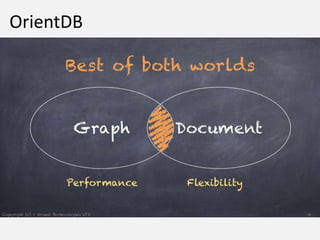
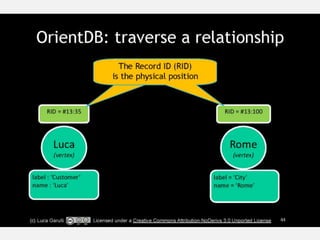
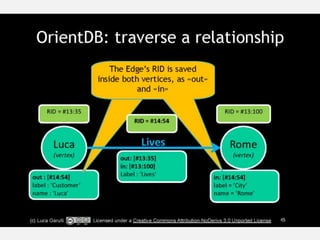
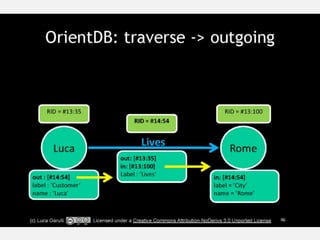
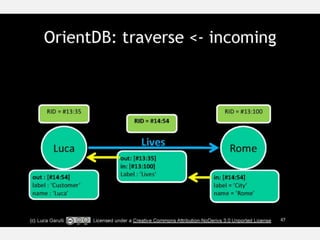
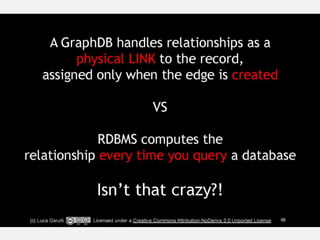
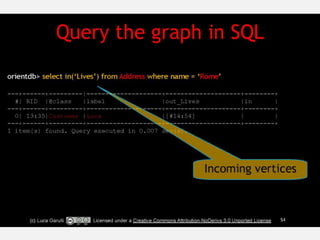
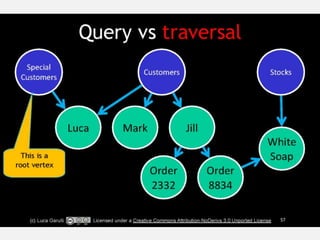
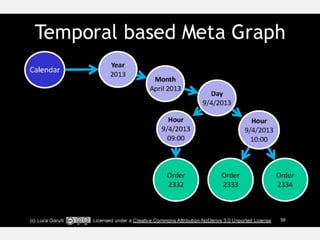
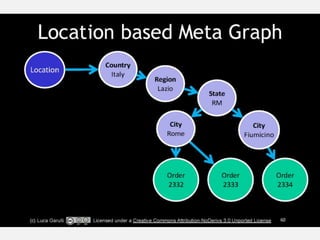
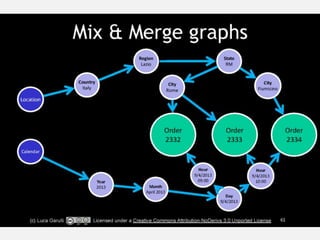
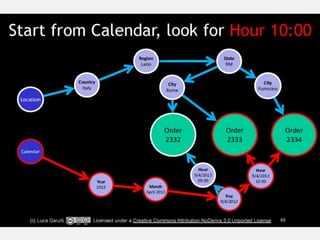
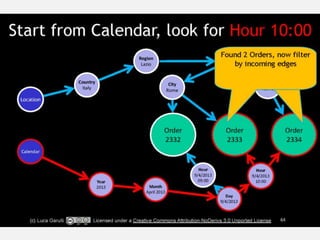
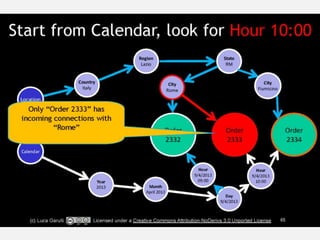
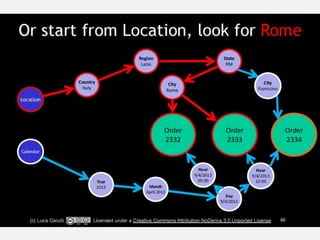
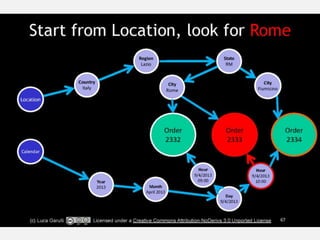
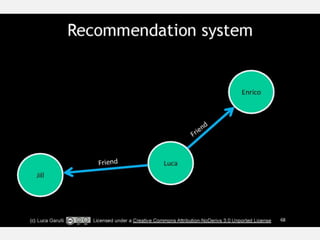
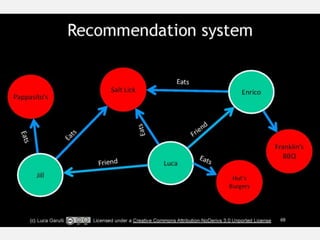
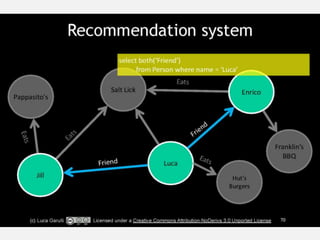
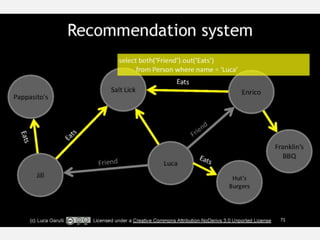
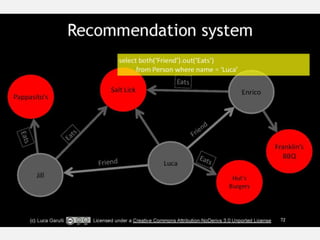
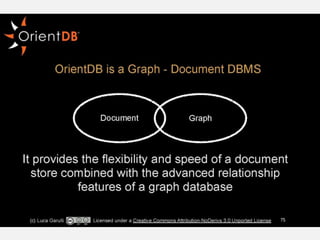
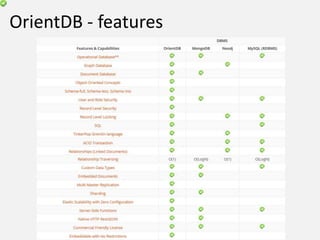
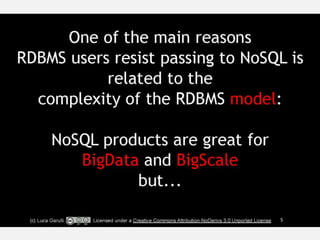
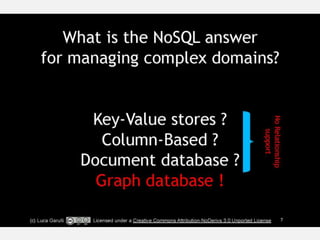
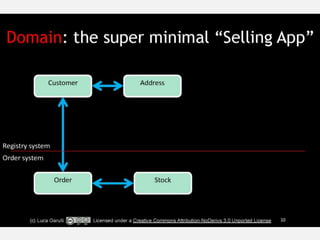
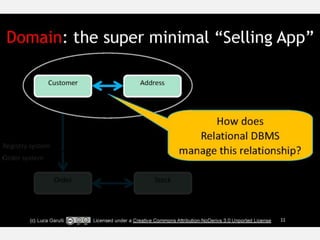
