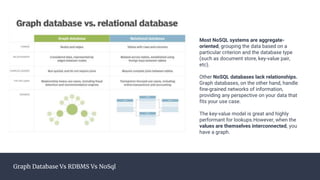
Graph databases offer greater flexibility and dynamicity compared to relational databases (RDBMS), allowing for granular relationships without strict schema constraints. They are particularly beneficial for use cases involving numerous connections, real-time recommendations, fraud detection, and context-aware services. However, they face challenges such as a lack of standardized query languages and may not be suitable for transaction-heavy applications.