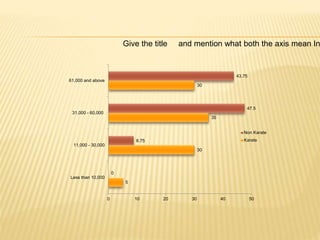
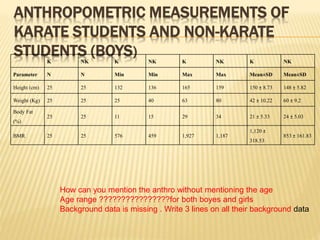
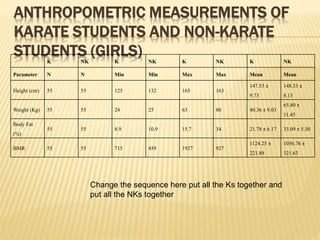
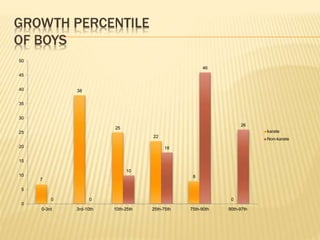
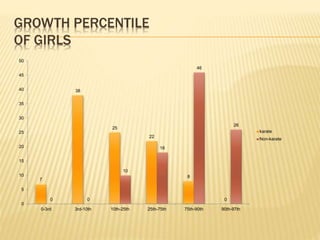
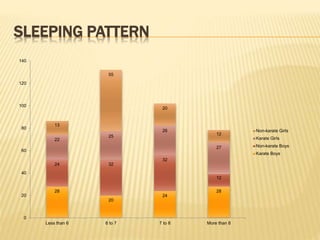
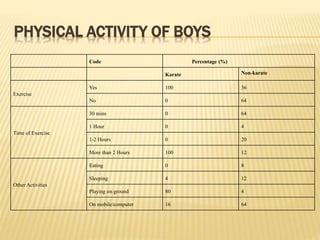
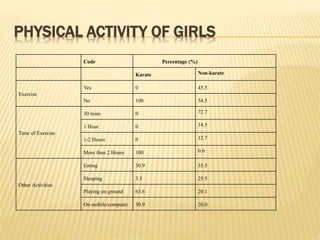
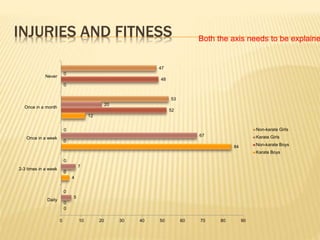
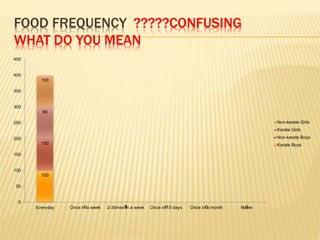
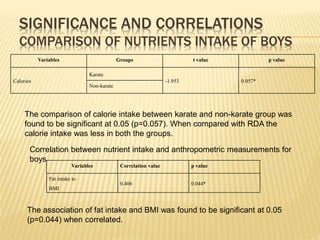
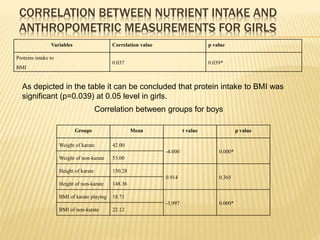
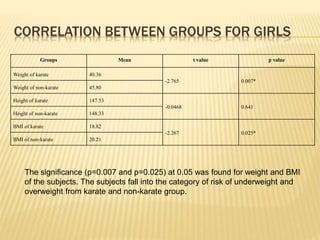
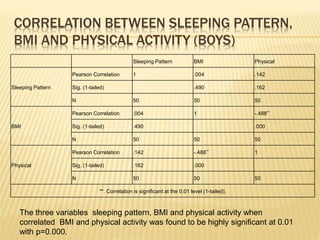
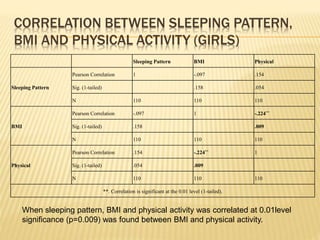
The study aimed to assess and compare the nutritional status, body composition, physical activity levels, and injury rates between karate students and non-karate students aged 13-17 years. It found that karate students generally had lower socioeconomic status and were underweight, while non-karate students had higher socioeconomic status and were overweight. Both groups had inadequate nutrient intakes compared to RDA values, but karate students' intake was more deficient due to their financial constraints. Significant correlations were also found between physical activity and BMI for both groups, as well as between fat intake and BMI for boys and protein intake and BMI for girls. The study highlights the vulnerability of karate students to nutritional deficiencies and injuries due to vigorous