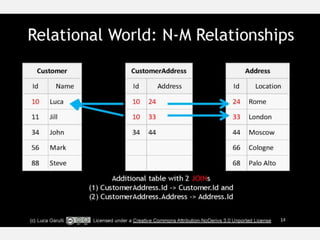
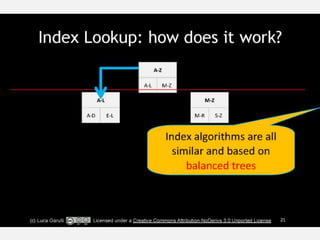
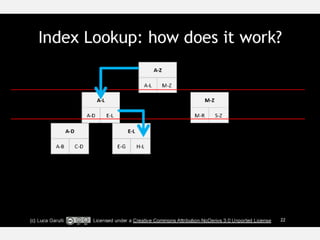
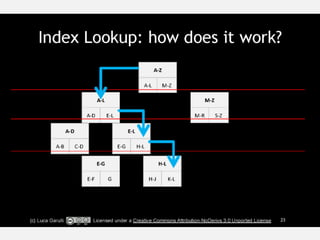
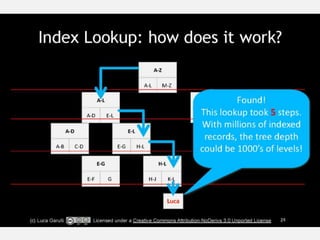
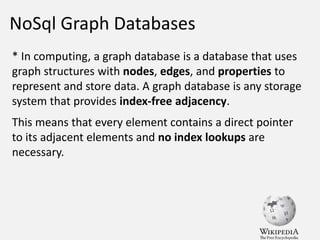
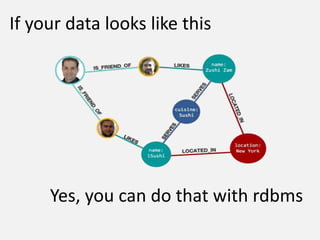
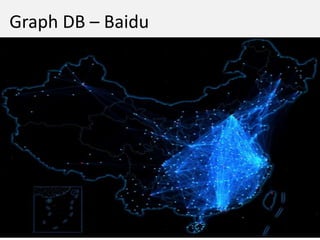
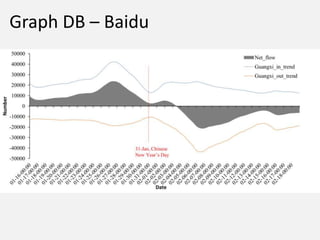
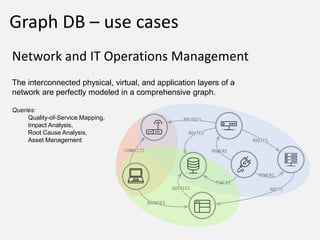
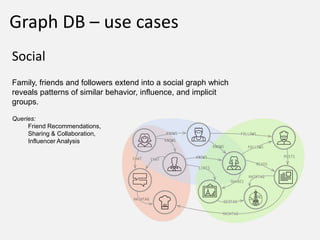
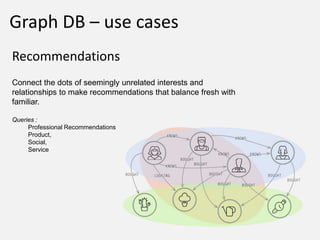
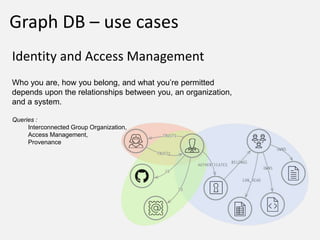
The document discusses NoSQL graph databases, highlighting their use in big data solutions and the advantages of representing data as nodes, edges, and relationships for efficient storage and retrieval. It covers various use cases including social networks, recommendations, and identity management, illustrating the interconnectedness of data in practical scenarios. OrientDB is presented as a leading document-based NoSQL graph database that simplifies relationship management through direct connections between records.


























![GraphDB definition explained
