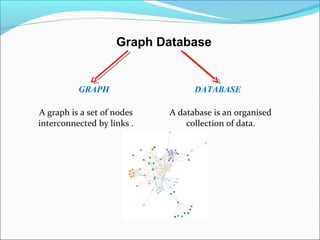
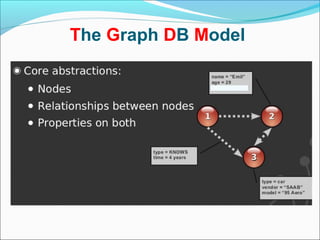
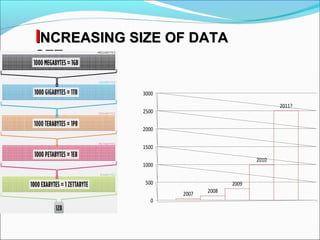
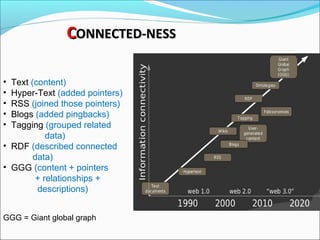
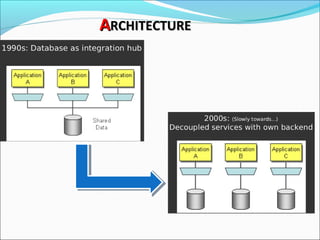
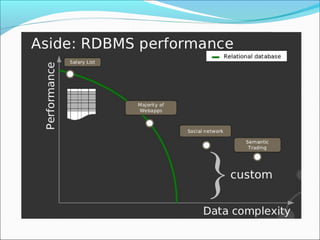
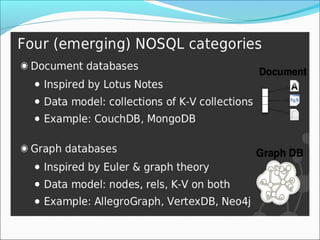
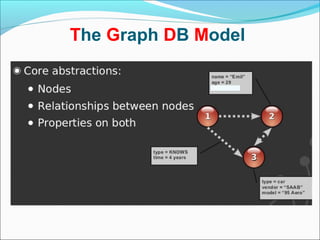
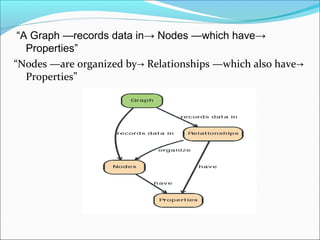
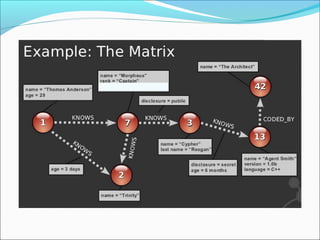
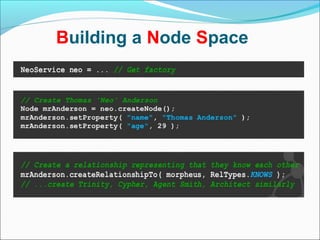
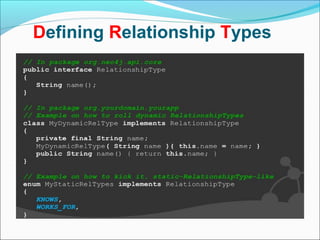
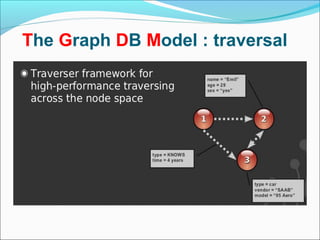
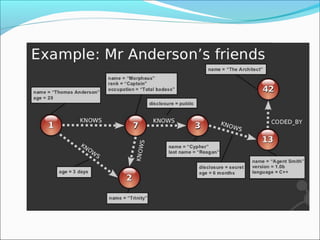
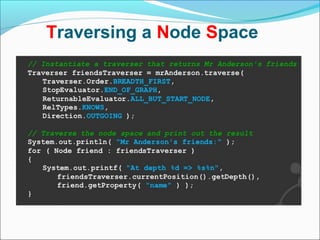
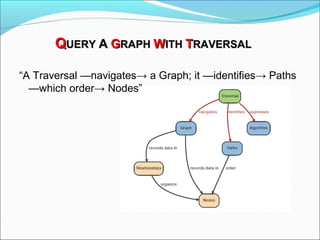
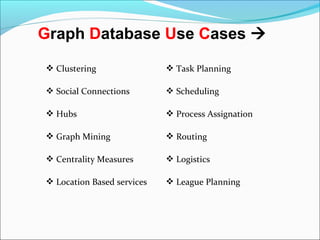
Graph databases use graph structures to represent and store data, with nodes connected by edges. They are well-suited for interconnected data. Unlike relational databases, graph databases allow for flexible schemas and querying of relationships. Common uses of graph databases include social networks, knowledge graphs, and recommender systems.