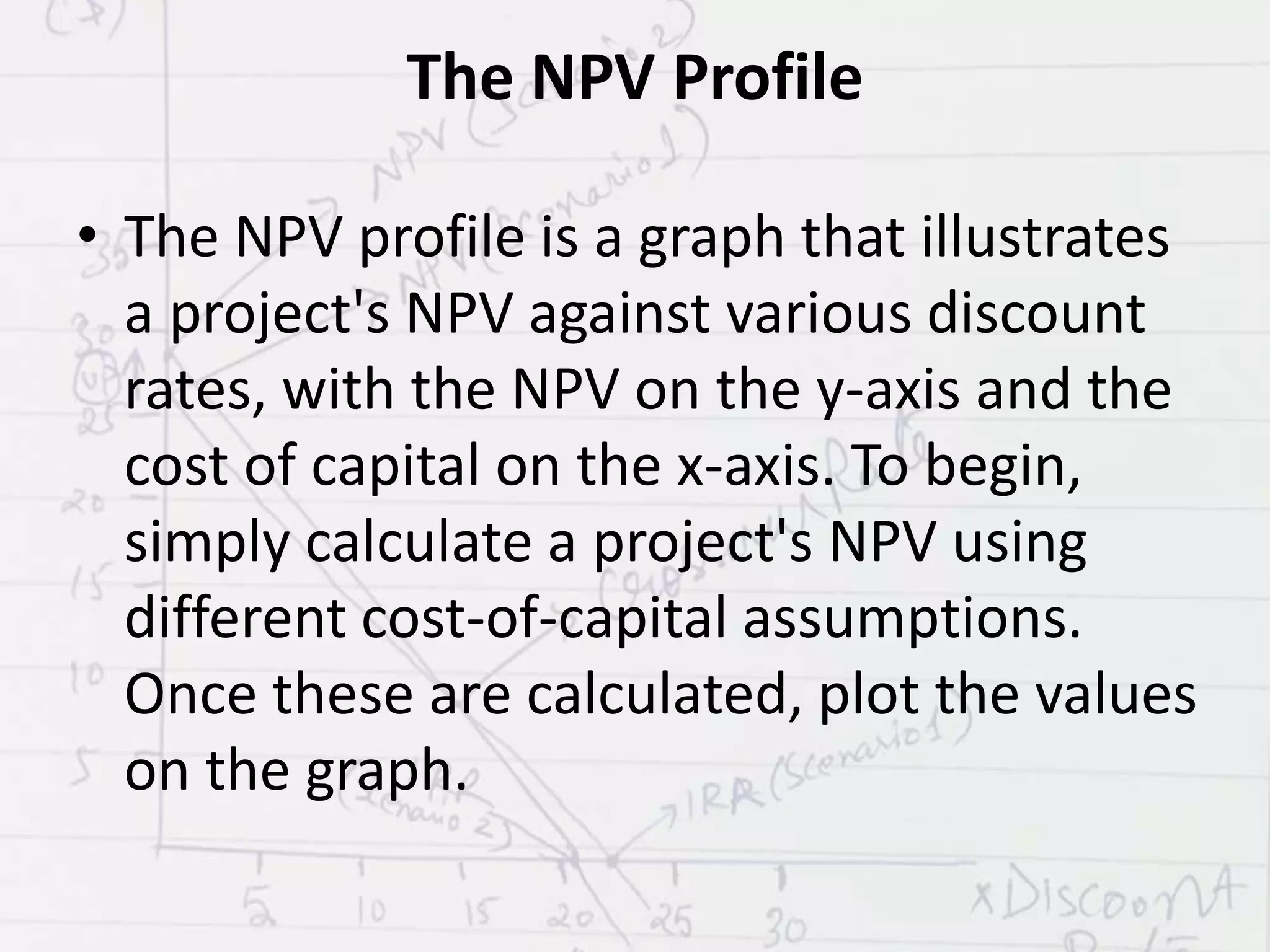
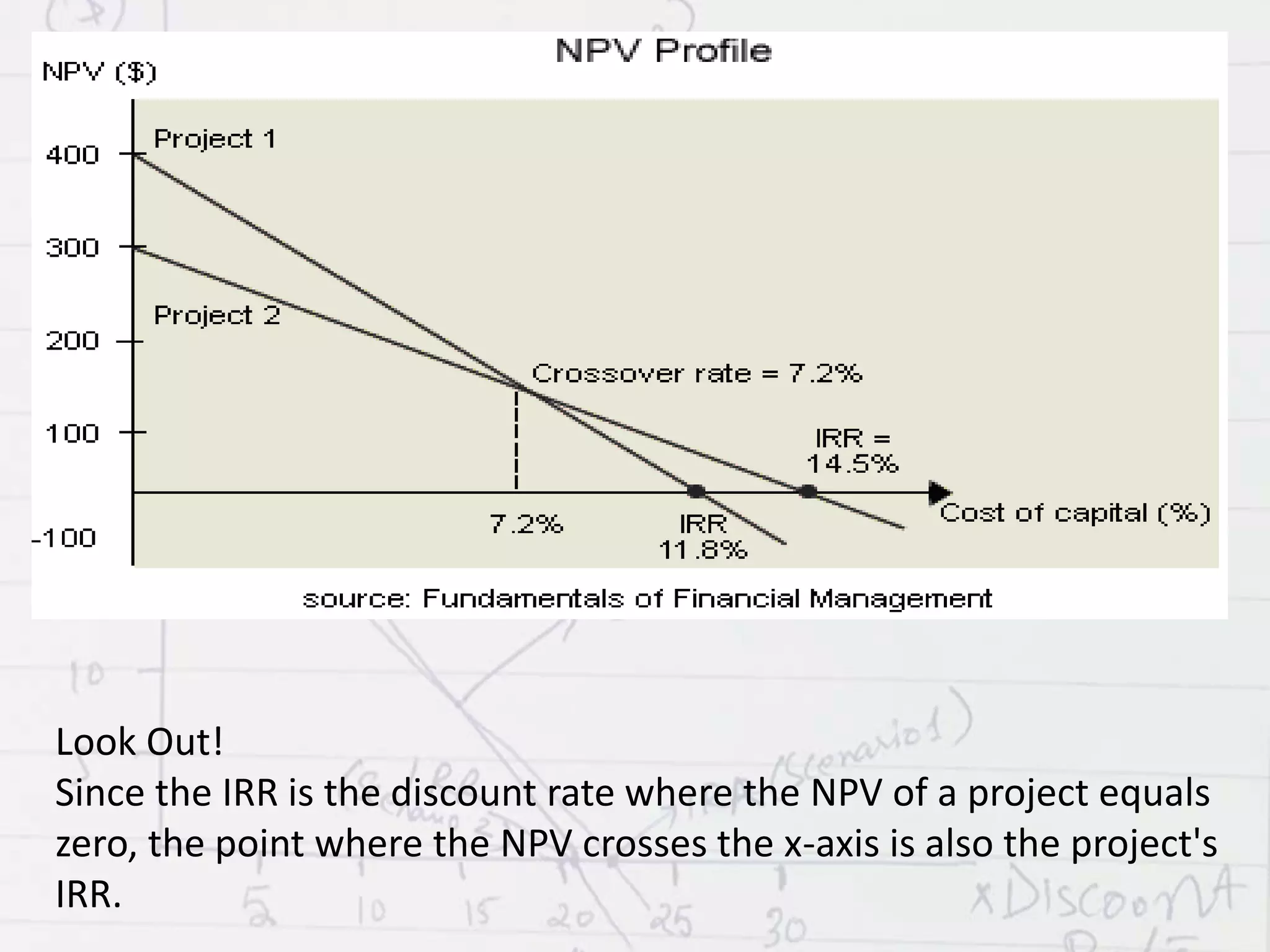
The NPV profile is a graph that plots a project's NPV on the y-axis against various discount rates on the x-axis. Higher discount rates mean cash flows occurring sooner are more influential to NPV. The NPV profile generally shows an inverse relationship between discount rate and NPV. The discount rate where NPV equals 0 is called the internal rate of return (IRR). NPV and IRR are methods to evaluate projects, with NPV measuring net dollars and IRR measuring return as a percentage. IRR is the discount rate that makes NPV equal 0.