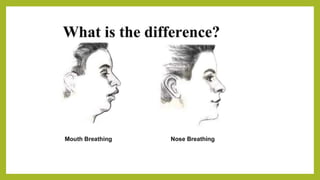
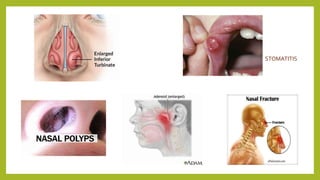
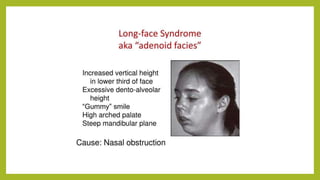
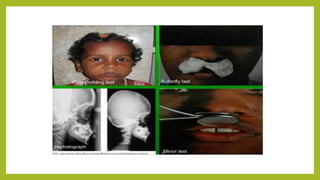
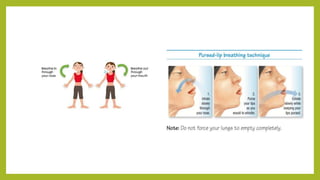
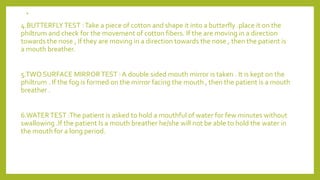
This document discusses mouth breathing habits. It defines mouth breathing and classifies it as anatomic, obstructive, or habitual. Common causes of mouth breathing include developmental anomalies, infections, tumors, and enlarged adenoids. Clinical features include increased facial height and retrognathic jaws. Diagnosis involves tests like mirror tests and asking patients to hold water in their mouth. Treatment focuses on eliminating causes, intercepting habits, exercises, and using oral screens during sleep.