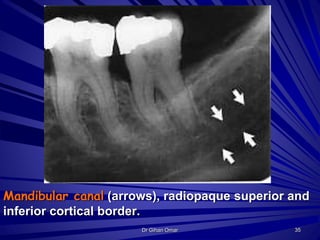
This document provides a radiographic overview of normal dental anatomy. It describes the appearance of teeth, roots, supporting structures like the lamina dura and periodontal ligament space. It also outlines maxillary and mandibular landmarks like the nasal cavity, maxillary sinus, mandibular canal and other radiopaque features. The document concludes by describing the radiographic appearance of various dental restorative materials and appliances.