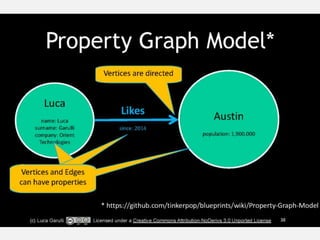
• DATA = NODES
• (NODES) are Fully Featured JSON Objects, Indexable to ensure uniqueness
• These are the population of your Graph Nation
• If it is an immutable thing, if you can anthropomorphize it, it should be a
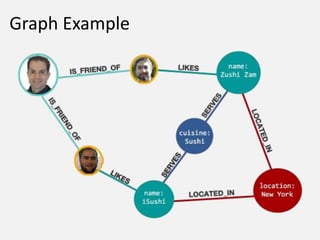
(NODE)(Computer, Email, Hash, Service Ticket, IDS Rule, Domain, Threat Actor)
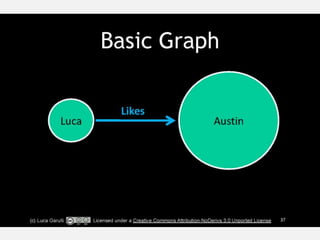
• JOINS = EDGES
• Every (NODE) must connect to at least one more… as must we all, else why exist?
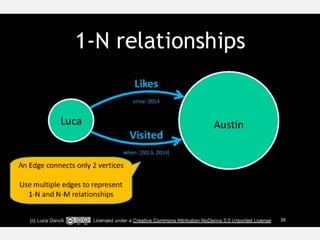
• Individual –EDGES-> are directional: (Chris)-->(You) or (You)-->(Chris)
• EDGES + CONTEXT = RELATIONSHIPS
• -[:RELATIONSHIPS]-> are Fully Featured JSON Objects!
• -[:RELATIONSHIPS]-> give context to the connections between (NODES)
• If it is an action or you can’t imagine holding it, it should be a -[:RELATIONSHIP]->
• (Chris) -[:TALKS]->(You) , but are (You)-[:LISTEN]->(Chris) ?
RELATIONSHIPS + NODES =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphdb-nosql-eugene-hanikblum-141119093955-conversion-gate01/85/NoSQL-Graph-Databases-Why-When-and-Where-55-320.jpg)