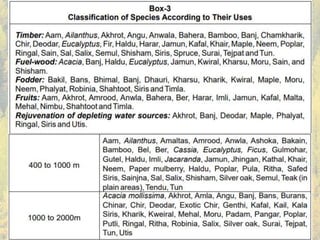
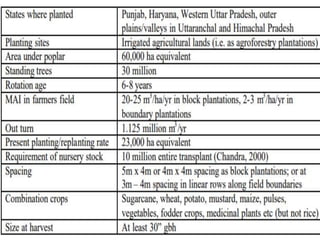
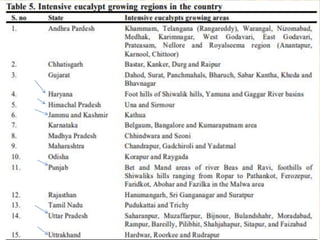
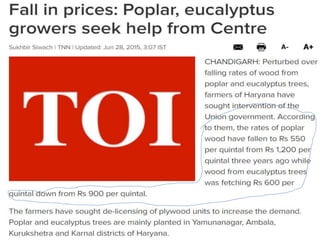
This document discusses plantation trees that are commonly grown in North India. It begins by providing context about the geography and climate of Northern India. The major trees discussed include poplar, eucalyptus, and chir pine. Poplar is described as one of the most popular species for agroforestry planting since 1980, due to its straight trunk, leaflessness in winter, and economic returns within 5-7 years. The document outlines how poplar is commonly intercropped with agricultural crops. Eucalyptus is noted for its introduction to India in the 18th century and its various uses such as charcoal, poles, timber, and paper/pulp. Other common North Indian tree species mentioned include ashoka