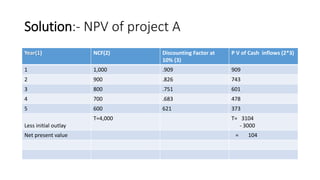
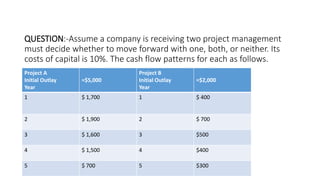
This document provides an overview of net present value (NPV) and internal rate of return (IRR) concepts and calculations for corporate finance. It defines NPV as the difference between the present value of cash inflows and outflows over time. NPV is used to analyze investment profitability by discounting future cash flows. IRR is the discount rate that makes the NPV equal to zero, representing the expected annual rate of return. The document provides examples of calculating NPV and IRR for projects and compares the results to the cost of capital to determine which projects to accept.