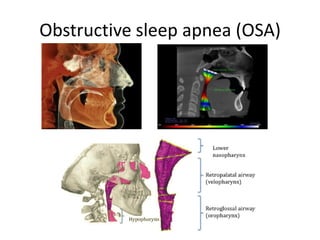
1. Enlarged adenoids are a major contributing factor to upper airway obstruction in children and can block nasal breathing, forcing mouth breathing.
2. Mouth breathing can lead to skeletal and dental abnormalities such as a narrow maxilla and mandible, increased overjet, and dental crowding.
3. Both adenoid growth and facial growth occur simultaneously during childhood, and adenoid obstruction of the airway can restrict normal facial development.