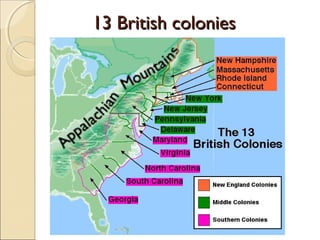
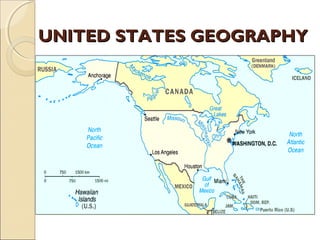
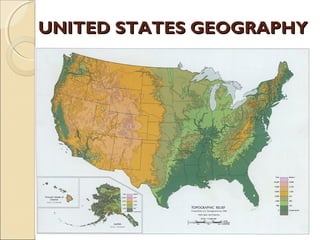
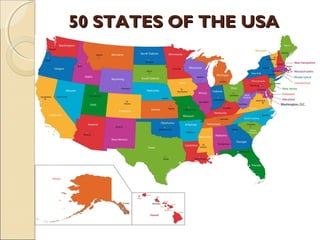
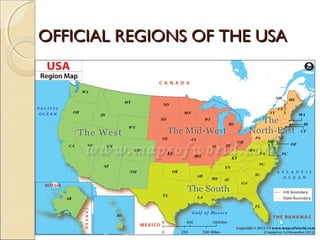
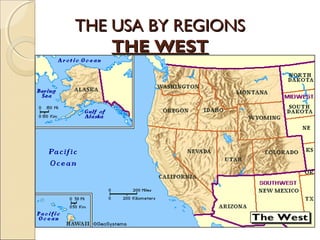
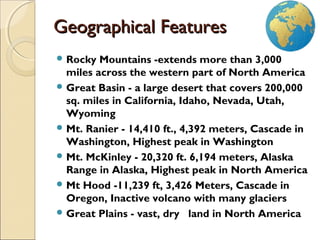
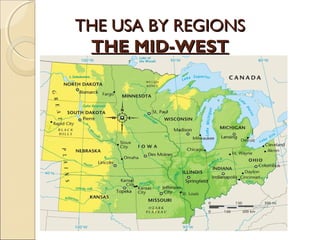
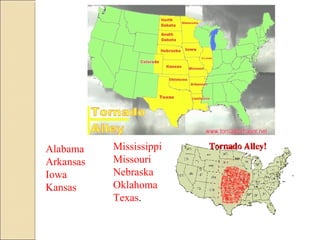
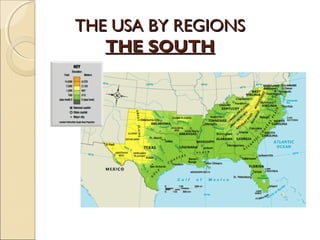
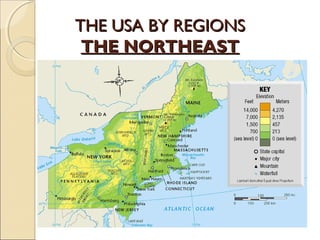
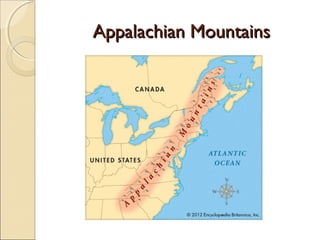
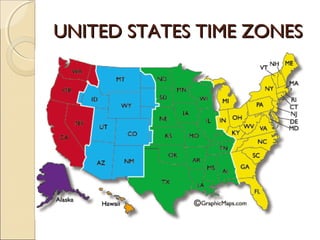
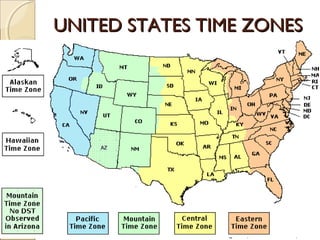
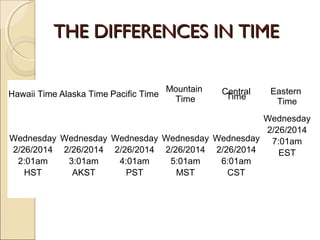
The document provides an overview of the geography, history, culture, and government of the United States. It notes that the US has 50 states across North America, with Washington DC as the capital and over 300 million people. The country's motto is E Pluribus Unum, meaning "out of many, one." The US geography is diverse, containing mountains, plains, deserts, and coastlines across its nine official regions: West, Midwest, South, Northeast, Alaska, Hawaii, Puerto Rico, Guam, and the US Virgin Islands.