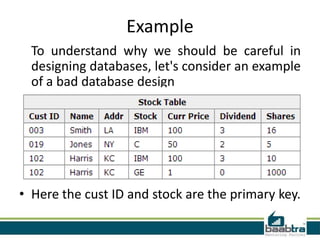
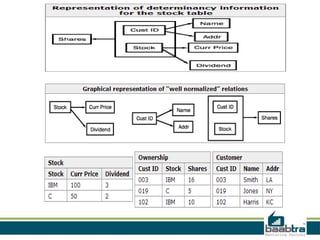
This document discusses database anomalies such as insertion, deletion, and modification anomalies. Insertion anomalies occur when new information cannot be added due to missing or incorrect data. Deletion anomalies happen when related data is lost upon deleting a record. Modification anomalies result from inconsistencies caused by partial updates or redundant data. The document provides an example of a bad database design that is prone to these anomalies and explains how normalization helps avoid anomalies by separating data into distinct tables.