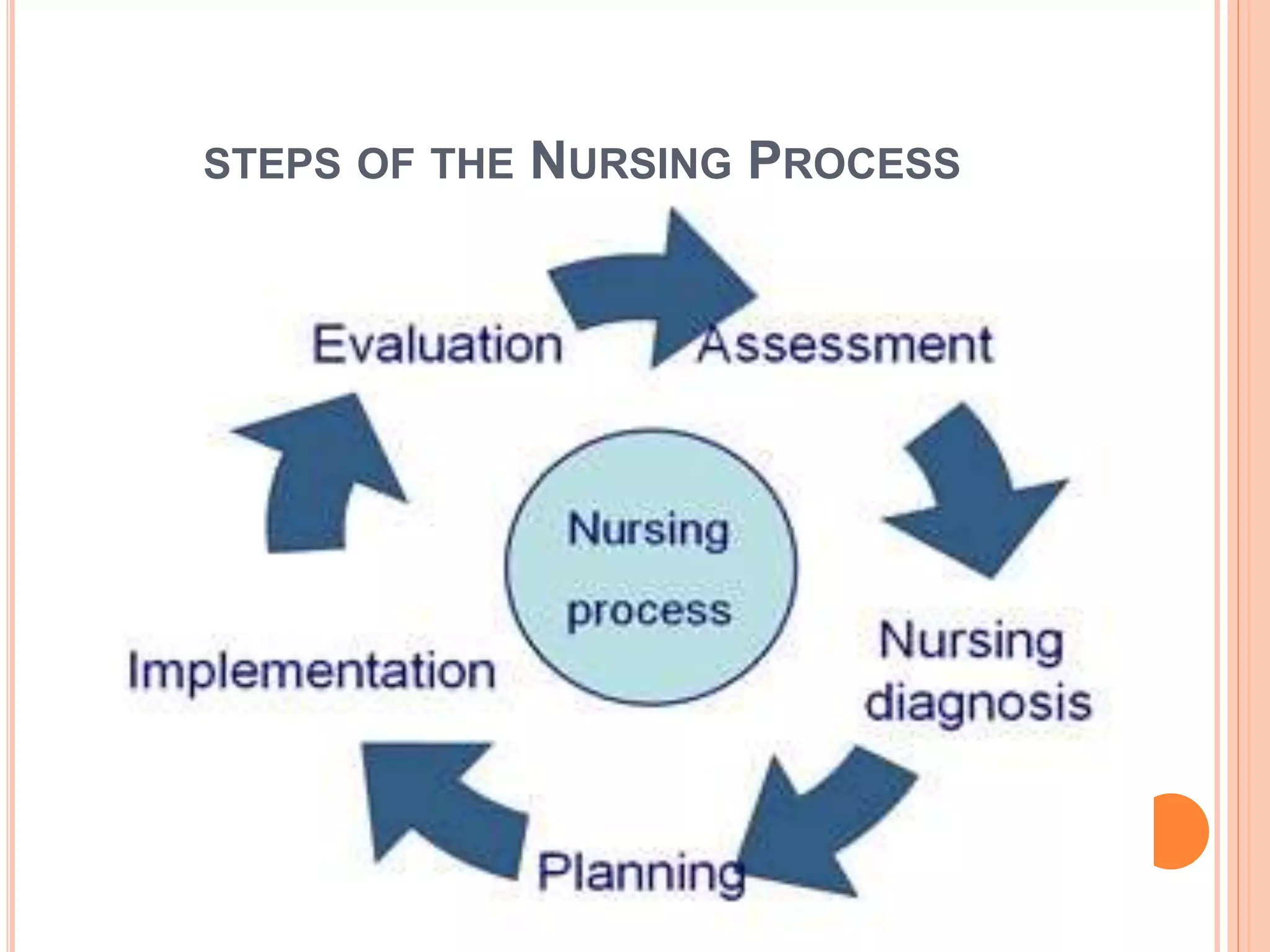
The nursing process provides a framework for delivering nursing care. It involves assessment, nursing diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. Assessment involves collecting subjective and objective data about a patient's health status and history through various methods like observation, interviews, physical exams, and record reviews. This collected data is then organized, validated, and recorded to identify nursing diagnoses and develop a care plan to address any issues. The nursing process aims to improve the quality of patient care through a systematic, individualized approach.