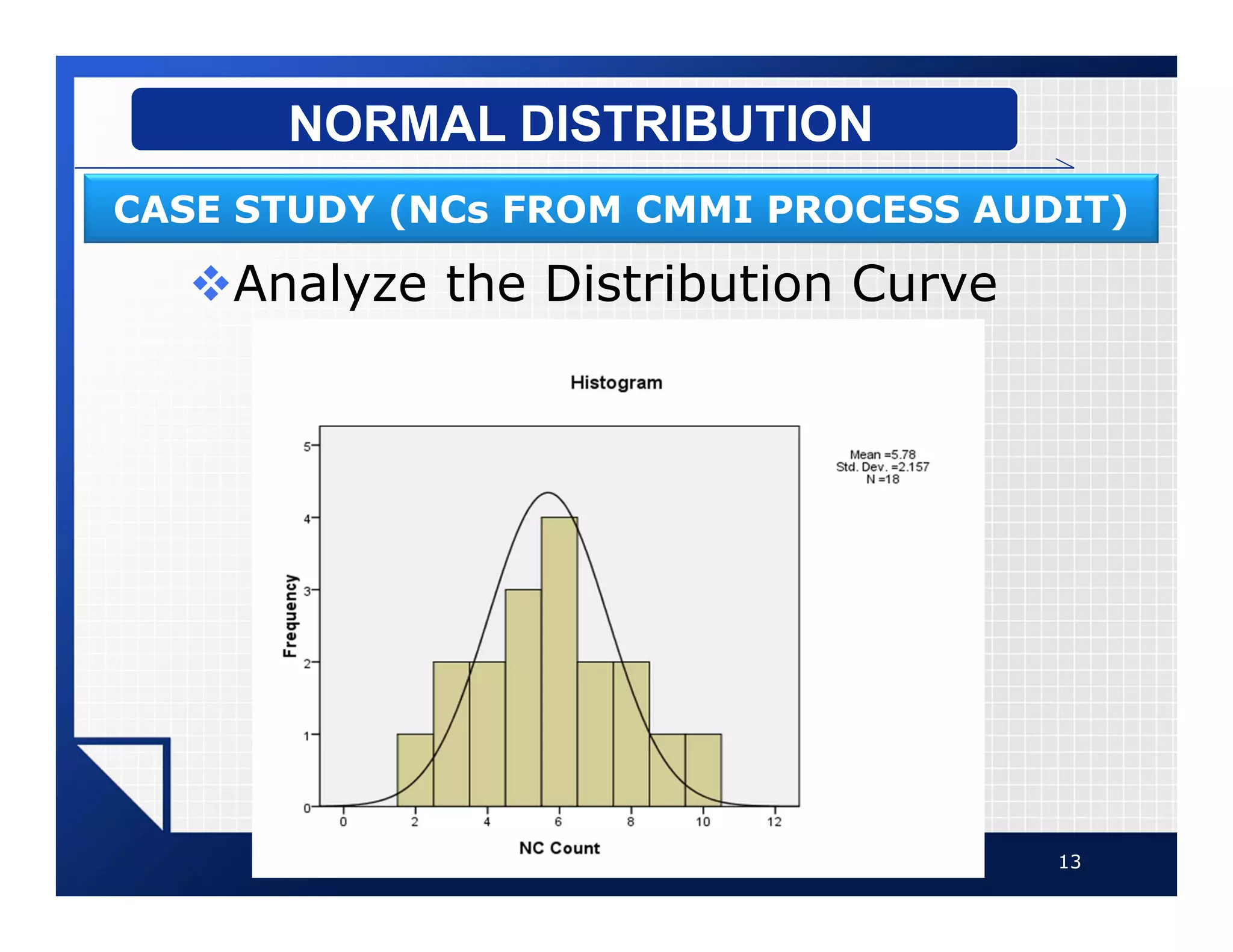
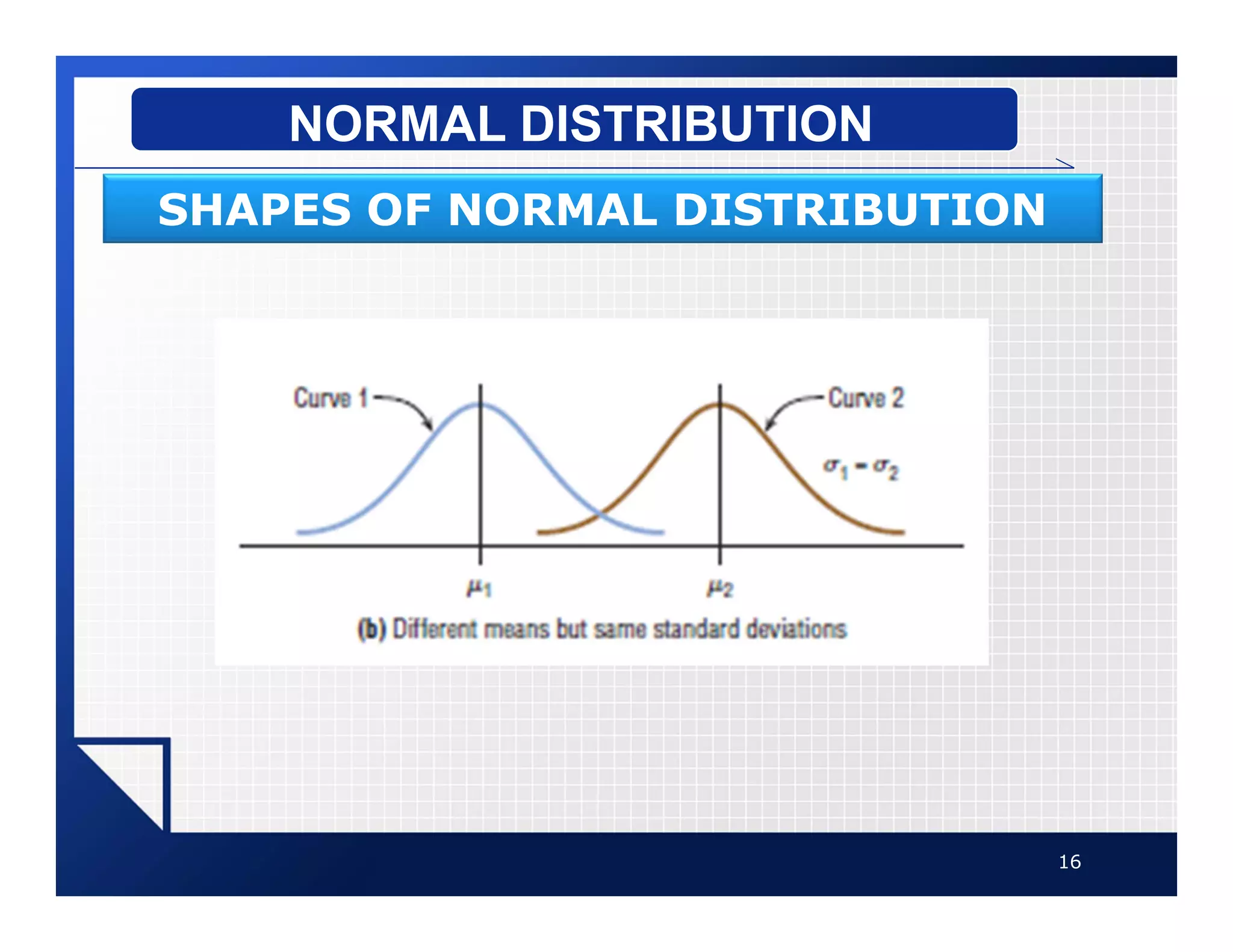
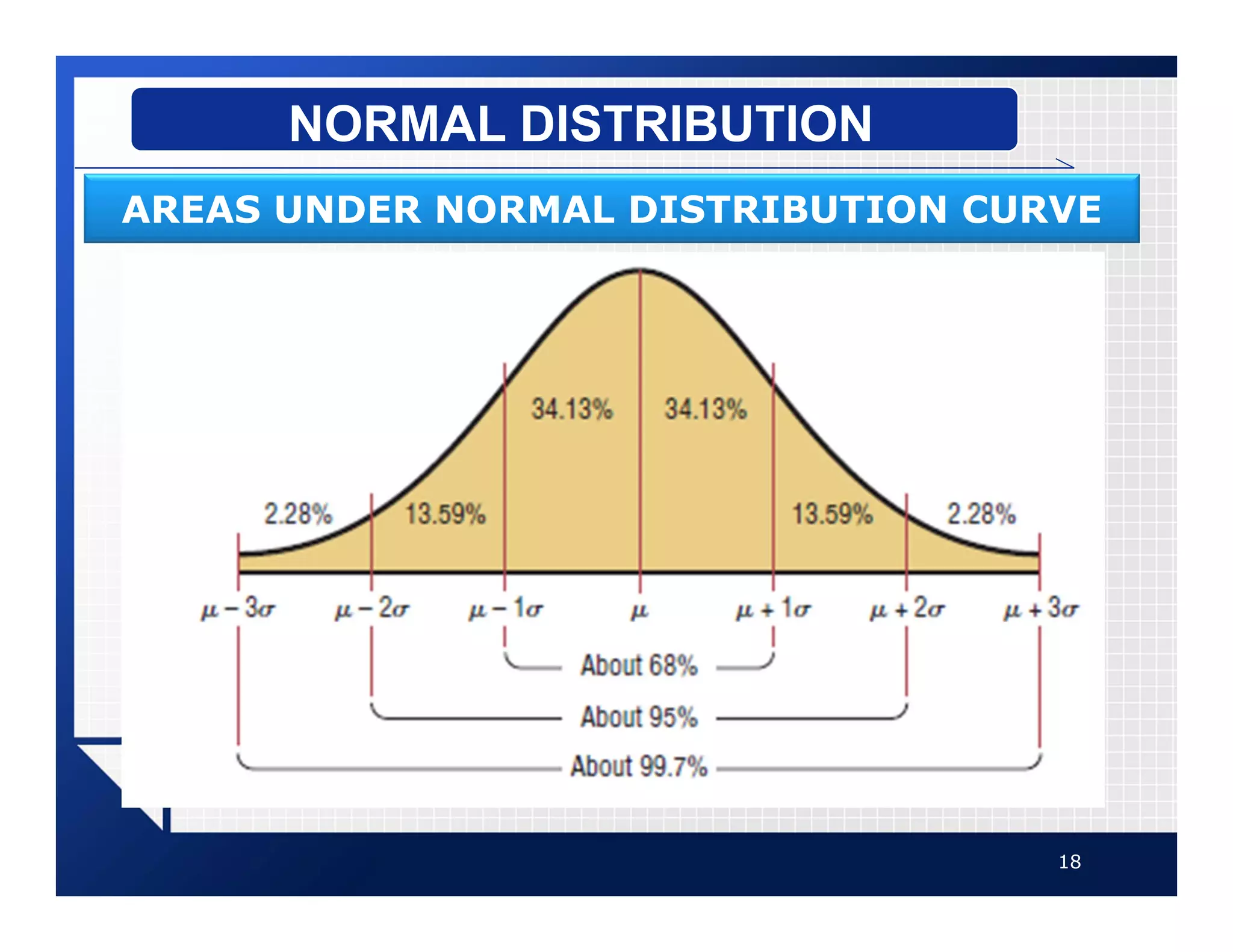
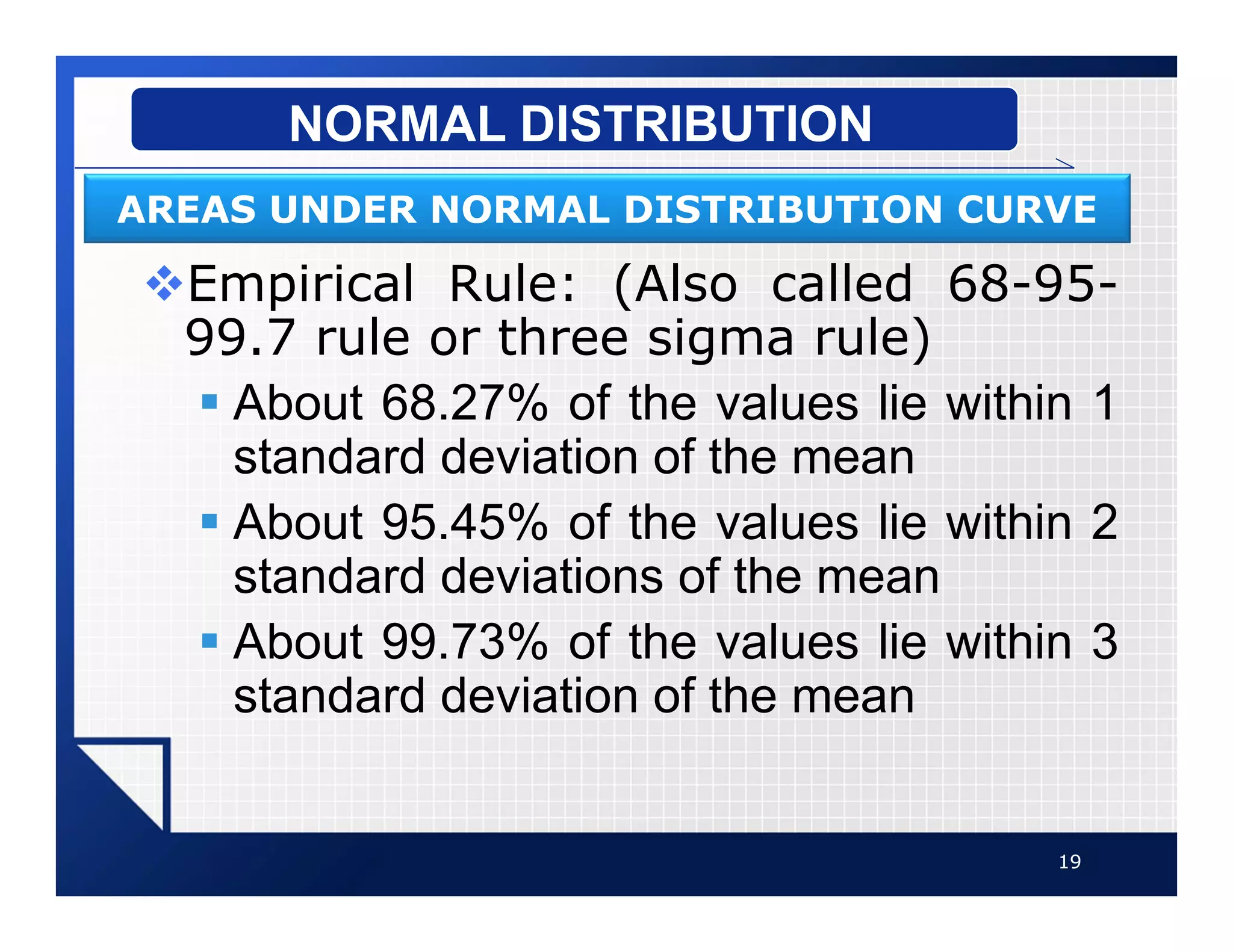
The document discusses normal distributions, which describe a continuous and symmetric bell-shaped distribution. A normal distribution is defined by its mean and standard deviation. It has several important properties including being symmetrical about the mean and having the mean, median and mode located at the center. As an example, the document analyzes non-conformances from a CMMI process audit, drawing a frequency distribution table and histogram to illustrate a normal distribution. It also discusses how the empirical rule can be used to determine the percentage of values that fall within a certain number of standard deviations from the mean.