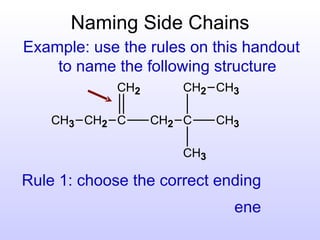
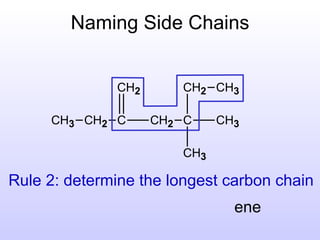
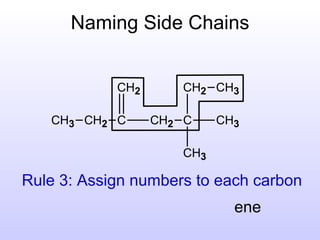
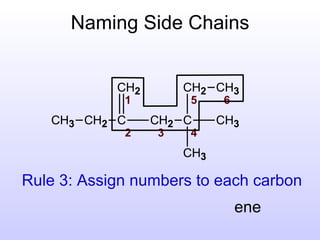
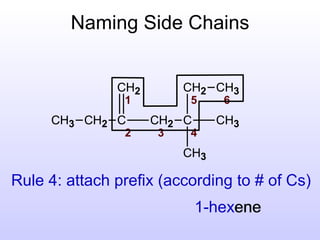
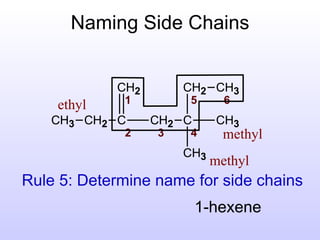
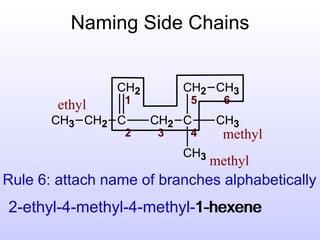
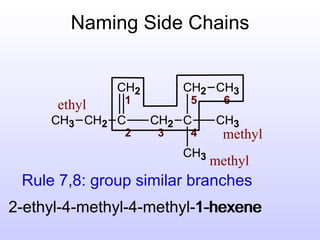
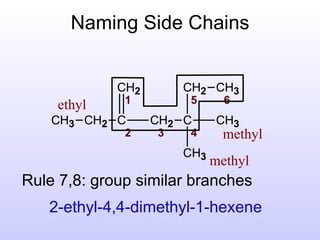
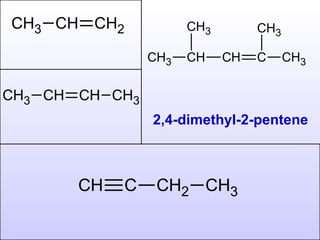
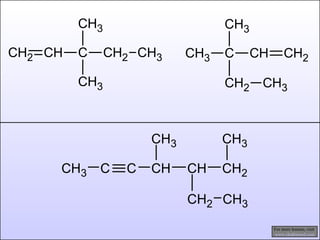
The document discusses the rules for naming hydrocarbons according to IUPAC nomenclature. It explains that the root or parent chain is the longest chain that can include any double or triple bonds. Side chains are called alkyl groups like methyl or ethyl. Numbers are assigned to the carbons in the parent chain with double or triple bonded carbons numbered first consecutively. The name of each side chain is determined and attached alphabetically to the parent name along with its carbon position. Identical side chains are grouped using prefixes. An example demonstrates applying the rules to name a hydrocarbon with multiple side chains.