Nutrients
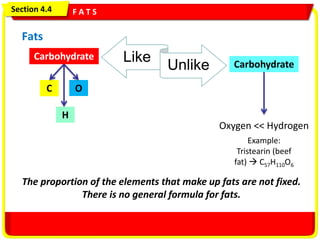
- 1. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 1 of 35 Fats Section 4.4 F A T S vvv Like Unlike C H O Carbohydrate Carbohydrate Oxygen << Hydrogen Example: Tristearin (beef fat) C57H110O6 The proportion of the elements that make up fats are not fixed. There is no general formula for fats.
- 2. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 2 of 35 Fats •Fats are commonly used as a store of energy, esp. by animals. •Fats can be broken down into fatty acids and glycerol by hydrolysis. •Enzyme is involved. Section 4.4 F A T S vvvvvv Enzyme
- 3. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 3 of 35 Sources of Fats Section 4.4 F A T S vvvvvv
- 4. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 4 of 35 •Soluble in organic solvent such as chloroform and ethanol. •Examples: • Fats • Waxes • Steroids Lipids Section 4.4 F A T S vvv
- 5. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 5 of 35 Saturated VS Unsaturated Fats Section 4.4 F A T S vvv
- 6. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 6 of 35 •Too much polysaturated fat and cholesterol in your diet can lead to coronary heart disease. •Unsaturated fats are thought to reduce the cholesterol level in the blood. Hence, unsaturated fats should replace animal fats in the diet as often as possible. •Unsaturated fats may be converted into trans fats during food production. •Trans fats are produced by cooking at very high heat. •Trans fats are bad Increase coronary heart disease Section 4.4 F A T S vvv Saturated VS Unsaturated Fats
- 7. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 7 of 35 Fats + Ethanol & Water a cloudy white emulsion Section 4.4 F A T S vvv How Can We Identify Fats?
- 8. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 8 of 35 •A source and store of energy •An isulating material that prevents excessive heat loss. •Eg: seals have blubber beneath the skin to reduce loss of body heat. •A solvent for fat-soluble vitamins and many other vital substances. •Eg: hormones. •An essential part of protoplasm, especially in cell membranes. •A way to reduce water loss from the skin surface. Sweating glands produce oily substance reduces the rate of evaporation of water. Section 4.4 F A T S vvv What Are the Function of Fats?
- 9. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 9 of 35 •Organic molecules made up of the elements Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen. Section 4.5 P R O T E I N S vvv Proteins C H O N PROTEIN S •Protein are always present in protoplasm. •Their molecules are the largest and most complicated of all the food substances
- 10. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 10 of 35 •Simpler compounds: amino acids. •Amino acids are made up of: Amino group (─NH2) Acidic group (─COOH) Side chain (R) •R: sulfur, acidic groups, amino groups, and/or hydroxyl groups (─OH) in place of one or more hydrogen atoms. vvv Section 4.5 P R O T E I N S Amino Acids Are the Building Blocks of Proteins
- 11. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 11 of 35 Section 4.5 P R O T E I N S vvv 20 Different Kinds of Amino Acids •They differ because of their different R groups.
- 12. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 12 of 35 Section 4.5 P R O T E I N S vvv Polypeptides •Condensation reaction: •Peptide bond is formed. 1 amino acid + 1 amino acid polypeptide
- 13. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 13 of 35 Section 4.5 P R O T E I N S vvv Polypeptides Amino acids Polypeptides Proteins
- 14. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 14 of 35 Section 4.5 P R O T E I N S vvv Why Must Proteins be Broken Down? •Enzymes take place! •During digestion. •Protein is hydrolysed into short polypeptides, which are in turn hydrolysed into amino acids. Protein Polypeptides amino acids Enzyme Enzyme
- 15. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 15 of 35 Section 4.5 P R O T E I N S vvv Different Squence of Amino Acids •There are only about 20 different naturally occurring amino acids. •However, each protein molecule has hundreds, or even thousands, of them joined together in a unique sequence. •This gives each protein its own individual properties.
