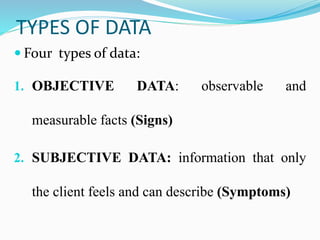
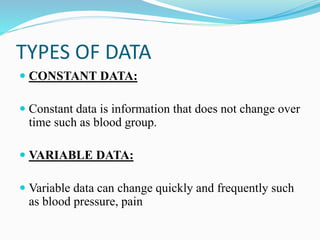
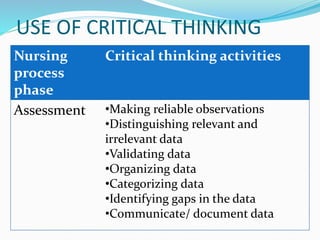
The document outlines the nursing process, defining it as a systematic method for planning and providing individualized nursing care. It covers the components, purposes, and methods of nursing assessment, emphasizing the importance of differentiating between subjective and objective data collection. Key aspects include the cyclical nature of the process, client-centered decision making, and collaboration among healthcare professionals.