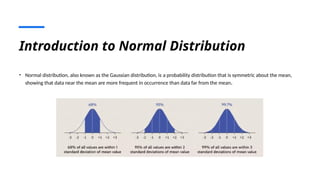
The document provides an overview of normal distribution, highlighting its significance in statistics, business, and government due to its properties and wide real-world applications. It discusses its role in various fields such as hypothesis testing, financial analysis, and public health, while also addressing challenges like skewed data and sensitivity to outliers. Despite limitations, normal distribution remains a foundational tool for data analysis and informed decision-making.