- 16. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 16 of 35 Section 4.5 P R O T E I N S vvv •The long chains of amino acids fold to give each type of protein molecule a specific shape. Proteins act as: Structural components of tissues (such as muscles) Hormones (such as insulin) Antibodies (part of the body's immune system) Biological catalysts (enzymes) •The particular shape that a protein molecule has allows other molecules to fit into it. This is particularly important for antibodies and enzymes. Different Proteins
- 17. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 17 of 35 Section 4.5 P R O T E I N S vvv Different Squence of Amino Acids •Proteins are made from long chains of smaller molecules called amino acids. •These long chains are folded into particular shapes. •This is important in relation to how antibodies and enzymes work. •Enzymes are biological catalysts. •There are optimum temperatures and pH values at which their activity is greatest. •Enzymes are also proteins. •If the shape of an enzyme changes, it may no longer work (it is said to have been 'denatured').
- 18. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 18 of 35 Section 4.5 P R O T E I N S vvv •Enzymes are biological catalysts - substances that increase the rate of chemical reactions without being used up. •Enzymes are proteins folded into complex shapes that allow smaller molecules to fit into them. The place where these substrate molecules fit is called the active site. •If the shape of the enzyme changes, its active site may no longer work. We say the enzyme has been 'denatured'. How Enzymes Work
- 19. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 19 of 35 •Biuret solution: blue solution made up of sodium hydroxide and copper (II) sulfate. •Violet (deep purple) occurs when proteins are present. Section 4.5 P R O T E I N S vvv How Can We Identify Proteins?
- 20. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 20 of 35 Section 4.5 P R O T E I N S vvv Where Are Proteins Found?
- 21. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 21 of 35 •Synthesis of new protoplasm, for growth and repair of worn-out body cells •Synthesis of enzymes and some hormones •Formation of antibodies to combat diseases.s Section 4.5 P R O T E I N S vvv Where Are the Functions of Proteins? Deficiency? •Need: 50─100 g protein/day •Kwashiorkor: Swollen stomachs Skin cracks and becomes scaly
- 22. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 22 of 35 Section 4.6 D N A vvv Deoxyribonucleic Acid •Almost all the cells in our body contain DNA inside their nuclei. •±2 m of DNA can be found in each cell nucleus. •Carries genetic information.
- 23. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 23 of 35 Section 4.6 D N A vvv Deoxyribonucleic Acid •A small segment of DNA carries a gene that stores information used to make a single polypeptide. •Polypeptides are used to make proteins proteins are responsible for determining the characteristics of an organism.
- 24. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 24 of 35 Section 4.6 D N A vvv Deoxyribonucleic Acid •Each DNA molecule contists of two strands twisted around each other (double helix). •A helix: coiled structure like a corkscrew or spring.
- 25. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 25 of 35 Section 4.6 D N A vvv Basic Units of Deoxyribonucleic Acid •Each nucleotide is made up of: A sugar A phospate group A nitrogen-containing base
- 26. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 26 of 35 Section 4.6 D N A vvv A Nitrogen-Containing Base • Adenine (A) • Cytosine (C) • Guanine (G) • Thymine (T) •Complementary bases are joined by hydrogen bonds.
- 27. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 27 of 35 Section 4.6 D N A vvv Types of Nucleotides
- 28. Section 8.1 Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Slide 28 of 35 Section 4.6 D N A vvv Deoxyribonucleic Acid •Nucleotides can be joined together to form long chains called polynucleotides. •Each gene is made up of a sequence of nucleotides. •The sequence of nucleotides (bases) can vary. •This results in many different genes. •The DNA molecule is made up of two anti-parallel polynucleotide chains. •Anti-parallel: because the two chains run in opposite directions. •The bases of one chain are bonded to those of the opposite chain according to the rule of base pairing.
