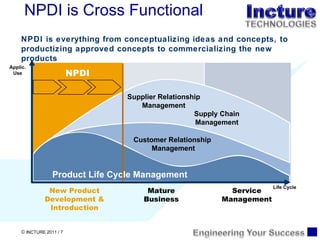
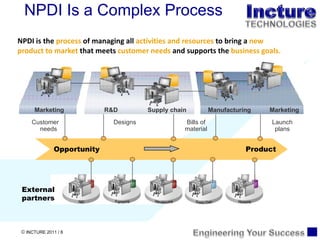
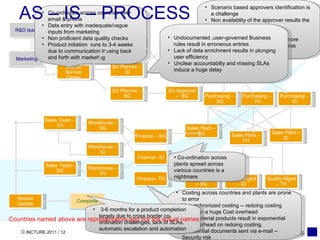
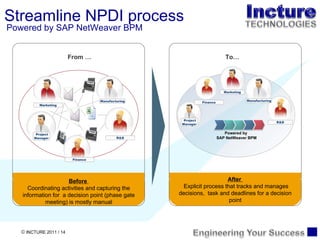
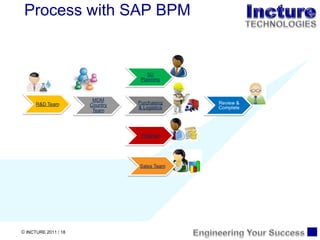
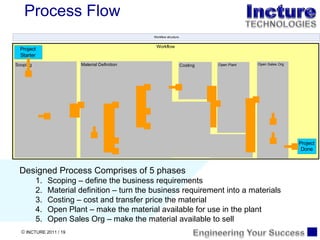
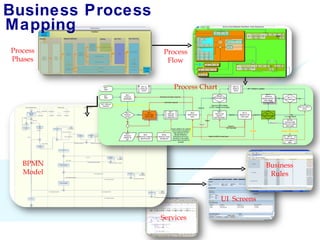
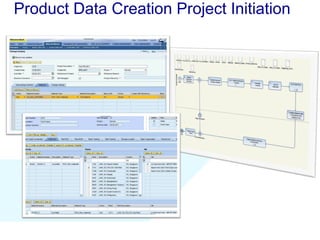
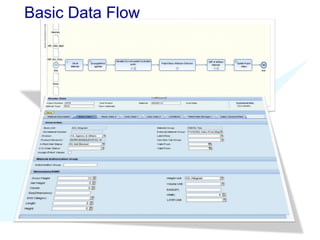
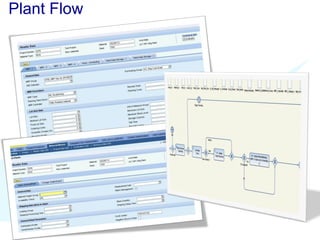
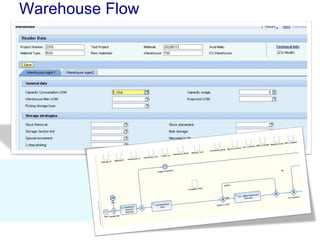
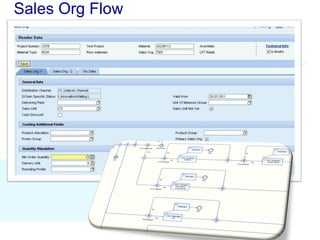
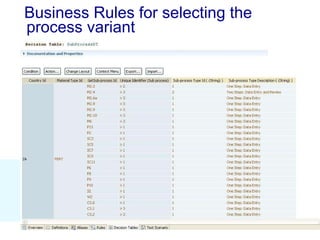
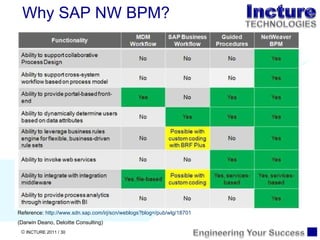
The document discusses using SAP BPM to streamline new product introduction processes. It describes challenges with current manual processes that involve coordination across multiple countries and entities. SAP BPM can help by modeling the new product process, automatically assigning tasks, integrating with SAP systems, and providing visibility and control over the end-to-end process. Key benefits of using SAP BPM include reduced cycle times, increased efficiency, improved data quality, and greater transparency.

![About the Presenter SOA-BPM Solution Architect Over 8 years of SAP solutions experience in PS, MM, EAM etc. Co-inventor of multiple patents in Enterprise SOA Worked on several BPM projects, including areas such as Claims Processing, Materials Mater Data and New Product Introduction Worked at SAP Labs in the past wherein was responsible for PIC Governance and Enterprise Services Repository Managed and Architected three large projects on Enterprise SOA Abhinava Pratap Singh SOA-BPM Solution Architect Incture Technologies Pvt. Ltd. [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/npiwithbpmwebinar-110906013634-phpapp01/85/Npi-with-bpm-webinar-2-320.jpg)