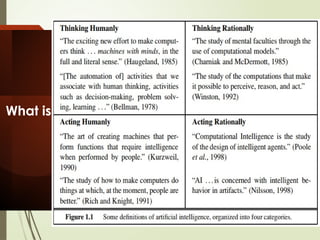
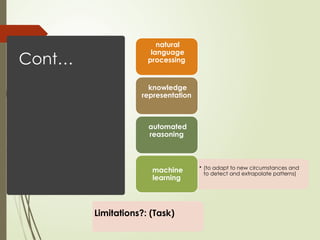
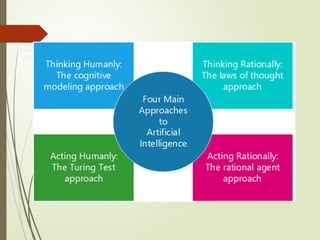
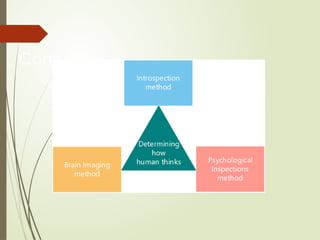
The document explains the concept of artificial intelligence (AI), defining it as the capacity for various cognitive functions such as reasoning and problem-solving. It discusses the historical context of AI, including pivotal moments like the 1956 Dartmouth workshop and the development of self-learning programs. Additionally, it highlights the Turing Test as a measure of computer intelligence and delves into methods for understanding human cognition and developing AI systems that think like humans.